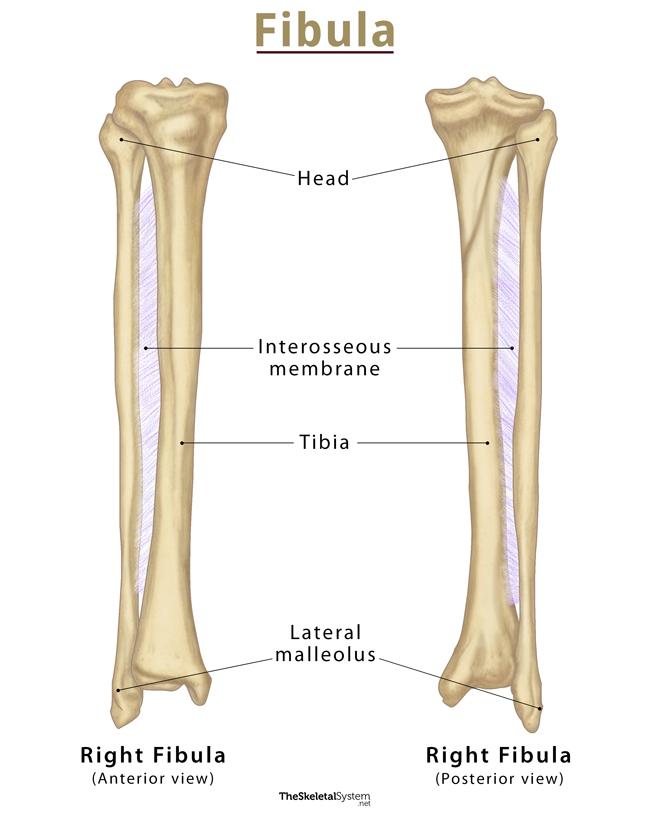
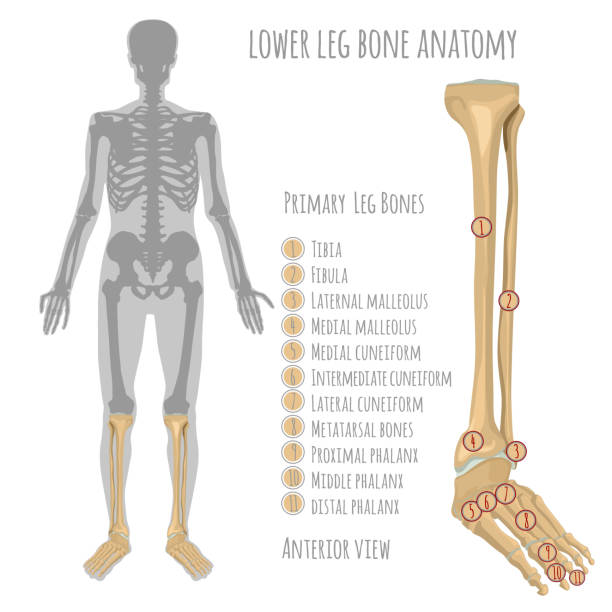
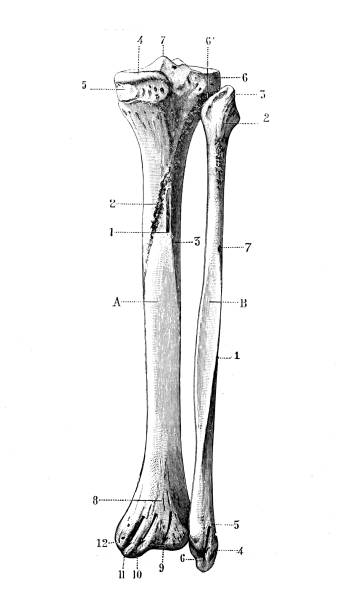
The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is a long bone located in the lower leg. It is the larger of the two bones in the leg, with the other being the fibula. The tibia is responsible for bearing most of the body's weight and serves as a point of attachment for many muscles.
The tibia is located between the knee and ankle joints and runs parallel to the fibula. It is a weight-bearing bone and is thicker and stronger than the fibula. The top of the tibia, called the proximal end, forms the knee joint with the femur, the bone in the thigh. The bottom of the tibia, called the distal end, forms the ankle joint with the talus, a bone in the foot.
The tibia has a number of bony protuberances, or prominences, that serve as attachment points for muscles and ligaments. The medial malleolus is a rounded prominence on the inner side of the ankle, and the lateral malleolus is a similar prominence on the outer side of the ankle. The tibial tuberosity is a bump on the front of the tibia that serves as an attachment point for the patellar ligament, which connects the knee cap to the tibia.
The tibia also has a number of articular surfaces, or smooth, polished areas that allow for smooth joint movement. The tibial plateau is a flat, concave surface on the top of the tibia that forms the knee joint with the femur. The tibial plafond is a smooth surface at the bottom of the tibia that forms the ankle joint with the talus.
In addition to its structural and functional roles, the tibia also plays a role in blood circulation. The tibia contains the tibial artery and vein, which carry blood to and from the lower leg and foot.
Overall, the tibia is a vital bone in the body, providing structural support and allowing for movement of the lower leg and foot. It is important to take care of the tibia and protect it from injury, as a fracture or other injury to the tibia can be debilitating and have long-term effects on mobility.