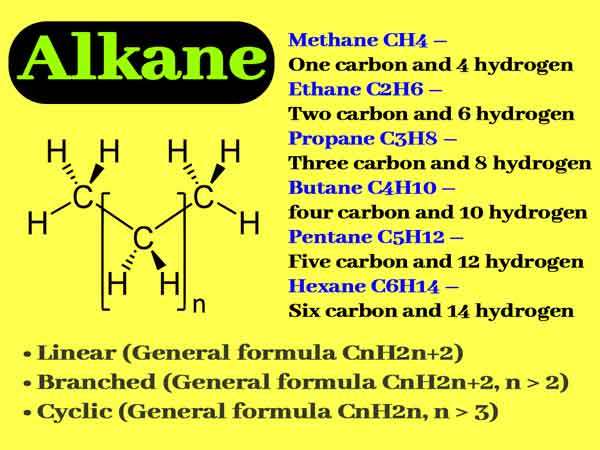
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that consist solely of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are a vital class of compounds that have a wide range of applications in various industries, including the energy, transportation, and chemical industries. Hydrocarbons are classified into two main categories: aliphatic and aromatic. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are further divided into two subcategories: saturated and unsaturated. Saturated hydrocarbons, also known as alkanes, have single bonds between all the carbon atoms, while unsaturated hydrocarbons, also known as alkenes and alkynes, have one or more double or triple bonds between the carbon atoms. Aromatic hydrocarbons, on the other hand, are characterized by a ring of six carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds.
One of the most important chemical properties of hydrocarbons is their reactivity. Hydrocarbons are generally non-polar molecules and have low electronegativities, which means that they are less reactive than many other types of compounds. However, this does not mean that hydrocarbons are completely unreactive. In fact, hydrocarbons can undergo various chemical reactions, such as combustion, polymerization, and halogenation.
Combustion is a chemical reaction that occurs when hydrocarbons react with oxygen to produce heat and light. This reaction is exothermic, which means that it releases energy. Hydrocarbons are commonly used as fuel because they can release a large amount of energy when they are burned. However, the combustion of hydrocarbons also produces carbon dioxide, which is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
Polymerization is the process of forming long chains of molecules by joining smaller units together. Hydrocarbons can undergo polymerization reactions to form polymers, which are large molecules that are made up of repeating units called monomers. Polymers are used in a wide range of applications, including the production of plastics, fibers, and rubber.
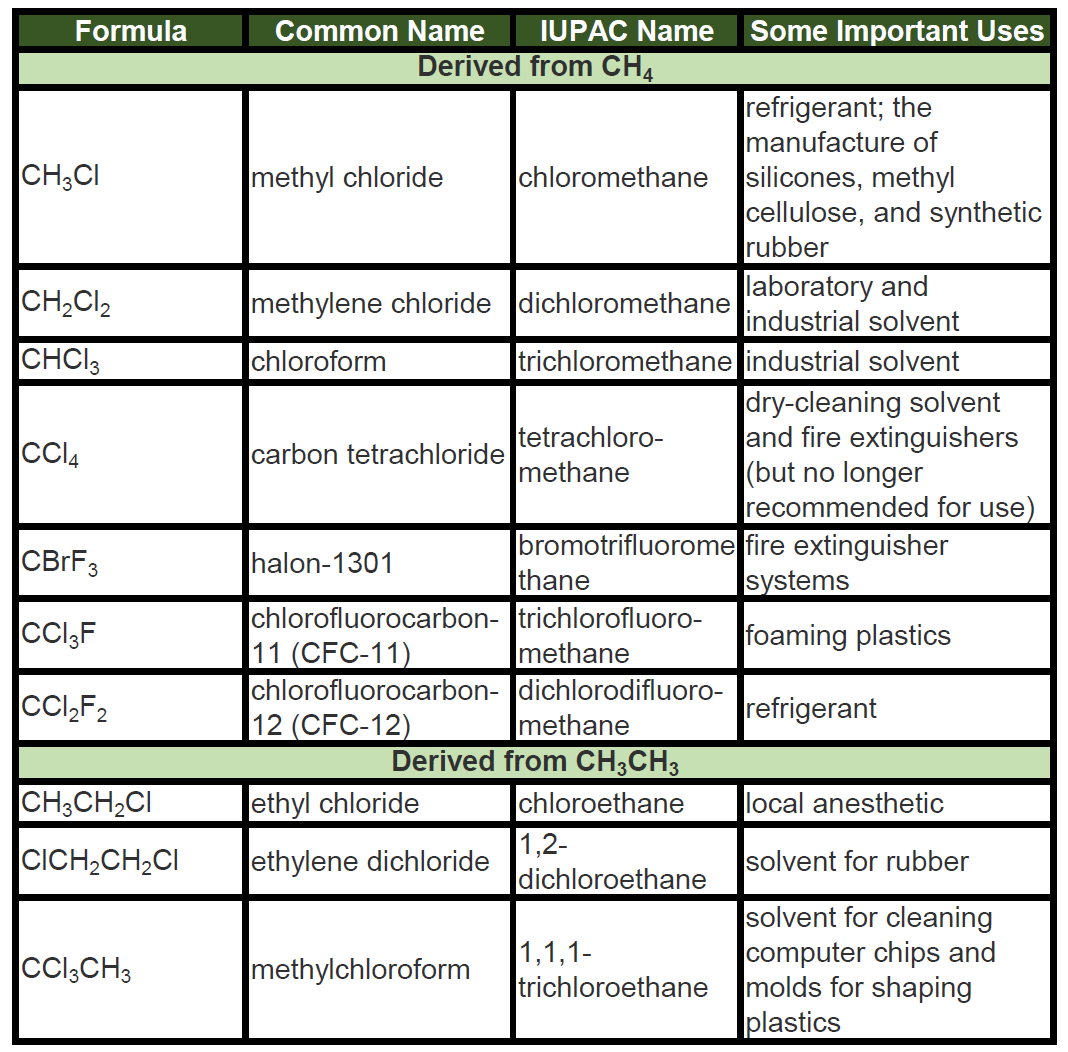
Halogenation is a chemical reaction in which halogen atoms, such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine, are added to hydrocarbons. This reaction can produce a variety of products, depending on the type of halogen and the conditions of the reaction. Halogenation reactions are often used to produce chlorinated and fluorinated hydrocarbons, which have a wide range of applications, including the production of refrigerants, solvents, and pesticides.
In addition to their reactivity, hydrocarbons also have physical properties that are important to consider. Alkanes, which are saturated hydrocarbons, have relatively high boiling points and are less volatile than alkenes and alkynes. Aromatic hydrocarbons, on the other hand, have lower boiling points and are more volatile than aliphatic hydrocarbons. The solubility of hydrocarbons also varies depending on their structure and the solvent being used. For example, alkanes are generally not soluble in water, while aromatic hydrocarbons are more soluble in water.
In conclusion, hydrocarbons are a diverse class of compounds that have a wide range of chemical and physical properties. They can undergo various chemical reactions, including combustion, polymerization, and halogenation, and have a range of physical properties, including boiling point and solubility. These properties make hydrocarbons useful in a variety of applications, including the energy, transportation, and chemical industries.