Tibia and fibula. Ankle Fractures (Tibia and Fibula) 2022-10-24
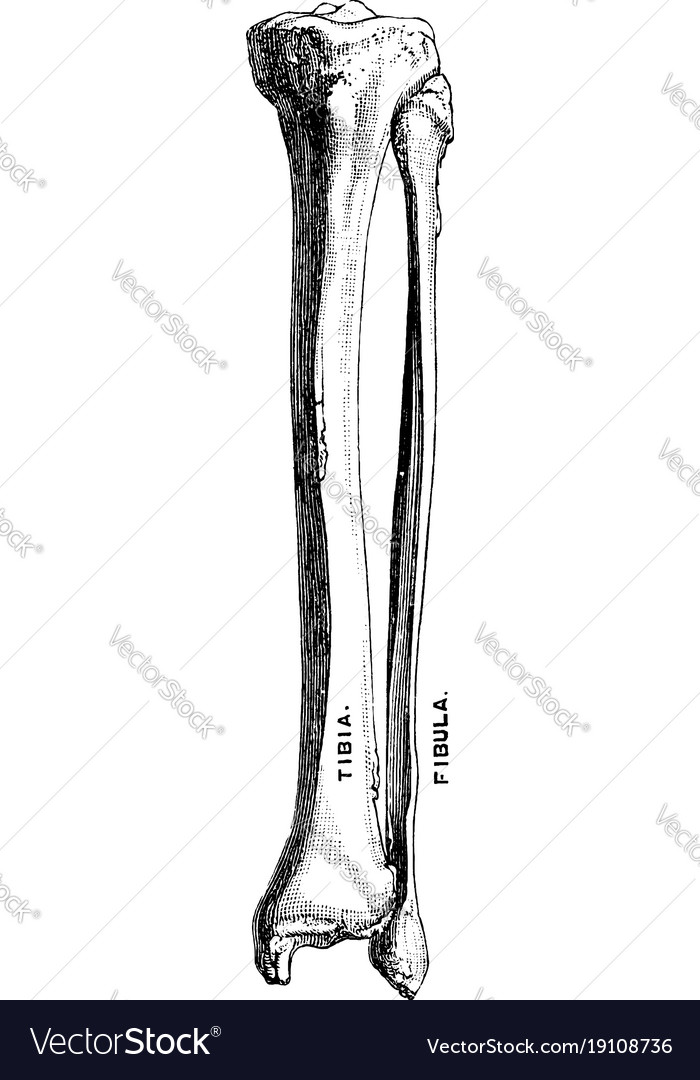
Tibia and fibula
Rating:
8,6/10
1380
reviews
The tibia and fibula are two bones located in the lower leg. The tibia, also known as the shinbone, is the larger of the two bones and is the primary weight-bearing bone in the leg. It is the innermost bone of the lower leg, and it articulates with the femur at the knee joint and the talus at the ankle joint.
The fibula, on the other hand, is a smaller and thinner bone that runs parallel to the tibia. It is located on the outer side of the lower leg, and it articulates with the tibia at the top and bottom ends. The fibula does not bear as much weight as the tibia, but it plays a crucial role in stabilizing the ankle and supporting the muscles of the lower leg.
Both the tibia and fibula are essential for movement and support in the lower leg. They work together to allow us to walk, run, and perform other activities that involve movement of the lower body. The tibia and fibula also provide protection for the muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in the lower leg.
Injuries to the tibia and fibula are common, especially in sports and other physical activities. Fractures of these bones can occur due to trauma or overuse, and they can range from simple to complex. Treatment for tibia and fibula fractures may involve immobilization with a cast or surgery to repair the bone.
Overall, the tibia and fibula are vital bones in the lower leg that play important roles in movement and support. Without them, our lower bodies would not be able to function properly.
Tibia and fibula, shaft—introduction

Ankle fractures range from simple injuries of a single bone to complex ones involving multiple bones and ligaments. It also separates muscles on the anterior and posterior parts of the leg. There are two main tibial approaches. ORIF often takes place as an emergency or urgent procedure. Swelling will decrease, and the patient is eventually able to weight bear and walk normally fully. This injury is produced by a strong external rotation force, one that would assuredly damage the lateral side of the ankle as well. Physical Therapy after Tibia and Fibula Fractures After surgery, physical therapy will begin as soon as the surgeon decides.
Next
The Structure & Function Of The Tibia And Fibula

Oblique fractures are typically unstable and can shorten. The tubes function as handles for manipulation of the fracture fragments. Fibula fracture treatment will vary according to the severity of the injury, but first aid should always include immobilization of the fractured leg and treatment of any bleeding that may result from the injury. This injury is important to detect given the proximity of the common peroneal nerve to the fibular fracture line. Proximally enter the knee joint by dividing the synovium. Some include trauma from a high fall, contact sports, or vehicle accidents. What kind of cast is used for a broken fibula? It is at most risk during the incision of the knee joint synovium.
Next
Tibia and Fibula Bone Quiz for Anatomy
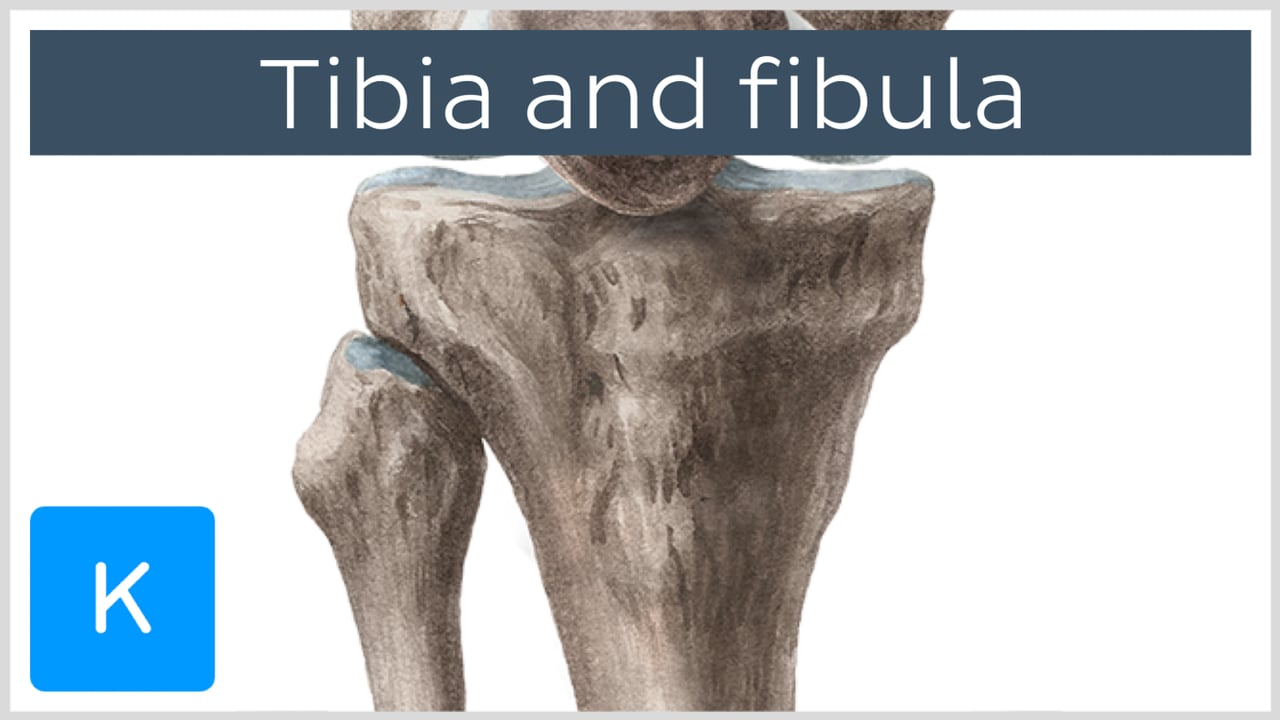
You may need to have your stitches or staples removed a week or so after your surgery. Deepening the wound provides access to all the structures that pass behind the medial malleolus. Unlike the fibula, the tibia transmits most of the bodyweight during standing, walking, running, etc. Description Ankle fractures are breaks of the distal tibia or fibula near or in the so-called malleolus affecting the tibiotalar ankle joint. The fascicles then take an oblique, superomedial, course and attach to the anterior surface of the lateral tibial condyle. To extend the approach distally, curve the incision over the medial side of the hind part of the foot.
Next
The Tibia and Fibula

Often there is a deformity present in the limb or a wound where the bone protrudes through the skin. Red Flags Blood on the skin is suggestive of an open fracture. Although the ligaments are needed to give the ankle its full stability, the bony congruity of the mortise and the talus is a necessary component as well forming the most congruent joint in the lower extremity. The skin over the lower third of the tibia is very thin; wounds in that area heal badly, especially in patients with chronic venous insufficiency. Identify and isolate the common peroneal nerve in its course behind the biceps tendon; trace it as it winds around the fibular neck Fig.
Next
What connects the tibia and fibula?
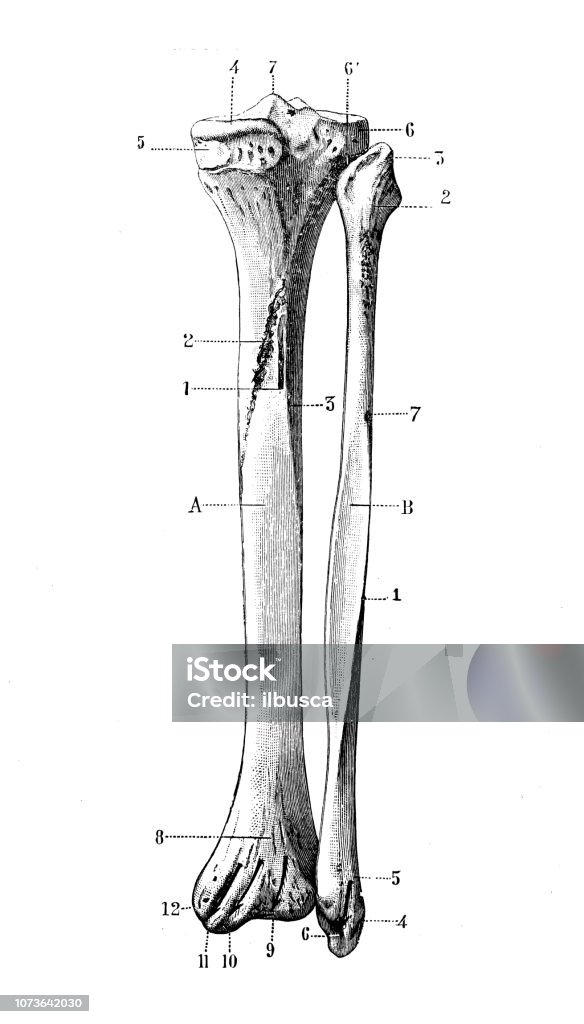
Ligaments and joint capsule As a fibrous joint, the inferior tibiofibular joint does not have an articular capsule, or its own synovial membrane. What is the fibula bone of the body? The lateral malleolus is the distal end of the fibula, whereas the medial and posterior malleoli are part of the tibia. What are the different types of tibia-fibula fractures? Figure 7: Mortise View of the Ankle right. To reach the posterior surface of the tibia from an anterior approach, continue the epi-periosteal dissection posteriorly around the medial border. They both course inferiorly and laterally, with the posterior ligament being thicker and wider than the anterior. Exsanguinate the limb either by elevating it for 3 to 5 minutes or by applying a soft rubber bandage. Usually, spiral and transverse fractures are stable enough for a cast.
Next
Ankle Fractures (Tibia and Fibula)
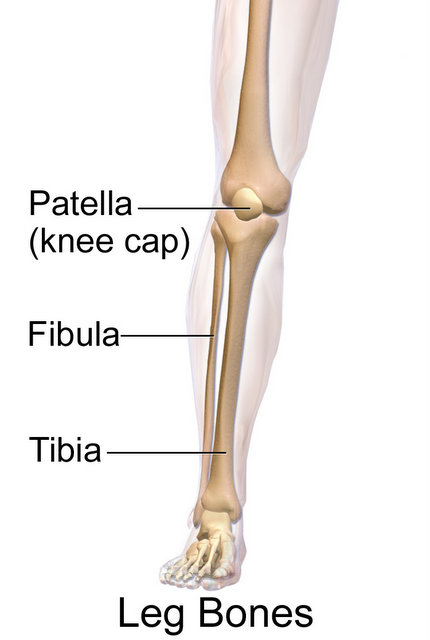
Ask your healthcare provider about the risks that most apply to you. As almost ¼ of tibial fractures are open fractures, the physical examination should include a careful evaluation and description of the extent of any soft tissue injury; likewise, given the high incidence of compartment syndrome and the susceptibility to injury of the tethered common peroneal nerve and popliteal artery, a carful neurovascular exam must be documented. Begin at the level of the tibial tubercle and extend the incision distally, ending 6 cm above the ankle. A fracture affecting both the medial and lateral malleoli is called a bimalleolar fracture, and one involving the medial, lateral, and posterior malleoli, the posterior aspect of the distal tibia, is called a trimalleolar fracture. The surface may crack and not bend in response to a new load. The peroneal compartment is bounded by the anterior intermuscular septum in front, by the posterior intermuscular septum behind, and by the fibula medially. Until the bone becomes stronger, a strong tug by the tendon can cause this part of the bone to break.
Next
Tibia and Fibula Shaft
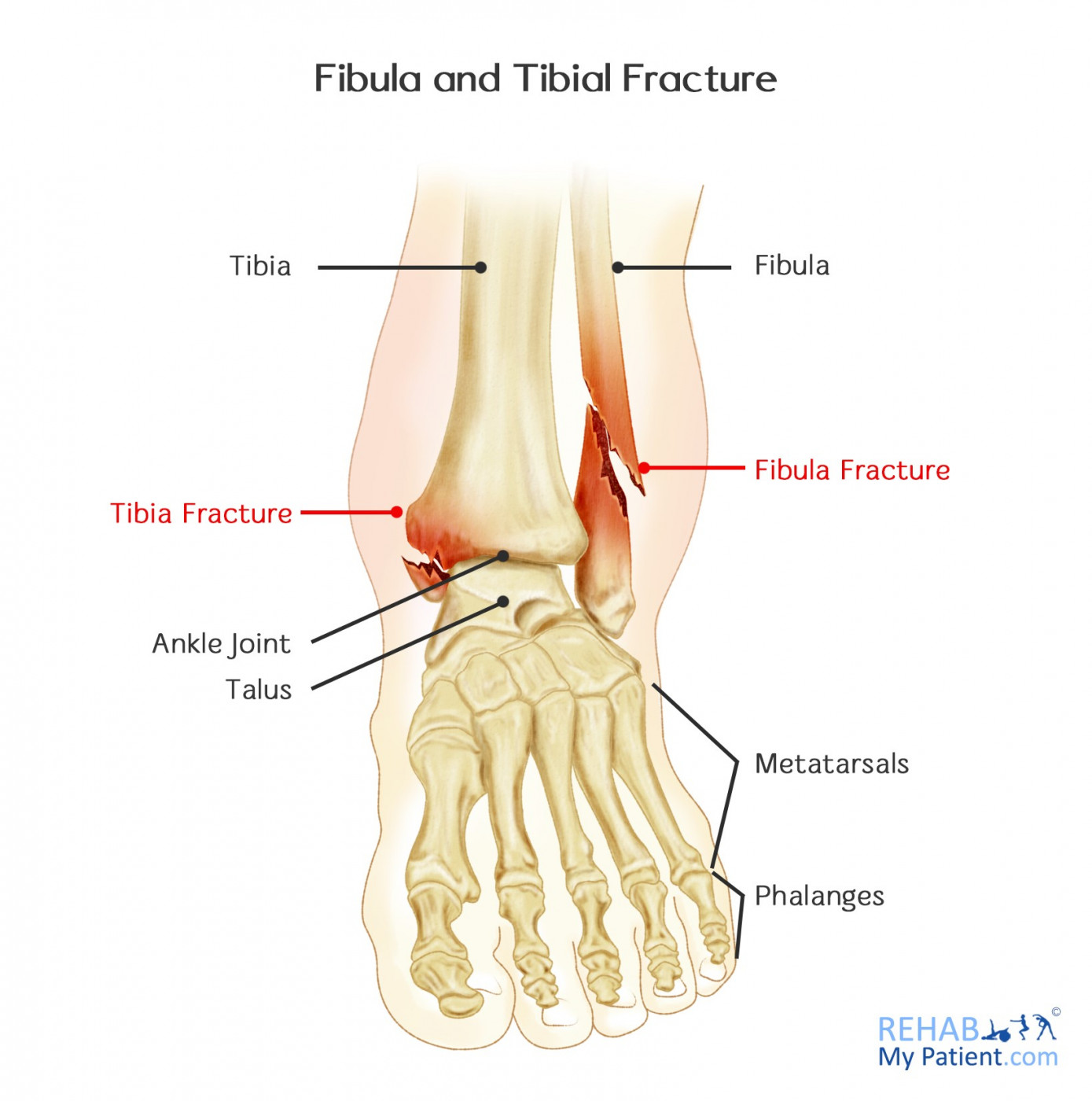
Synonyms: Anterior ligament of lateral malleolus, Ligamentum anterior malleoli lateralis The articular surfaces of the distal tibiofibular joint are held together by the interosseous ligament, and the anterior, posterior and transverse tibiofibular ligaments. Figure 11-3 Deepen the incision proximally through subcutaneous tissue to expose the lateral aspect of the knee joint capsule. The hardware can be left in the joint permanently unless it causes irritation, in which case it can be removed once the fracture has healed. Tunneling should be performed deep to the plane of the saphenous nerve and vein, especially in the distal tibia. Normally, for Compound Tibia or Fibula Fracture, it takes roughly 6 to 8 months for an individual to recover and get back to normal activities. Open fractures require administration of antibiotics and tetanus prophylaxis as indicated.
Next
Tibiofibular joints: Anatomy, movements

The fibula is also translated superiorly in this movement, which is followed by a superior gliding movement within both the inferior and superior tibiofibular joints. With timely and proper treatment, a broken tibia-fibula can heal completely. Note that minimal traction is required to reduce a fresh tibial shaft fracture. Fibula shaft fractures may occur in conjunction with tibia fractures through any of the above mechanisms. Continue dissecting posteriorly, staying on the posterior surface of the fibula. The tibia is one of two bones that make up the lower leg, the other being the fibula. It traverses the anterior aspect of the joint.
Next
Tibia and fibula series
Edinburgh: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. This will help to ensure that your bone density is maintained over time. The tibia or shinbone connects the knee to the ankle. For example, a twisting injury to the foot and ankle may send force through the syndesmosis and interosseous membrane, up the leg. There are two bones in the shin area: the tibia and fibula, or calf bone. Provide first-line treatment to open fractures wound management and dislocations gross reduction and splinting. Because the distal tibia has a large subcutaneous surface, access to the bone is easy through the skin incisions lying directly over the bone.
Next
What is the function of tibia and fibula?

The posterior surface of the tibia is deep and is not suitable for MIPO. The long saphenous vein and the saphenous nerve will be just anterior to the surgical approach; these structures should be identified and preserved. Tibia and Fibula Fractures By Louis Corpora, PTA Tibia and Fibula Anatomy The tibia and fibula are the two long bones of the lower leg. Twisting with the foot planted on the ground and the body rotating around it is the most common mechanism of injury. This is going to articulate with the medial and lateral condyles of the tibiofemoral joint. The major ligaments of the ankle are: the anterior tibiofibular ligament 2 , which connects the tibia to the fibula; the lateral collateral ligaments 3 , which attach the fibula to the calcaneus and gives the ankle lateral stability; and, on the medial side of the ankle, the deltoid ligaments 4 , which connect the … What bone connects your leg bones together? It contains the peroneal muscles, which evert the foot.
Next







