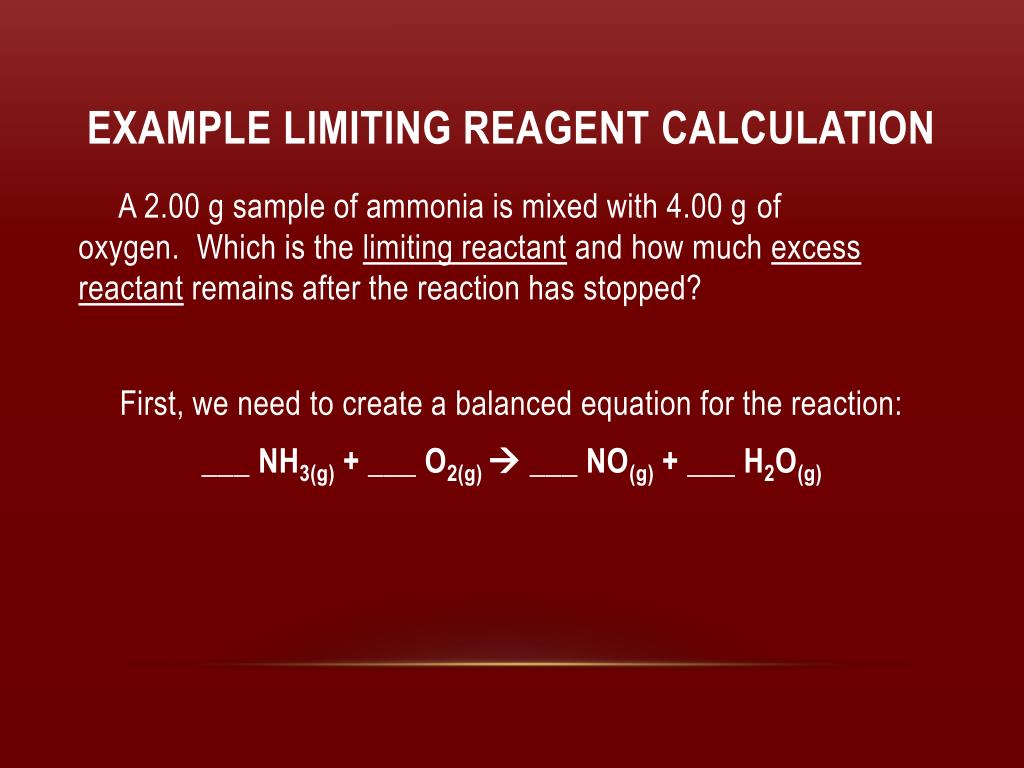
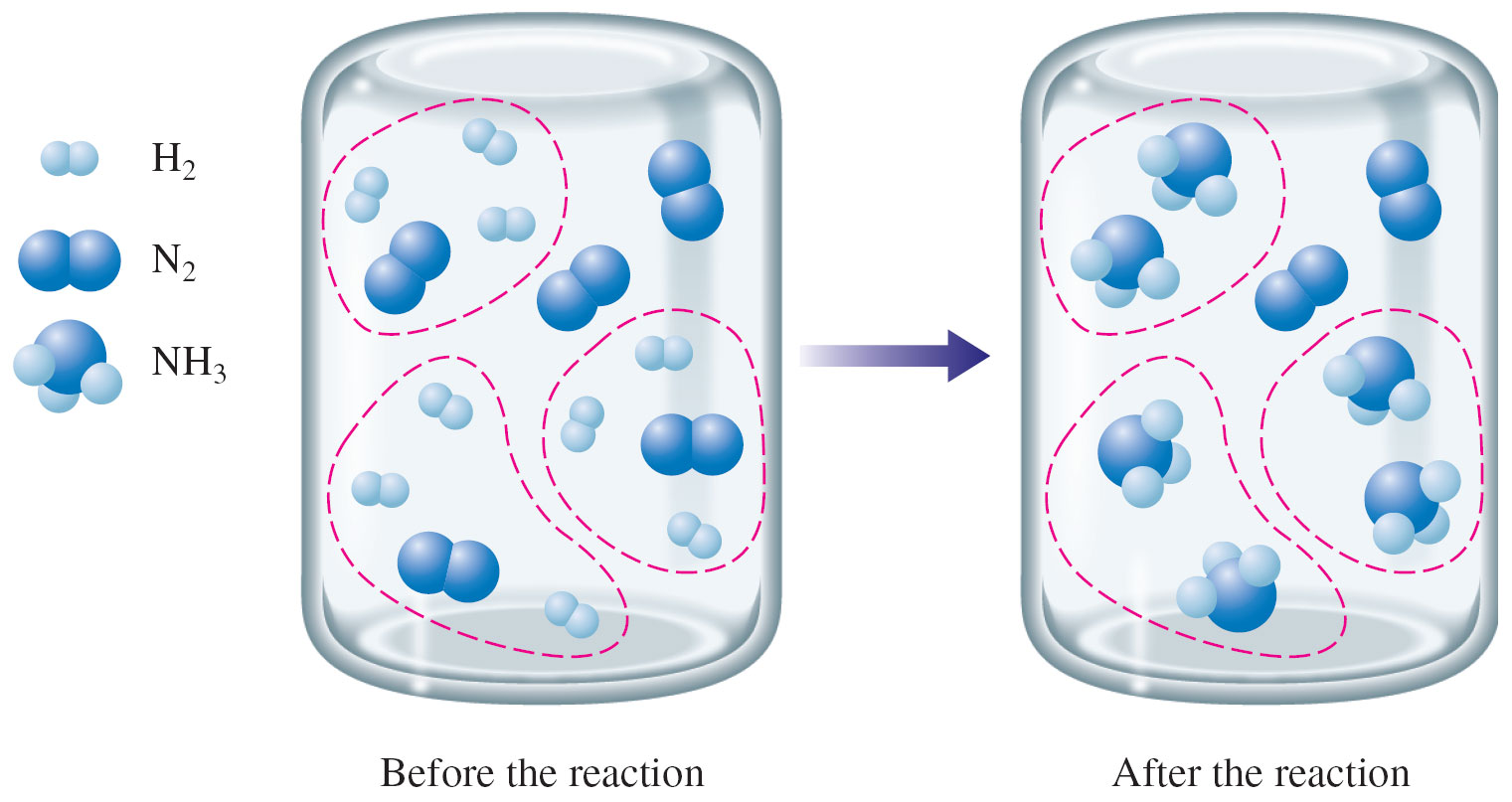
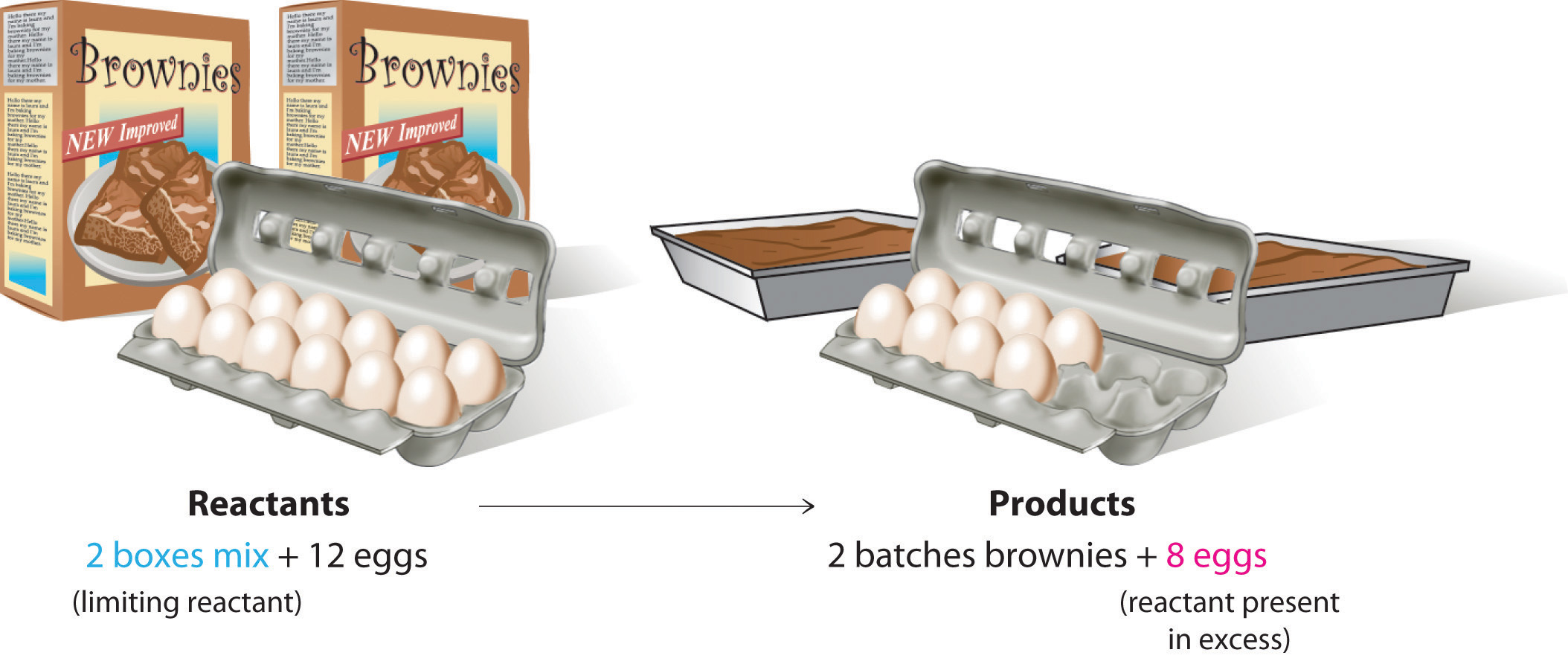
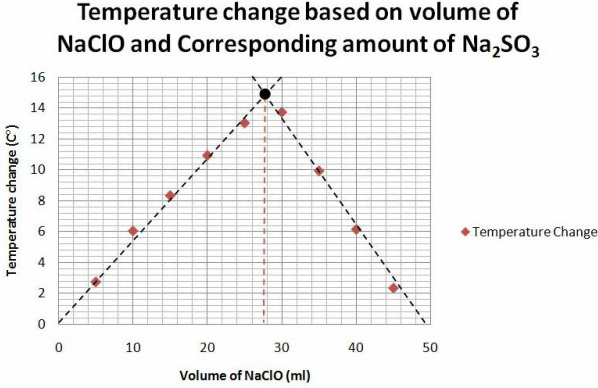
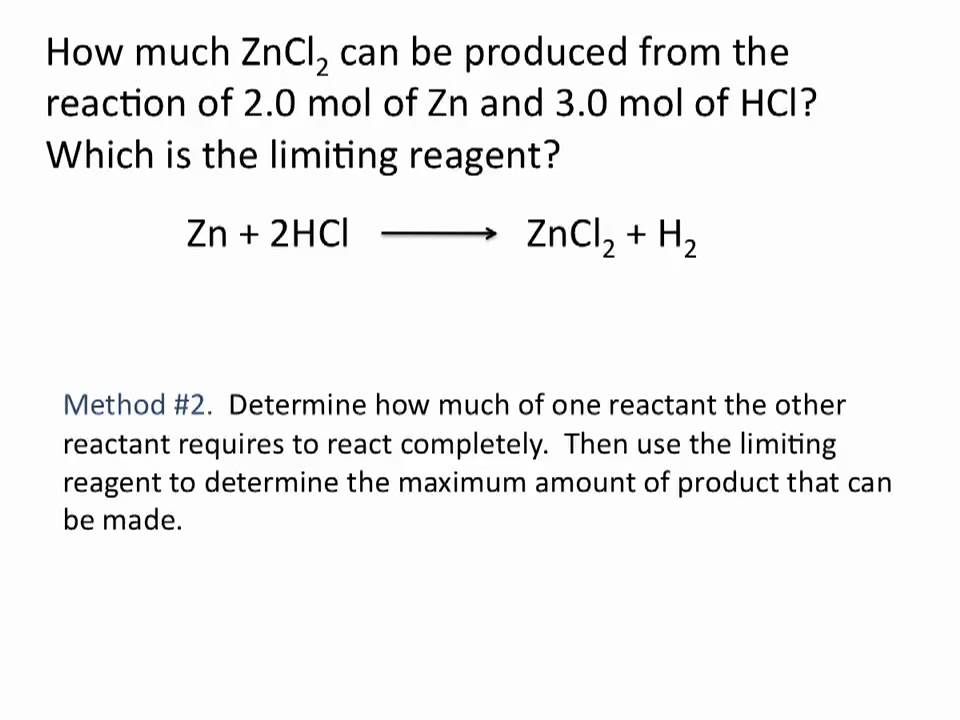
The limiting reactant, also known as the limiting reagent, is the reactant that is completely consumed before the other reactants in a chemical reaction. It is the reactant that determines the maximum yield of the product that can be obtained from a reaction.
In a chemical reaction, reactants are combined in a specific ratio to form products. However, the actual amount of reactants that are present may not always be in the ideal ratio. In such cases, one reactant may be present in excess while the other may be present in limited quantity. The reactant present in excess is referred to as the excess reactant, while the reactant present in limited quantity is referred to as the limiting reactant.
The limiting reactant plays a crucial role in determining the yield of the product in a chemical reaction. This is because the reaction will continue until the limiting reactant is completely consumed. Once the limiting reactant is used up, the reaction will come to a halt even if there is still an excess of other reactants present.
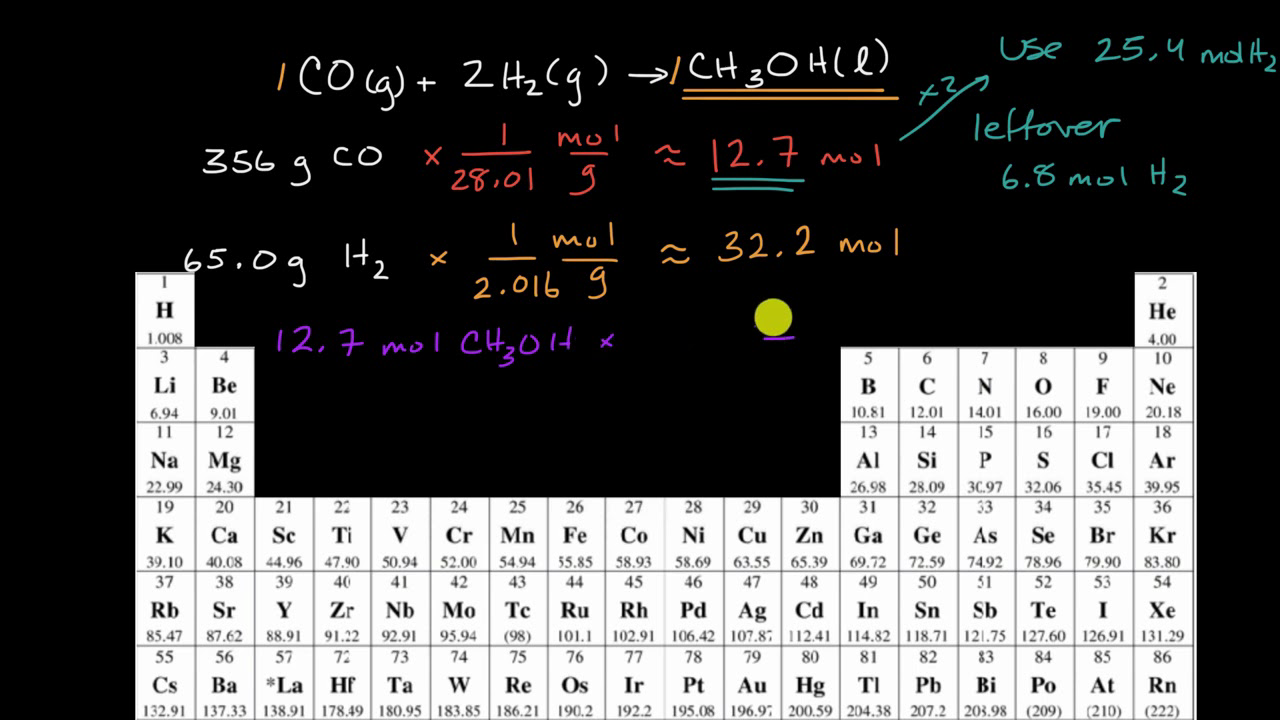
To determine the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction, the number of moles of each reactant must be calculated. The number of moles of each reactant can be determined by dividing the mass of the reactant by its molecular weight. The reactant with the lowest number of moles is the limiting reactant.
For example, consider the following chemical reaction: 2H2 + O2 -> 2H2O
Let's assume that we have 2 grams of hydrogen and 4 grams of oxygen. The number of moles of hydrogen can be calculated by dividing its mass by its molecular weight (2 grams / 2 grams/mole = 1 mole). Similarly, the number of moles of oxygen can be calculated by dividing its mass by its molecular weight (4 grams / 16 grams/mole = 0.25 moles). In this case, the number of moles of hydrogen is greater than the number of moles of oxygen. Therefore, oxygen is the limiting reactant and hydrogen is the excess reactant.
In conclusion, the limiting reactant is the reactant that determines the maximum yield of the product that can be obtained from a chemical reaction. It is the reactant that is completely consumed before the other reactants, thereby bringing the reaction to a halt.