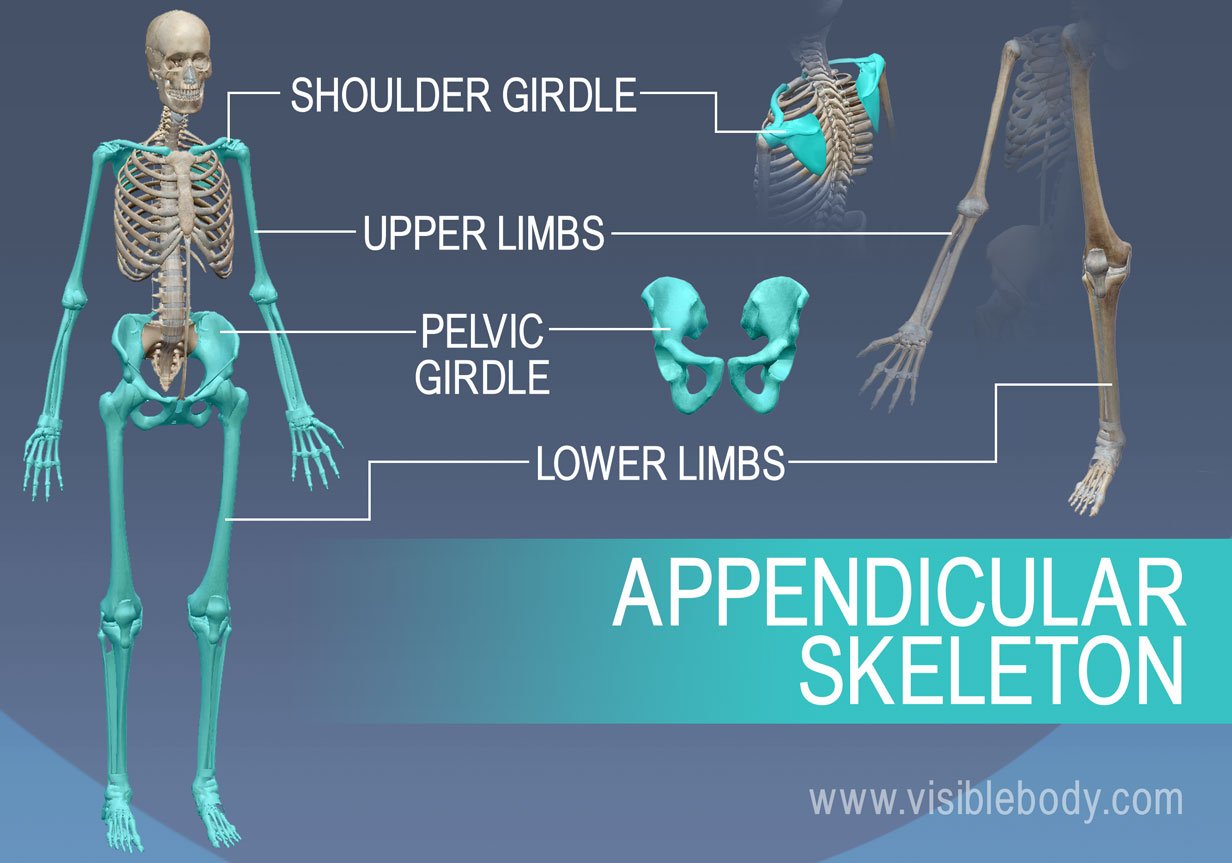
The appendicular bones are the bones of the limbs and girdles, which include the upper limbs (arms) and lower limbs (legs). These bones provide support for movement, as well as protection for the body's vital organs.
One type of appendicular bone that has a styloid process is the ulna, which is one of the two bones in the forearm. The styloid process of the ulna is a thin, pointed projection located on the posterior (back) side of the bone, near the wrist. It functions as a point of attachment for muscles and ligaments that help to stabilize the wrist and hand.
Another appendicular bone that has a styloid process is the radius, which is the other bone in the forearm. The styloid process of the radius is located on the lateral (outer) side of the bone, near the wrist. Like the styloid process of the ulna, it serves as a point of attachment for muscles and ligaments that help to stabilize the wrist and hand.
In addition to the ulna and radius, the styloid process can also be found on some other appendicular bones, including the tibia (shinbone) and the fibula (a thin bone located alongside the tibia). The styloid process of the tibia is located on the medial (inner) side of the bone, near the ankle, and serves as a point of attachment for muscles and ligaments that help to stabilize the ankle and foot. The styloid process of the fibula is located on the lateral (outer) side of the bone, near the ankle, and has a similar function.
Overall, the styloid process is a common feature of many appendicular bones, and it plays a important role in the stability and movement of the limbs and girdles.
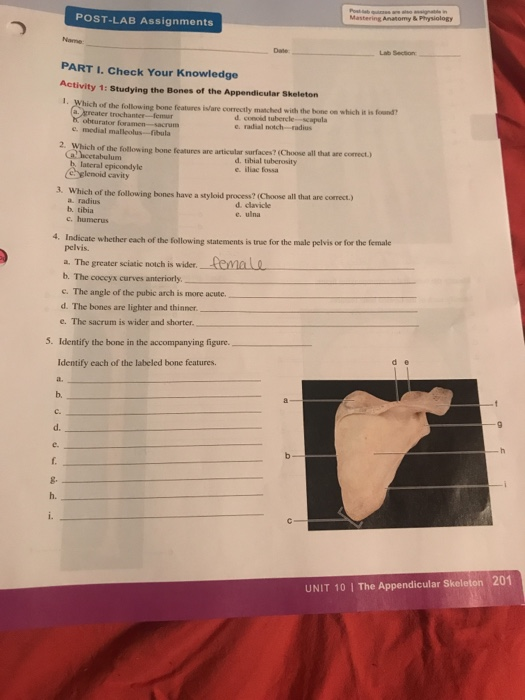
Which of the following bones have a styloid process? (Select all that apply.) a. radius b. tibia c. humerus d. clavicle e. ulna

The dog skeleton anatomy consists of bones, cartilages, and ligaments. You will find a small radial tuberosity at the distal end of the neck on its medial aspect. Dog humerus anatomy The humerus is a relatively very long, slender, and slight spiral twist bone in the arm of a dog. It locates at the tendinous insertion of the brachiocephalic muscle. They form no joint with each other or with the sacrum bone of the dog. The caudal surface extends distally and continues with the lateral supracondylar crest.
Appendicular skeleton

The proximal half of the fibula may be twisted. On the other hand, the medial epicondyle is a prominence on the medial aspect of the condyle just proximal to the medial border of the articular surface of the trochlea. The body of the dog tibia is slender and irregular. These are short but essential osteological features from the dog radius and ulna bones. The dog sacrum consists of a base, an apex, wings, and two dorsal and pelvic surfaces.
You will find two different parts of the dog skeleton — axial and appendicular. Again, the cranial ramus fuse with the ilium bone and help form the acetabulum. The accessory carpal bone locates at the palmar side of the ulnar carpal. What coxal bone do they apply to? The term "trochlea" comes from the Greek word for hook, because of the appearance of this notch on the outside of the elbow joint. The processes of the typical vertebra are — transverse, spinous, articular, accessory, and mammillary. A normal trochlea has sharp edges and a smooth surface. Body of the dog femur The caudal surface of the dog femur is almost flat.

Again, the pelvic girdle of the dog comprises of ilium, ischium, pubis, and acetabular bone. Humerus and Radioulnar joint Figure 6. Hindpaw or pes of dog skeleton anatomy The hind paw of the dog skeleton consists of the tarsus, metatarsus, phalanges, and associate sesamoid bones. The head of the radius is more proximal. Again, the metacarpal II, III, IV, and V are the main metacarpal that irregular rod shape with a uniform diameter.