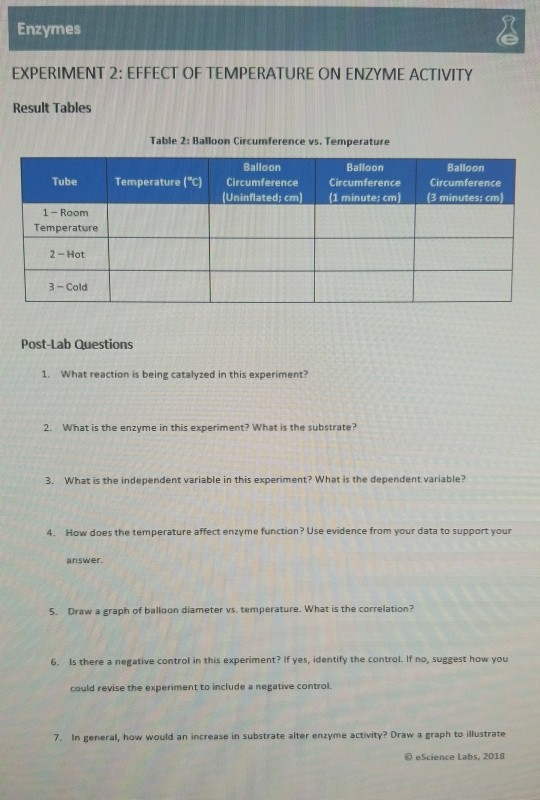
Temperature is an important factor that can affect the activity of enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in the body and are essential for many of the functions that sustain life. They are highly specific and only catalyze specific reactions, but they are also sensitive to their environment, including temperature.
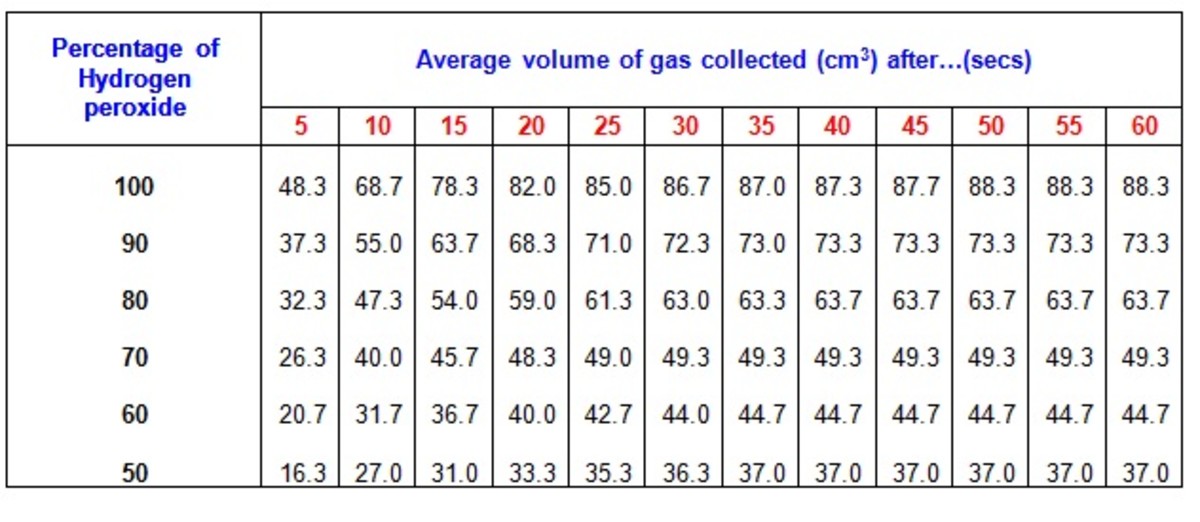
In a laboratory setting, it is possible to study the effects of temperature on enzyme activity by performing experiments with a purified enzyme and measuring the rate of the reaction it catalyzes. One way to do this is to measure the production of a product of the reaction, such as the amount of oxygen produced in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme catalase.
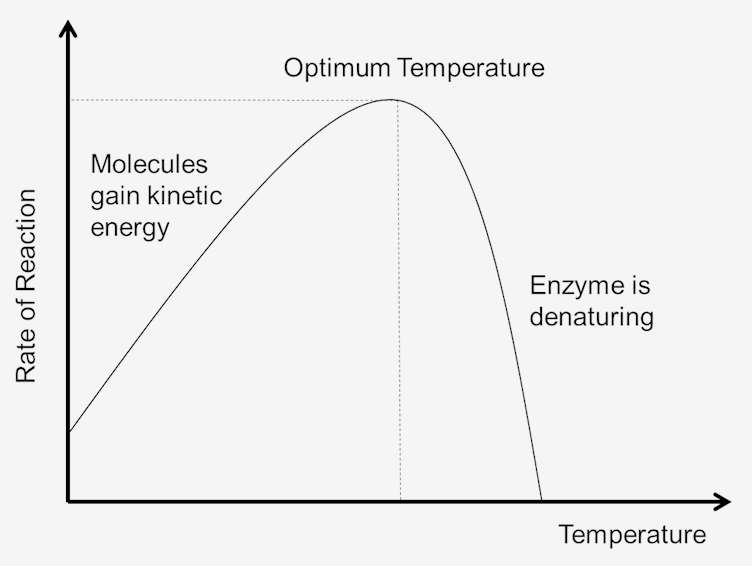
When the temperature is increased, the kinetic energy of the enzyme and substrate molecules also increases. This can lead to an increase in the rate of the reaction, as the molecules have more energy and are more likely to collide and react with each other. However, as the temperature continues to rise, the enzyme can begin to denature, or lose its three-dimensional structure. When this happens, the enzyme is no longer able to catalyze the reaction, and the rate of the reaction will decrease.
In general, enzymes have an optimal temperature at which they are most active, and the rate of the reaction will be highest at this temperature. For human enzymes, this is typically around 37°C, the body's normal temperature. However, enzymes from other organisms, such as bacteria, may have a different optimal temperature.
It is also important to note that enzymes can be sensitive to changes in pH, as well as temperature. Like temperature, pH can affect the enzyme's three-dimensional structure and, as a result, its activity.
In summary, temperature can have a significant effect on enzyme activity. As the temperature increases, the rate of the reaction may increase up to a certain point, but then it will begin to decrease as the enzyme denatures. It is important to consider temperature and other environmental factors when studying enzymes in the laboratory.