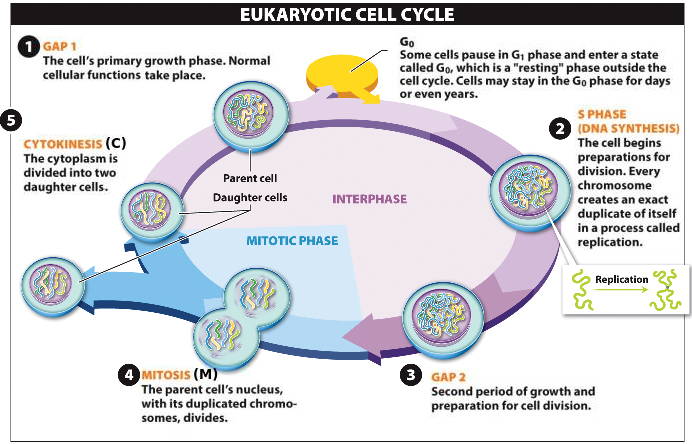
The stage of mitosis that takes the longest is the metaphase stage.
During the metaphase stage, the chromosomes, which have already replicated during the preceding interphase, line up in the middle of the cell. This process is known as chromosome alignment. The chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers, which are made up of microtubules, and are pulled towards the opposite poles of the cell.
The metaphase stage is crucial for the proper segregation of the replicated chromosomes to the daughter cells. If the chromosomes are not properly aligned and separated, it can lead to genetic disorders and abnormalities in the resulting cells.
The metaphase stage can take anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the type of cell and the specific organism. This is longer than the other stages of mitosis, which include prophase, anaphase, and telophase.
In prophase, the chromatin in the nucleus condenses into visible chromosomes and the nucleolus disappears. In anaphase, the centromere of each chromosome splits and the sister chromatids are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. Finally, in telophase, the cell begins to divide, forming two daughter cells that each contain a complete set of chromosomes.
Overall, the metaphase stage of mitosis is a crucial and time-consuming process that ensures the proper segregation of genetic material to the daughter cells. Without this step, the resulting cells could have genetic abnormalities, leading to potential health problems in the organism.
What is the longest part of the mitosis cycle?

S Phase Synthesis of DNA The synthesis phase of interphase takes the longest because of the complexity of the genetic material being duplicated. The first and longest phase of mitosis is prophase. There is an important checkpoint in the middle of mitosis, called the metaphase checkpoint, during which the cell ensures that it is ready to divide. If not fertilized, the egg is passed from the reproductive tract during menstrual bleeding, which starts about two weeks after ovulation. Anaphase typically is a rapid process that lasts only a few minutes, making it the shortest stage in mitosis. Prophase I is the longest and arguably most important segment of meiosis, because recombination occurs during this interval.
Which Stage Of The Cell Cycle Lasts The Longest
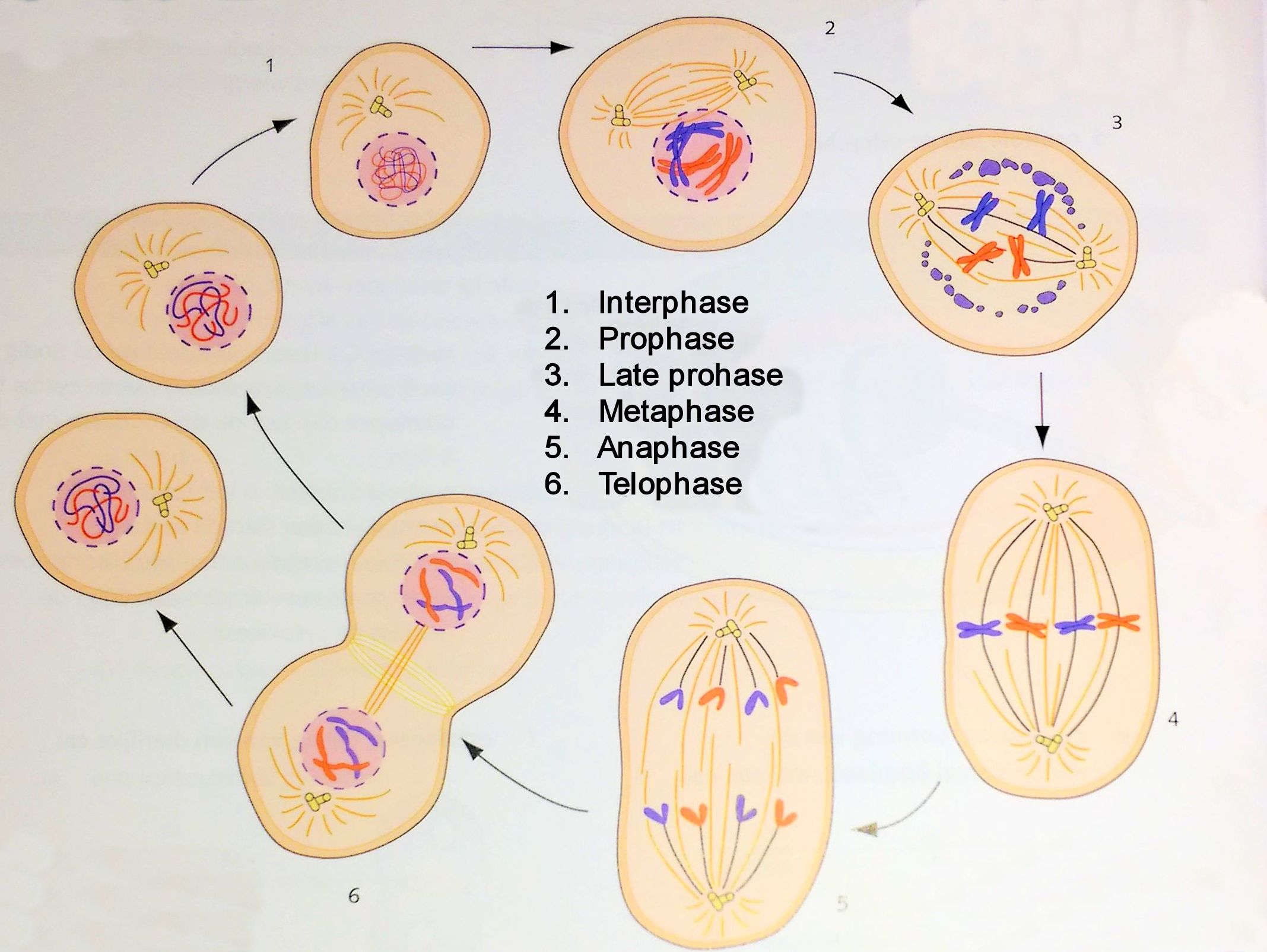
The stages of the cell cycle are in order as follows not including sex cells : Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis. Why is the longest stage of mitosis? What is the longest and shortest phase of mitosis? Cells usually remain in G1 for about 10 hours of the 24 total hours of the cell cycle. The spindle disappears, two nuclear envelopes reform one around each set of daughter chromosomes. In fact, nerve cells stop at about the time we are born. The five stages of cell cycle are — interphase, which is in turn classified into G1, S and G2 phase, Mitosis, also called as the M phase, which is further divided into 4 parts prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase and Cytokinesis. For example, muscle and nerve cells.
Which stage in the cell cycle is the longest? Explained by FAQ Blog

According to the data table, prophase is the longest stage of mitosis. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Is mitosis a continuous process? Terms in this set 7 Interphase. In mitosis, until the cell divides it always has double the DNA. During telophase, the processes that occured during prophase are reversed. During interphase, the chromosomes divide and exist in the form of chromatin fibers.
The longest phase of mitosis is
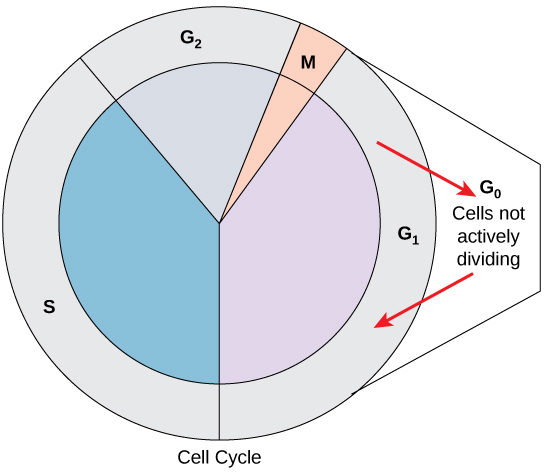
What is metaphase in mitosis? Cytokinesis, the division of cytoplasm, occurs immediately after mitosis. What does G1 produce? The function of the kinetochore is to provide a site for attachment of spindle fibers to pull apart the sister chromatids at the time of cell division. What is the shortest phase in cell division? Diploid cells within the testes undergo meiosis to produce haploid sperm cells with 23 chromosomes. Other cell materials such as lipids for the membrane may also be produced. Female sex cells, or gametes, develop in the ovaries by a form of meiosis called oogenesis. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to spindle fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. A single diploid cell yields four haploid sperm cells through meiosis.
which stage of mitosis takes the longest? Which one is the shortest? How do you know this?...

What is the phase of mitosis? What cycle stage is the longest? During anaphase, sister chromatids break apart, and chromosomes start moving to opposite ends of the cells. What is the longest phase of the cell cycle the shortest phase? How long is each phase of the cell cycle? Among the phases of mitosis, prophase is the longest and anaphase is the shortest. What are the 8 stages of mitosis in order? Which is the longest phase G1 or S? In anaphase, the shortest stage of mitosis, the sister chromatids break apart, and the chromosomes begin moving to opposite ends of the cell. Anaphase is the shortest phase of mitosis. It is the longest phase of the cell cycle, cell spends approximately 90% of its time in this phase. Why is G1 the longest? How long is each phase of mitosis? Which type of meiosis happens in the ovaries? The kinetochore microtubules shorten as the chromatids are pulled toward opposite poles, while the polar microtubules subsequently elongate to assist in the separation.