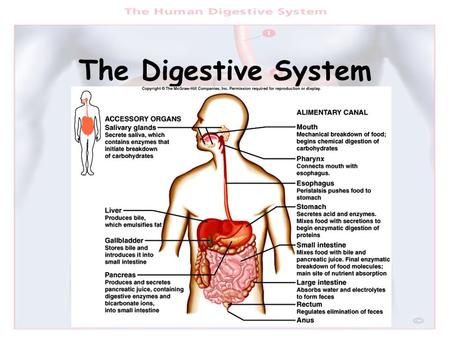
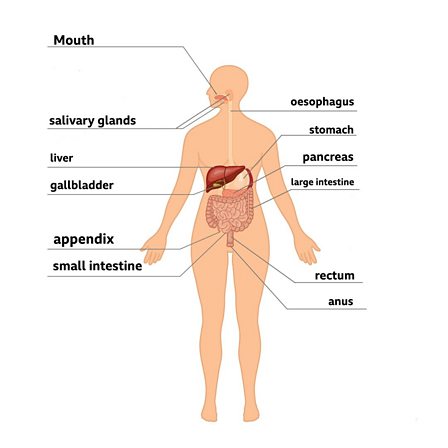
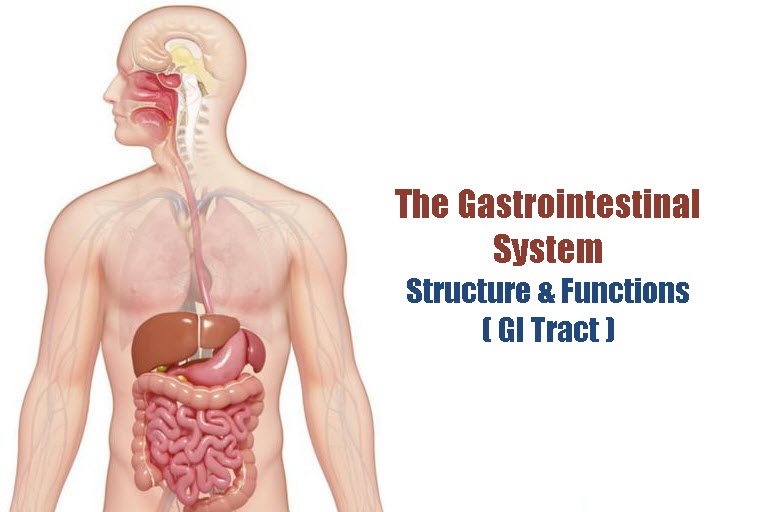
The digestive system is a complex network of organs and glands that work together to convert food into energy and nutrients. It is essential for maintaining the overall health and well-being of an individual.
The structure of the digestive system begins with the mouth, which is responsible for mechanically breaking down food through chewing and grinding. The food is then mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that begin the process of breaking down carbohydrates.
The next organ in the digestive system is the esophagus, a muscular tube that transports the food to the stomach through a series of contractions known as peristalsis.
The stomach is a muscular sac that mixes and grinds the food, as well as secretes digestive enzymes and stomach acid. This acid helps to kill any harmful bacteria present in the food, and the enzymes break down proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
After leaving the stomach, the partially digested food enters the small intestine, which is the primary site of nutrient absorption. The walls of the small intestine are lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. The small intestine also receives digestive enzymes and bile from the pancreas and liver, which help to break down the remaining nutrients.
The large intestine, or colon, is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from the undigested food material and forming the stool. The stool is then stored in the rectum until it is eliminated through the anus.
In addition to these organs, the digestive system also includes the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, which produce bile and digestive enzymes that aid in the digestion process.
The main function of the digestive system is to provide the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly. These nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, provide energy and support the growth and repair of tissues. The digestive system also helps to eliminate waste products from the body.
Overall, the digestive system plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of an individual by efficiently breaking down and absorbing nutrients from food and eliminating waste products.
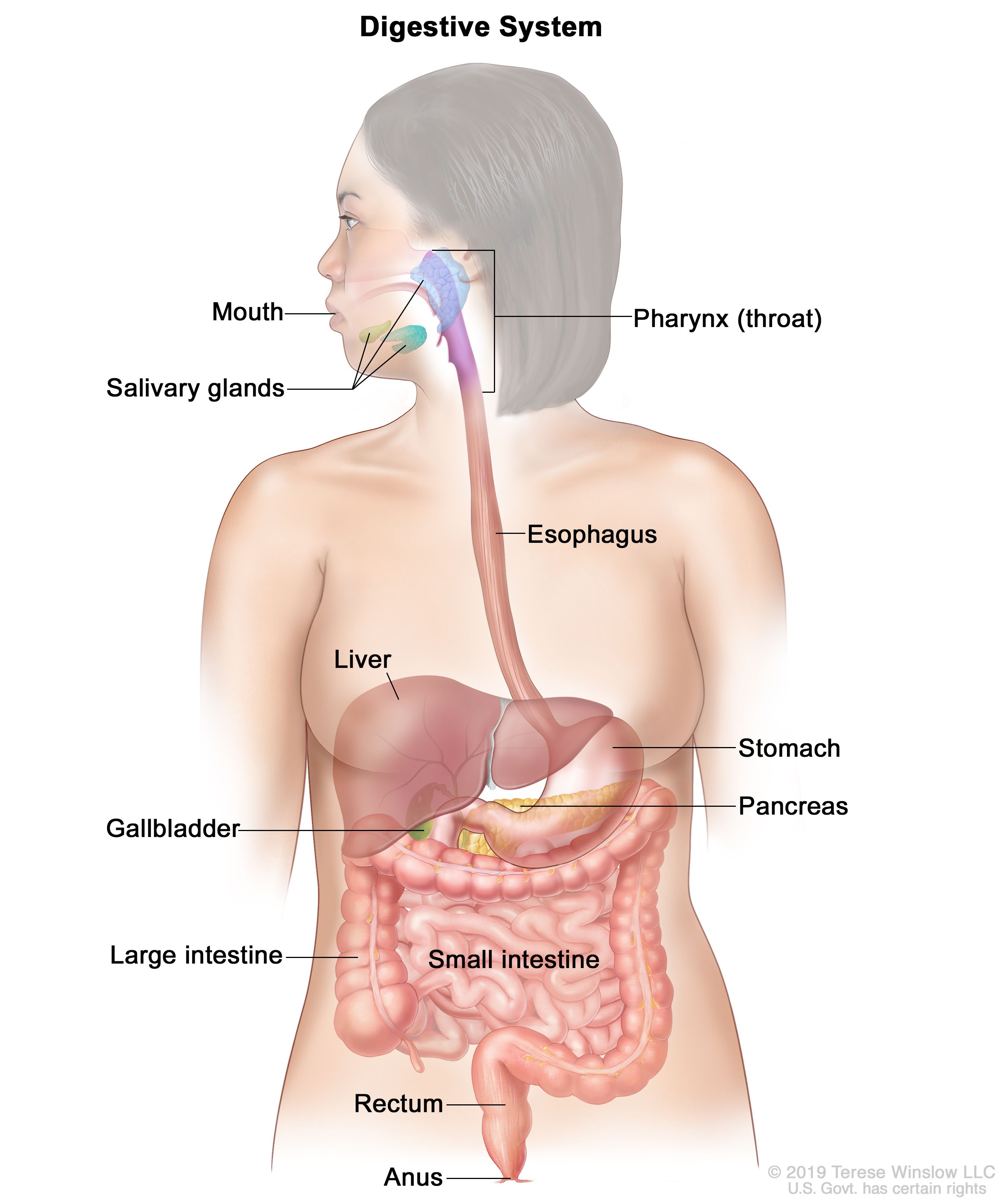
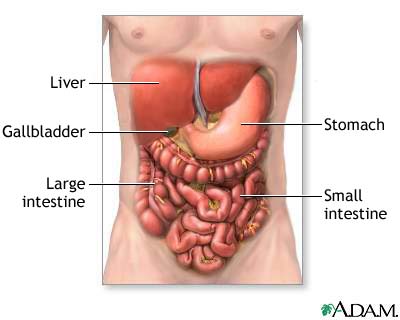

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-digestive-system--artwork-136811327-599a0ae603f4020011c410a6.jpg)