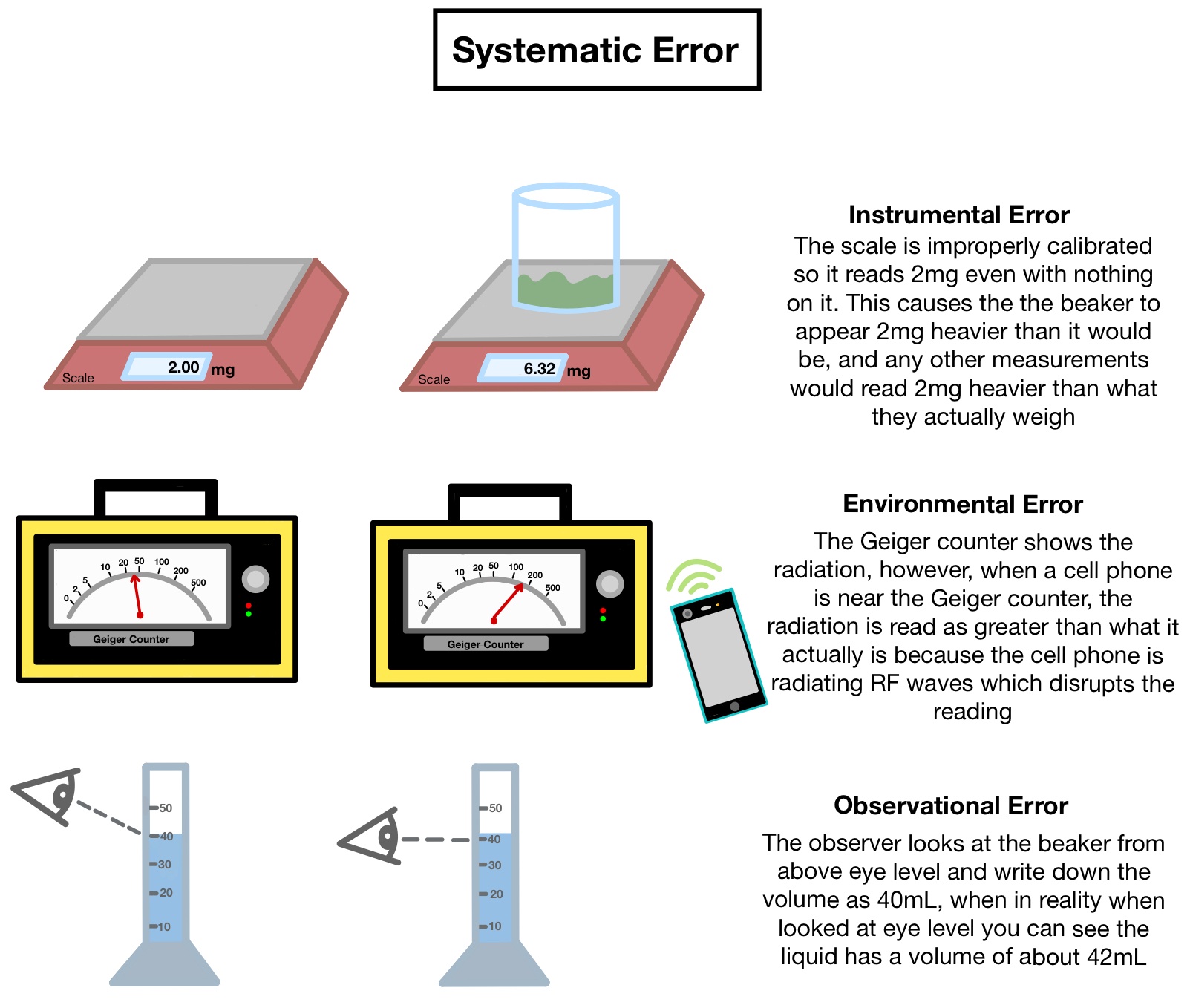
Systematic observation is a research method in which a researcher carefully and systematically observes and records the behavior of individuals or groups in a controlled environment. Systematic observation is a valuable tool for understanding complex social and psychological phenomena, and it is used in a wide range of fields, including psychology, sociology, anthropology, education, and public health.
One example of systematic observation can be seen in the work of Stanley Milgram, a social psychologist who conducted a series of experiments in the 1960s to study the effects of authority on obedience. In these experiments, participants were told to administer increasingly intense electric shocks to a confederate (an actor posing as a subject) whenever they made a mistake on a learning task. The goal of the study was to investigate whether people would obey authority figures even when it meant causing harm to others.
To conduct the study, Milgram set up a laboratory in which the participants and confederates were seated in separate rooms. The participants were told that the study was about the effects of punishment on learning, and they were given the role of "teacher." The confederates were told to pretend to be "learners" and to respond to the shocks with increasingly distressed responses as the intensity of the shocks increased.
Milgram carefully observed and recorded the behavior of the participants as they administered the shocks, noting their reactions to the confederate's responses and their level of obedience to the experimenter's instructions. Through systematic observation, Milgram was able to gain insight into the psychological processes underlying obedience to authority, and his findings had significant implications for our understanding of social influence and power dynamics.
Another example of systematic observation can be seen in the work of Jane Goodall, a primatologist who studied the social and behavioral patterns of chimpanzees in the wild. Goodall conducted her research by observing and recording the behavior of individual chimpanzees in their natural habitat, using a variety of techniques including structured observations, focal animal sampling, and ad libitum sampling.
Goodall's systematic observations allowed her to make detailed and accurate observations of the chimpanzees' behavior, including their communication patterns, social relationships, and feeding habits. Her findings helped to shed light on the complex social and cognitive abilities of chimpanzees and contributed to our understanding of the evolution of human behavior.
Overall, systematic observation is a powerful research method that allows researchers to carefully and systematically study the behavior of individuals or groups in a controlled environment. Through systematic observation, researchers can gain insight into complex social and psychological phenomena and make important contributions to our understanding of the world around us.