A summary trial is a type of criminal proceedings in India that is governed by the Code of Criminal Procedure (CRPC). It is designed to provide a quick and efficient means of disposing of minor offenses that do not warrant the full procedure of a regular trial.
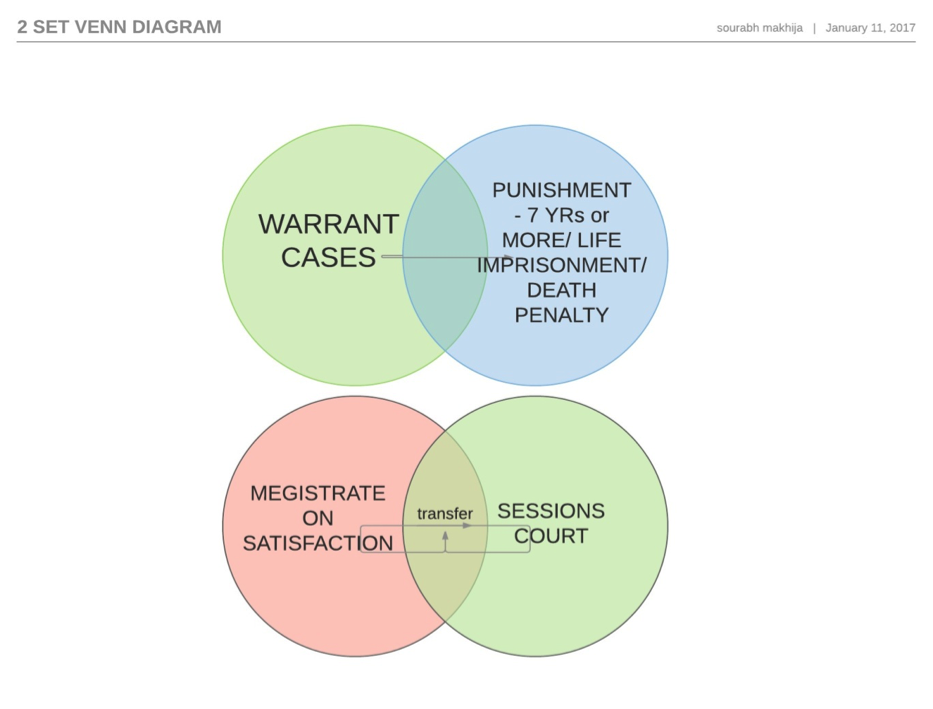
Under the CRPC, a summary trial is held in cases where the offense is punishable with imprisonment for a term not exceeding two years or with fine not exceeding one thousand rupees. These offenses are typically classified as "petty offenses" and are considered less serious than other crimes.
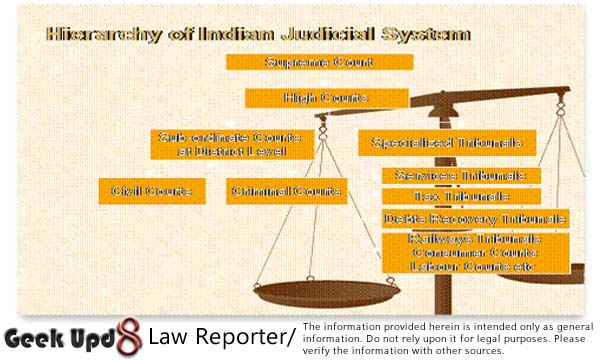
The summary trial procedure is simpler and less formal than a regular trial. It is conducted by a Magistrate, who is a judicial officer responsible for handling criminal cases in a particular jurisdiction. The Magistrate is assisted by a clerk, who records the proceedings.
The accused person has the right to be present at the summary trial and to be represented by a lawyer. However, the accused is not entitled to a jury trial in a summary trial. Instead, the Magistrate alone is responsible for determining the guilt or innocence of the accused based on the evidence presented.
The prosecution must present its case first, followed by the defense. Both sides have the opportunity to present evidence and call witnesses to testify. The Magistrate may also ask questions to clarify the testimony or to gather additional information.
Once the prosecution and defense have presented their cases, the Magistrate will consider the evidence and arguments and make a decision on the guilt or innocence of the accused. If the accused is found guilty, the Magistrate will pronounce the sentence.
One of the advantages of a summary trial is that it is generally quicker and less expensive than a regular trial. It is also less formal, which may make it more accessible to people who are not familiar with the legal system. However, the accused does not have the same rights and protections in a summary trial as they would in a regular trial, and the decision of the Magistrate is final and cannot be appealed.
Overall, the summary trial procedure under the CRPC serves an important role in the criminal justice system by providing a quick and efficient means of resolving minor offenses. It allows for the fair and just resolution of cases while minimizing the burden on the courts and the legal system.