The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is exchanged between the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. It is a critical component of the Earth's climate system, as it helps to regulate the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere.
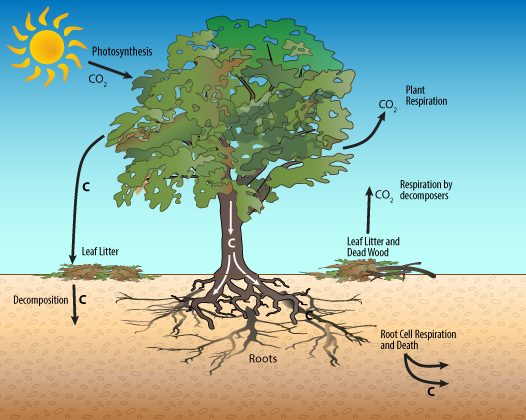
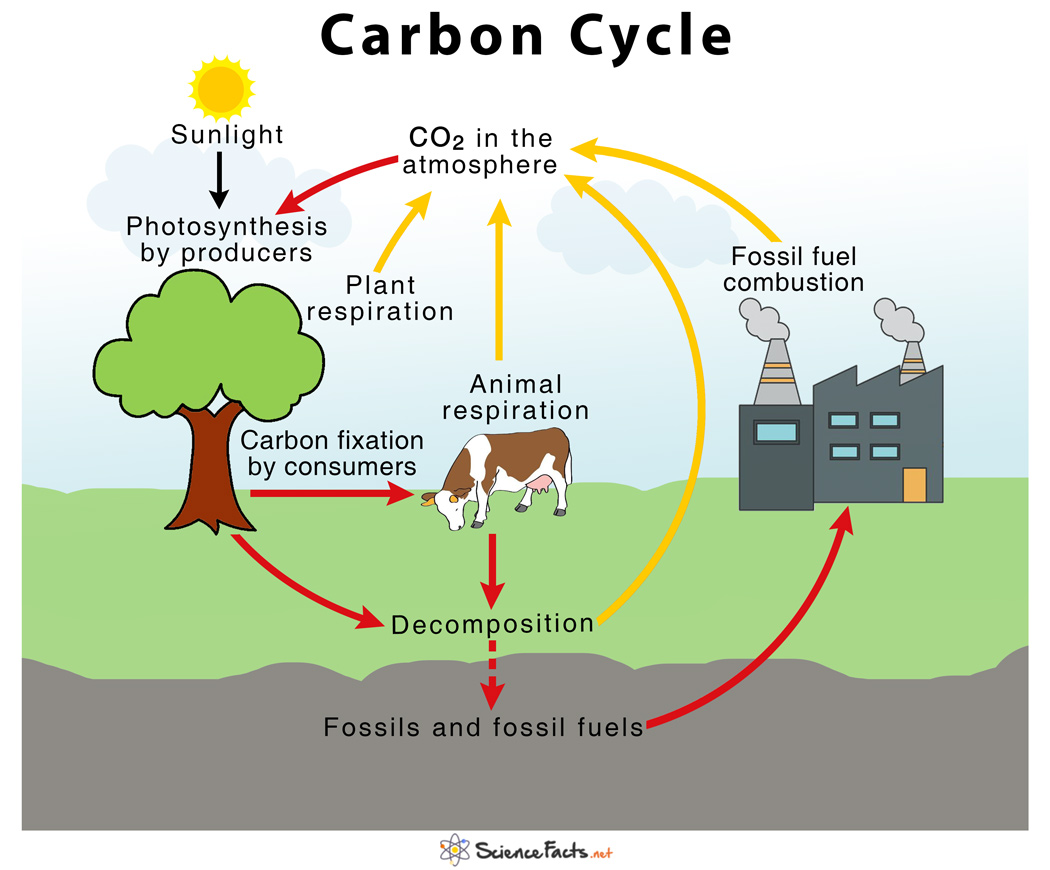
Carbon is constantly being exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, and land through various processes. For example, plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis and convert it into organic matter. When animals consume plants or other organisms, the carbon is transferred from the plants to the animals. When animals respire or decompose, the carbon is returned to the atmosphere as CO2.
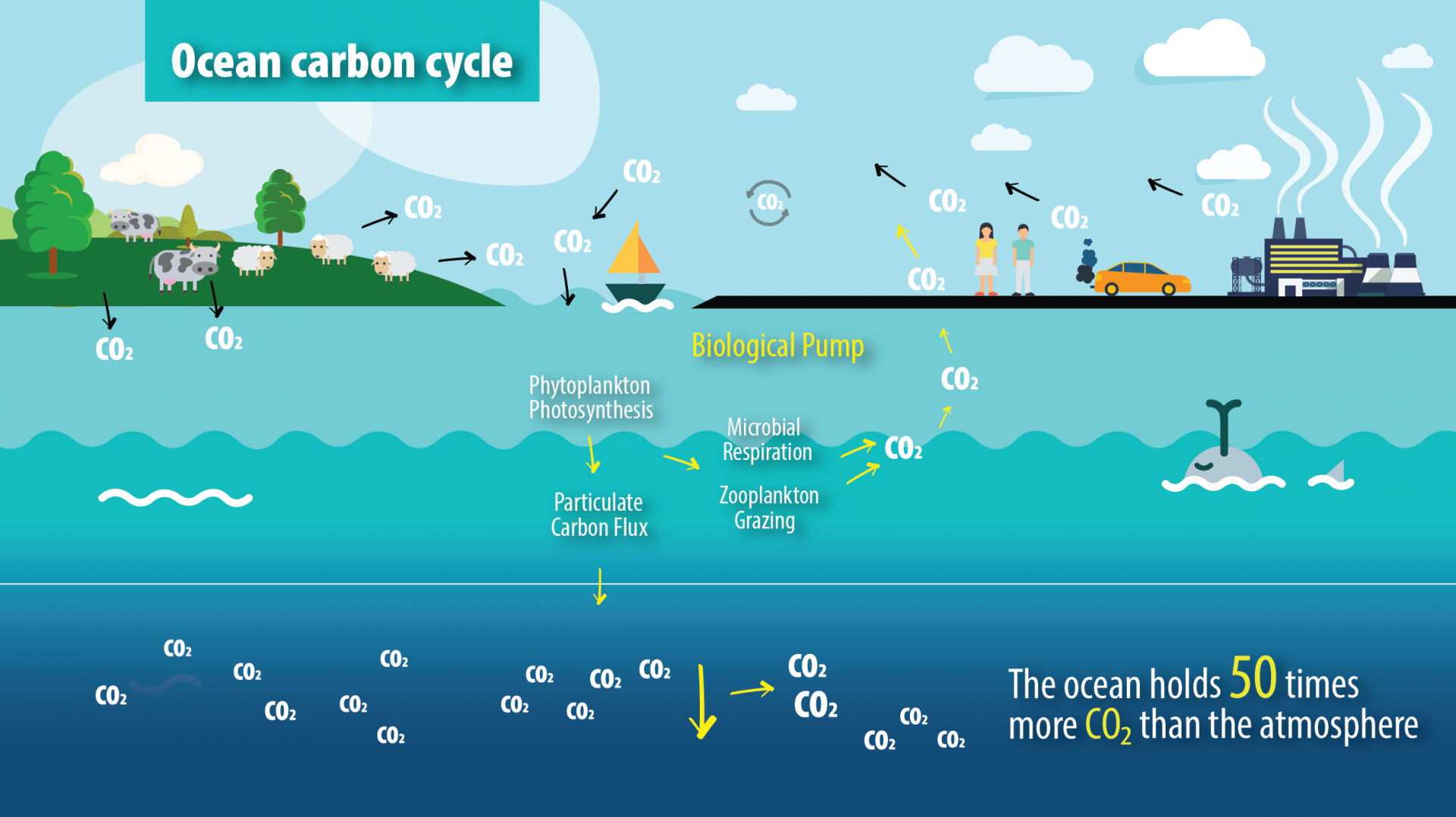
The oceans also play a role in the carbon cycle. They absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, and the carbon is then transferred to marine plants and animals through the process of photosynthesis. When these organisms die, the carbon is returned to the oceans in the form of organic matter. Some of this organic matter sinks to the ocean floor and is converted into fossil fuels, such as oil and natural gas, over millions of years.
Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have a significant impact on the carbon cycle. The burning of fossil fuels releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, leading to an increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Deforestation also contributes to an increase in atmospheric CO2, as trees absorb CO2 as they grow and release it when they die or are burned.
Overall, the carbon cycle is a complex process that plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. It is important to understand the carbon cycle and how human activities can affect it in order to mitigate the negative effects of climate change.
Carbon cycle — Science Learning Hub
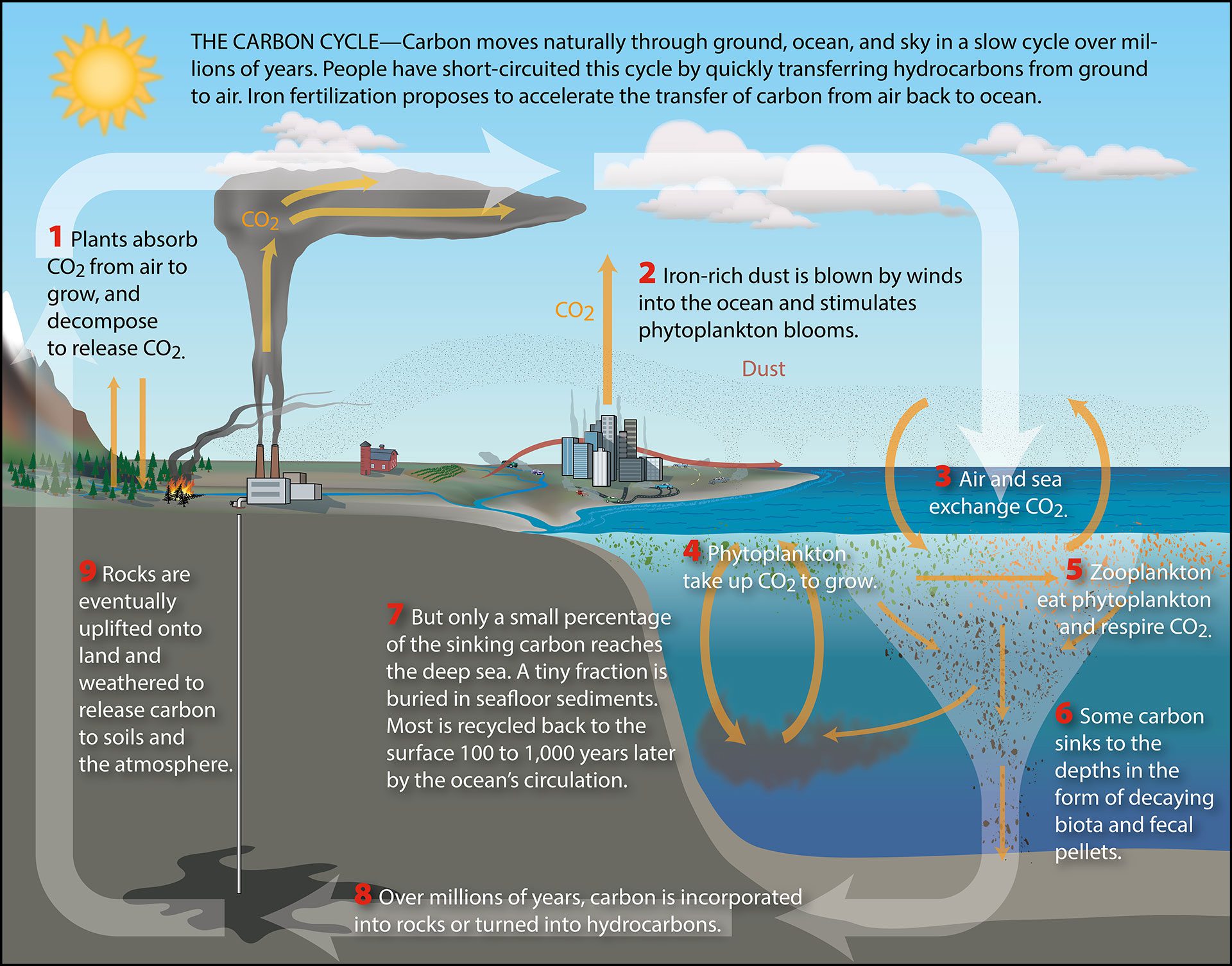
Acknowledgement: The University of Waikato. Carbon dioxide is released from the burning of fossil fuels to power farming equipment, from the mining of minerals and the making of fertilizer. The effects of historic events such as the Great Depression of 1929-1939, World Wars, the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, and the Kuwait oil fires of 1991 can be seen. Carbon, just like all other elements, cycles through the environment and is constantly in the process of changing forms and locations. The most common of these are the carbon and nitrogen cycles. Carbon is a greenhouse gas, meaning it traps the heat from the Sun, and stops it from escaping into space. When temperatures remain cold all year-round organic material decays very slowly, and it remains in the soil.
Carbon cycle
Activity: Better understanding the carbon cycle To further review the carbon cycle, and better understand the human impacts on it, use this interactive graphic from Woods Hole laboratories: Table 7. The Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen is an element that is found in both the living portion of our planet and the inorganic parts of the Earth system. Now as the phytoplankton mature, there are a couple of different things that can happen. Before being released, the extra carbon from the short-term cycle is held for a long period. Compare the production of CO 2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion across world regions in 1900, 1950, and 2011 in Figure 7. Carbon moves through our planet over longer time scales as well. Impacts of slash and burn agriculture and biomass burning, a Slash and burn agriculture in Maaninka, Finland.
The carbon cycle
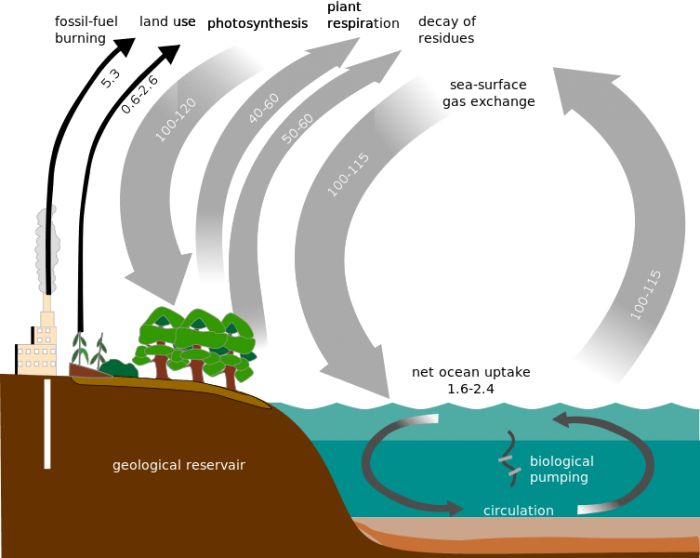
Remember, you are what you eat! Our body takes the carbon molecules contained in this biomass, and uses them, along with the oxygen we breathe in, for cellular respiration to create the adenosine triphosphate ATP we need for energy. This carbon from land, as well as carbon atoms in CO 2 absorbed by the ocean from the atmosphere, can become incorporated into calcium carbonate CaCO 3 shells made by algae, plants, and animals. It can form millions of stable and diverse compounds, ranging from simple to extremely complex. These shells become buried. The oceans, and other bodies of water, absorb some carbon from the atmosphere. When considering the flux of respiration, living organisms are the source of carbon, and the atmosphere is the sink. This makes the Earth warmer, causing global warming.
Biogeochemical Cycles
This is particularly apparent when comparing the data for Western Europe to that of India and Southeast Asia. Carbon Sources Carbon sources refers to all the elements — organic or inorganic, which release Carbon in some form into the atmosphere. This is released in the form of Carbon dioxide. Thus, deforestation typically releases carbon dioxide, unless all the material is used for construction, or for paper products. As countries become more industrialized, their reliance on and combustion of fossil fuels tends to increase.