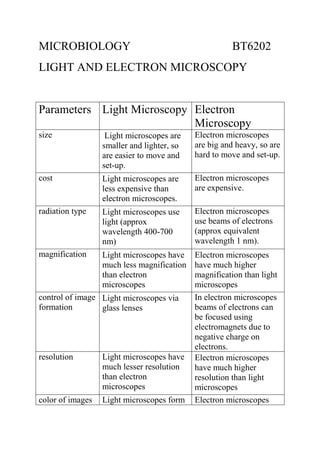
Light microscopes and electron microscopes are both tools used to observe and study small objects or structures, but they operate in fundamentally different ways.
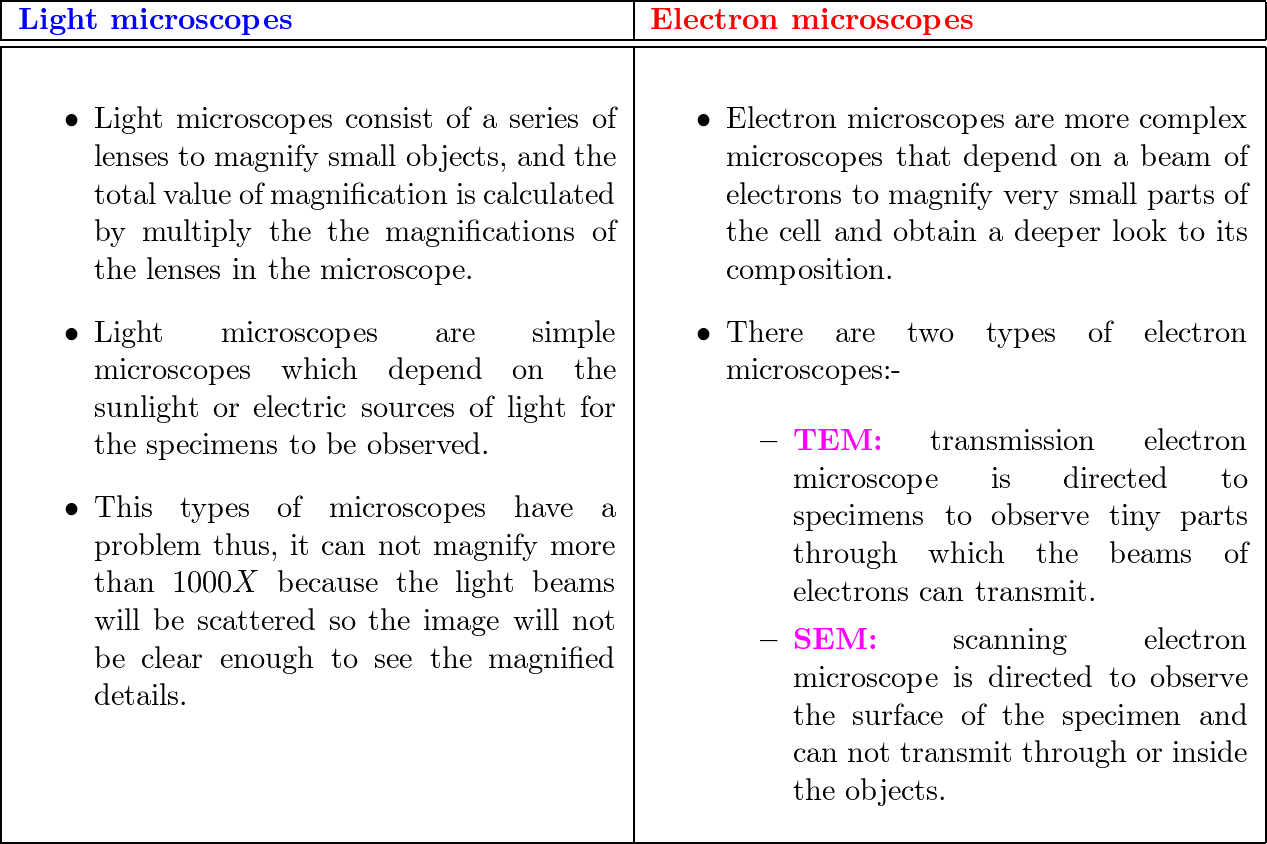
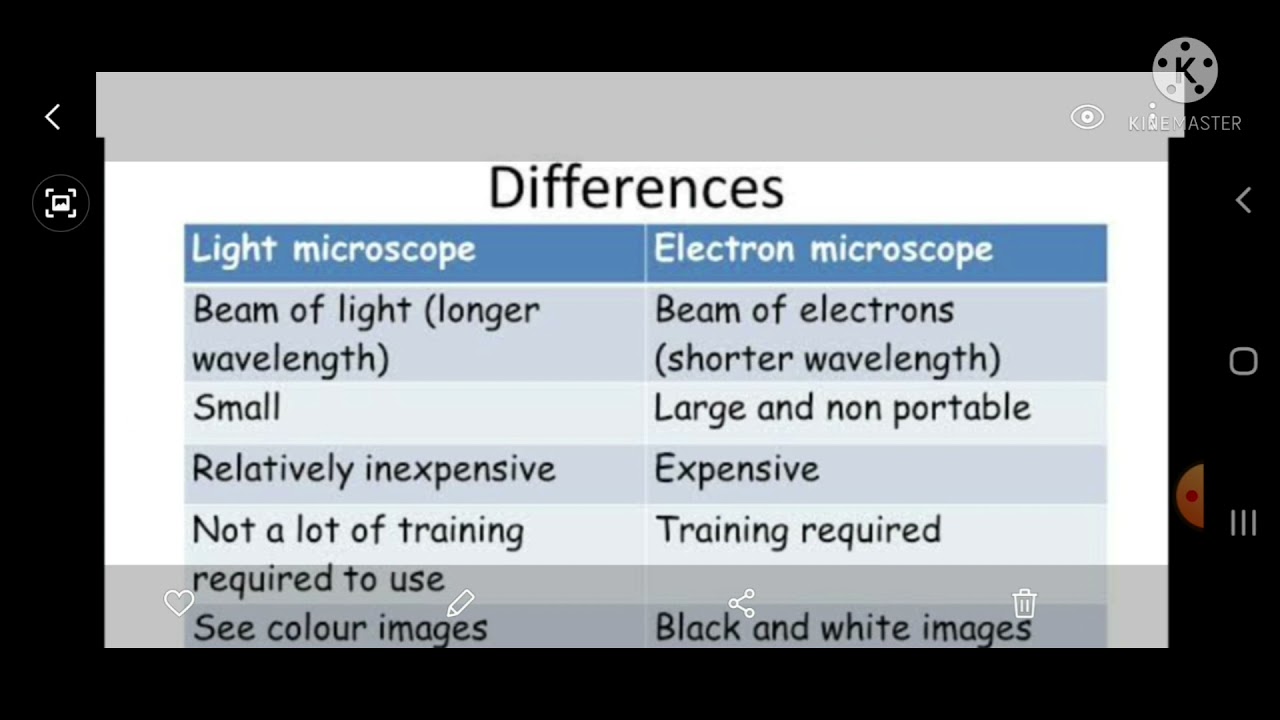
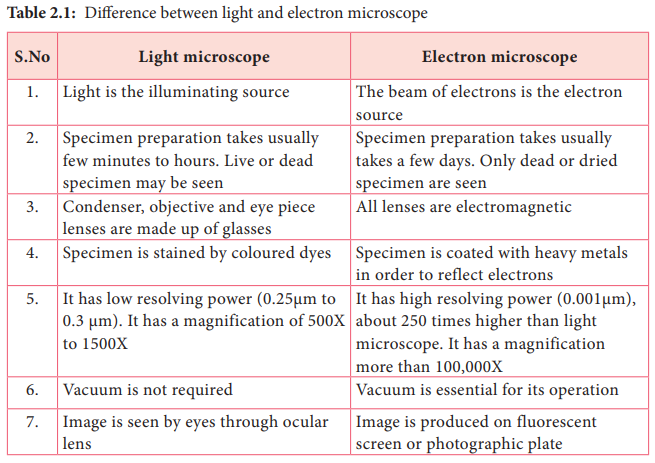
Light microscopes use lenses and light to magnify and image small objects. The lenses in a light microscope are made of transparent materials, such as glass or plastic, and work by refracting, or bending, light in a way that magnifies the image of the object being viewed. Light microscopes can magnify objects up to about 1,000 times their original size and have a resolution, or the smallest distance between two points that can be distinguished as separate, of around 0.2 micrometers. This means that light microscopes can distinguish objects as small as 0.2 micrometers apart.
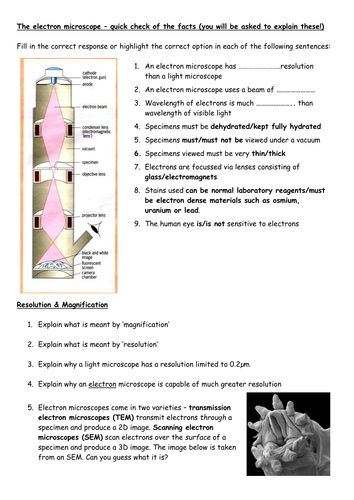
Electron microscopes, on the other hand, use a beam of electrons to magnify and image small objects. Electrons are much smaller than light waves and have a much shorter wavelength, so they are able to produce a higher resolution image than light microscopes. Electron microscopes can magnify objects up to about one million times their original size and have a resolution of around 0.002 nanometers. This means that electron microscopes can distinguish objects as small as 0.002 nanometers apart.
One major difference between light microscopes and electron microscopes is the way they produce an image. Light microscopes produce an image by transmitting light through or reflecting it off the object being viewed. Electron microscopes, on the other hand, produce an image by directing a beam of electrons at the object and detecting the electrons that are scattered by the object. This scattered electron beam is then used to create an image of the object.
Another difference between light microscopes and electron microscopes is the type of samples they can be used to observe. Light microscopes are limited to viewing samples that are transparent or relatively thin, as the light needs to pass through the sample to produce an image. Electron microscopes, on the other hand, can be used to view a wide range of samples, including thick, opaque samples.
In terms of cost and complexity, electron microscopes are generally more expensive and complex than light microscopes. This is due to the fact that they require a vacuum chamber to operate and use specialized equipment, such as an electron gun, to produce a beam of electrons. Light microscopes, on the other hand, are relatively simple and inexpensive, making them more accessible to a wider range of users.
Overall, light microscopes and electron microscopes are both useful tools for studying small objects and structures, but they operate in fundamentally different ways and have different capabilities and limitations. Light microscopes are useful for viewing transparent or thin samples and have a lower resolution than electron microscopes, while electron microscopes are capable of viewing a wider range of samples and have a higher resolution than light microscopes.