The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, was a Bronze Age civilization that flourished in the Indus Valley region of modern-day Pakistan and northwest India. The civilization is known for its well-planned cities, advanced architecture, and sophisticated systems of governance, trade, and social organization.
The Indus Valley Civilization is thought to have developed around 2500 BCE, and it reached its peak of prosperity around 2000 BCE. The civilization was characterized by its urban centers, which were home to large populations of people who lived in well-planned and orderly cities. These cities were connected by a network of roads and waterways, and they were surrounded by fields and farms that provided the necessary food and resources for the population.
One of the most distinctive features of the Indus Valley Civilization was its advanced system of governance. The civilization was divided into several city-states, each of which was ruled by a powerful ruler or a council of elders. These rulers were responsible for maintaining order and enforcing laws within their city-states, and they also oversaw the collection of taxes and the distribution of resources.
The Indus Valley Civilization was also known for its sophisticated system of trade and commerce. The civilization was located at the crossroads of several major trade routes, and as a result, it was able to access a wide range of goods and resources from other parts of the world. The Indus Valley Civilization was also a major producer of goods, including textiles, jewelry, and ceramics, which were traded with other civilizations in the region.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Indus Valley Civilization was its advanced system of social organization. The civilization was divided into several social classes, including rulers, priests, merchants, and farmers, and each class had its own distinct roles and responsibilities. The Indus Valley Civilization was also home to a number of religious and cultural institutions, including temples, shrines, and universities, which played a central role in the lives of the people.
Despite the many achievements of the Indus Valley Civilization, it ultimately declined and was eventually replaced by other civilizations in the region. The reasons for the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization are not fully understood, but it is thought that a combination of factors, including changes in the climate, internal conflicts, and invasions by outside powers, may have contributed to its downfall.
Today, the legacy of the Indus Valley Civilization lives on through the many artifacts and ruins that have been discovered in the region. These artifacts, including seals, pottery, and sculptures, provide valuable insights into the culture, society, and daily life of the people of the Indus Valley Civilization, and they continue to fascinate historians and scholars around the world.
Indus Valley Civilization Short note pdf

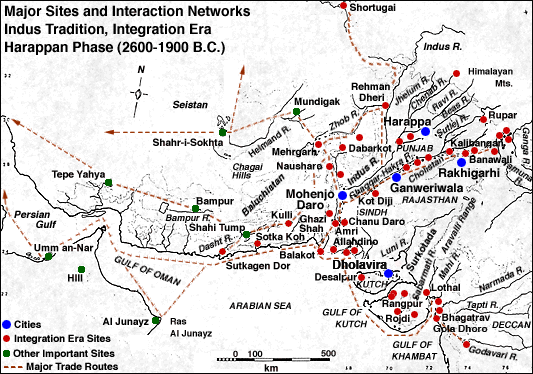
The urban phase involved a delicate balance of relation between the cities, town, villager, farmer communities and nomadic people. In the earlier Mesopotamian sequence, rural abandonment and population concentration in walled urban precincts is suggestive of Materials circumscription, competition and intra-regional warfare. Thereafter, each urban phase characterised by systematic town planning, widespread brick work, art of writing, use of bronze tools and red ware pottery painted with black designs gradually disappeared. This map depicts the geographical span of the Indus Valley Civilization IVC , showing the location of Rakhigarhi blue , other significant IVC sites red , and sites to the north and west from other archaeological cultures other colors. During the peak of the KotDiji Culture, the site was divided into a citadel and a lower town Standardised bricks; terracotta cakes fish-scale and intersecting-circle designs on pottery and other traits found in the Indus Valley Civilization were already in use at the site.
Indus Valley Civilization Short Notes

Sutkagendor It is situated in Baluchistan, Pakistan near the border of Iran. This civilization was spread across Jammu in the North, Narmada Estuary in the south, Makran coast in the west and meerut in the east. Found at one city is an enormous, well-built bath, which may have been a public bath. Leshnik has cogently suggested that it was a tank for the reception of sweet water, channelled from higher ground inland to an area where the local water supplies were anciently, as still today, saline. These civilizations arose at different times — the earliest of these, Mesopotamia, arose some 6,000 years ago, while the earliest Andean civilization, the Chavin, opens in new tab developed in approximately 900 B. It is on display in the National Museum, Karachi, Pakistan.
The Indus Valley Civilization History Essay

Despite these reports, Harappa was raided even more perilously for its bricks after the In 1861, three years after the dissolution of the East India Company and the establishment of Archaeological work in Harappa thereafter lagged until a new viceroy of India, Farther south, along the Illustrated London News: "Not often has it been given to archaeologists, as it was given to In the next issue, a week later, the British Assyriologist After the partition of India in 1947, when most excavated sites of the Indus Valley Civilisation lay in territory awarded to Pakistan, the Archaeological Survey of India, its area of authority reduced, carried out large numbers of surveys and excavations along the Ghaggar-Hakra system in India. These composite tools were reusable as the original blades could be replaced with new ones when the old ones were broken. Mohenjodaro, one of the largest cities of the Indus Valley Civilization, covers an area of approximately 12 km. But it is also commonly referred to as the sarasvati Civilization. A thick layer of ash over parts of the site suggests an incident with fire, after which the site exhibits the exclusive influence of the Harappan Culture. Flood-supported farming led to large agricultural surpluses, which in turn supported the development of cities.