The unification of Italy and Germany in the 19th century was a significant event in European history that had far-reaching consequences. Both countries had been divided into various states and territories, each with its own rulers and political systems, for centuries. The process of unification involved the abolition of these states and the creation of a single, united nation under a central government.
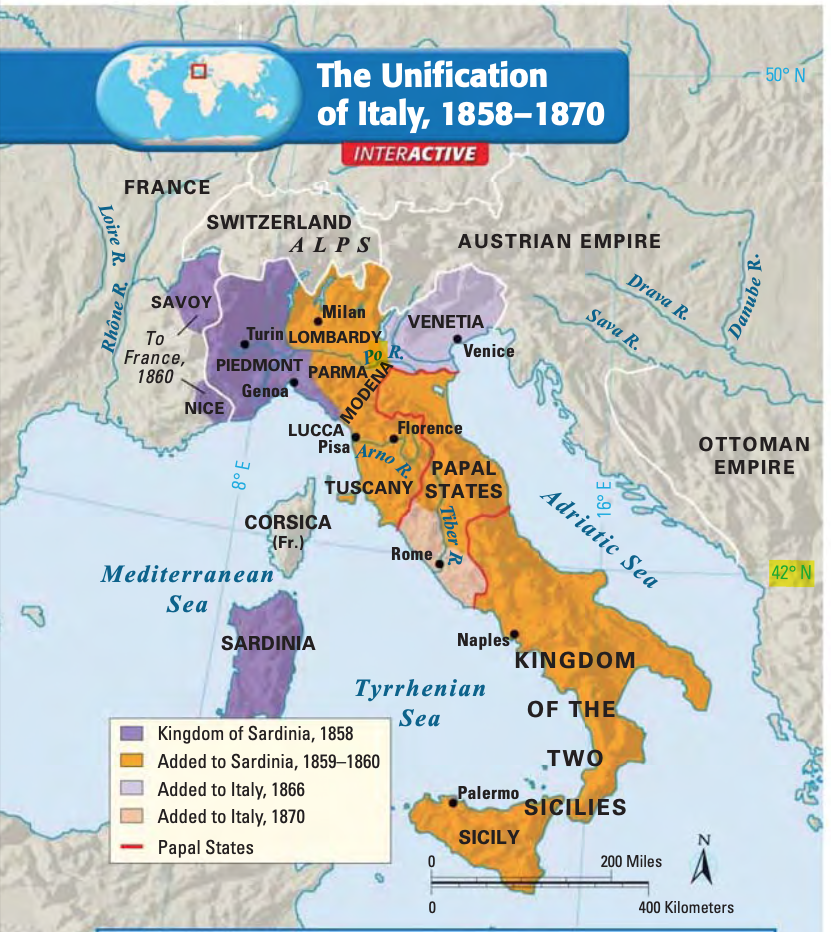
The unification of Italy was led by the statesman Count Camillo Benso di Cavour and the military leader Giuseppe Garibaldi. Cavour, the prime minister of the Kingdom of Sardinia, pursued a policy of diplomatic and military maneuvers to bring about the unification of Italy. He formed alliances with other European powers and used military force to annex territories to the Kingdom of Sardinia. Garibaldi, on the other hand, was a popular hero who led a series of military campaigns to unite the various states of Italy under the banner of a single, united nation.
The unification of Germany was led by the statesman Otto von Bismarck. Bismarck, the prime minister of Prussia, pursued a policy of "blood and iron" to bring about the unification of Germany. He used military force to annex territories to Prussia and formed alliances with other German states to create a unified German nation.
Both the unification of Italy and Germany were driven by a number of factors, including nationalism, economic interests, and a desire for political stability and power. Nationalism played a significant role in both unifications, as people in both countries began to see themselves as part of a larger, shared national identity. Economic interests also played a role, as the creation of a single, unified market would allow for the expansion of trade and the growth of industry. Finally, both unifications were driven by a desire for political stability and power. By uniting the various states and territories under a single government, leaders in both Italy and Germany hoped to create more stable and powerful nations.
The unification of Italy and Germany had a significant impact on European politics and history. Both countries became major powers in Europe, and their unification contributed to the emergence of a more cohesive and interconnected European political system. It also had consequences beyond Europe, as the growth of these two nations led to an increase in imperialism and colonialism, as they sought to extend their influence around the world.
In conclusion, the unification of Italy and Germany in the 19th century was a major event in European history that had far-reaching consequences. It was driven by a combination of nationalism, economic interests, and a desire for political stability and power, and it had a significant impact on European politics and history.