Distal parenting, also known as "helicopter parenting," refers to a style of parenting in which parents are overly involved in their children's lives and try to control every aspect of their experiences. This type of parenting tends to produce children who are reliant on their parents for guidance and decision-making, and may struggle with self-regulation and independence.
One potential negative outcome of distal parenting is that children may lack the ability to solve problems on their own. When parents are constantly hovering and solving problems for their children, the children may not develop the skills and confidence needed to handle challenges independently. This can lead to a lack of resilience and an increased dependence on others for support.
Another potential consequence of distal parenting is that children may have difficulty developing their own sense of identity and autonomy. When parents are constantly directing and controlling their children's lives, the children may have little opportunity to explore their own interests and preferences. This can lead to a lack of self-direction and a reliance on external validation and approval.
In addition, distal parenting may lead to a lack of social skills and the inability to form and maintain healthy relationships. When children are not given the opportunity to interact with others and navigate social situations on their own, they may struggle with social interactions and have difficulty building and maintaining friendships.
Overall, distal parenting tends to produce children who are reliant on their parents and may struggle with independence, problem-solving, self-direction, and social skills. It is important for parents to strike a balance between providing support and guidance for their children, while also allowing them the opportunity to learn and grow on their own.
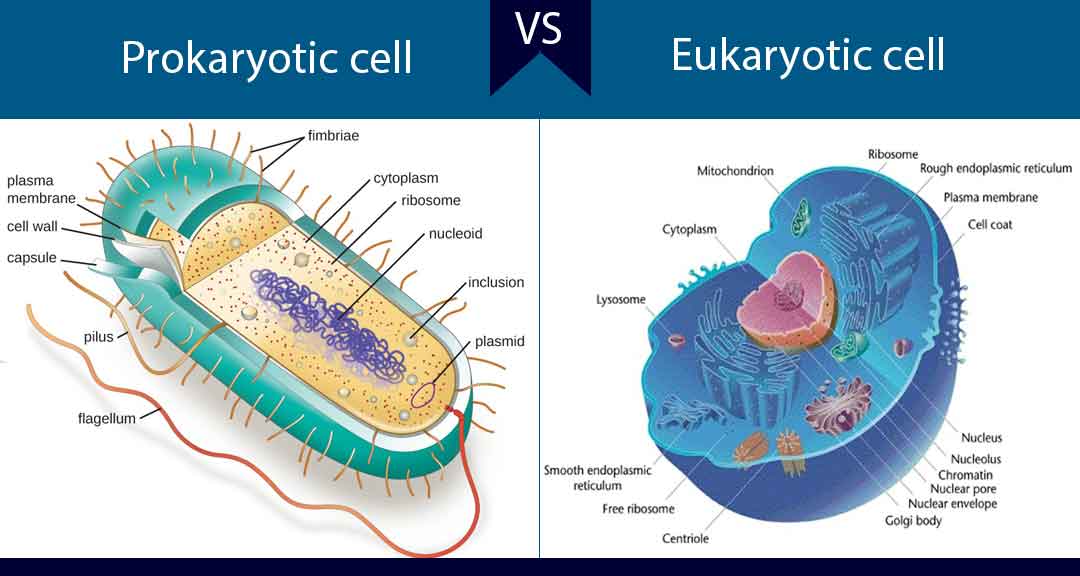
Eukaryote

The space between the two membranes is called the intermembrane space, and the space inside the inner membrane is called the mitochondrial matrix. Additionally, some agents such as enzymes within plant vacuoles break down macromolecules. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1 a membrane-bound nucleus; 2 numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3 several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. The Nuclear Envelope The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that constitutes the nucleus' outermost portion Figure 4. They are also the structural elements of centrioles, flagella, and cilia.
Eukaryotic Cells
The nuclear envelope is punctuated with pores that control the passage of ions, molecules, and RNA between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. This is mainly to account for the fact that eukaryotic signature proteins were not found anywhere else by 2002. Plasmodesmata are numerous channels that pass between the cell walls of adjacent plant cells, connecting their cytoplasm and enabling signal molecules and nutrients to be transported from cell to cell Figure 13a. Most are membrane-bound structures that are the sites of specific types of biochemical reactions. Some bacteria also perform photosynthesis, but they do not have chloroplasts.
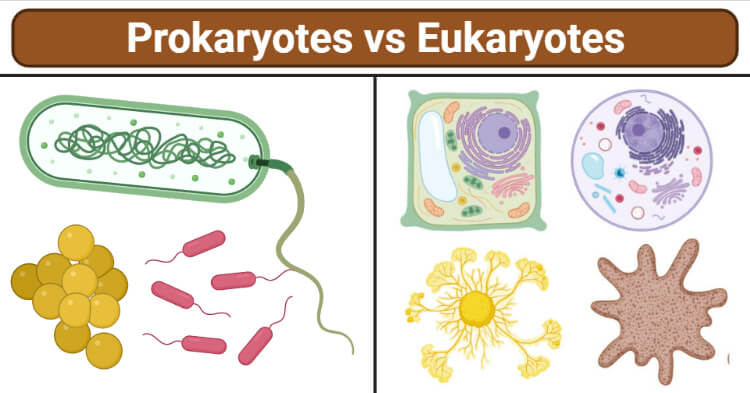
Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Structure & Examples
Pinocytosis involves the intake of specific substances usually extracellular fluid into the cell. Molecular Biology and Evolution. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment, chlorophyll, which captures the light energy that drives the reactions of photosynthesis. Alternatively some products produced by the cell can leave in a vesicle through The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane known as the Vesicles may be specialized for various purposes. The centrosome consists of two centrioles that lie at right angles to each other. Retrieved 21 April 2019. Another distinguishing feature between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum is that rough endoplasmic reticulum is an extension of the nuclear membrane, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum may either be an independent collection of sacs, or a continuation of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
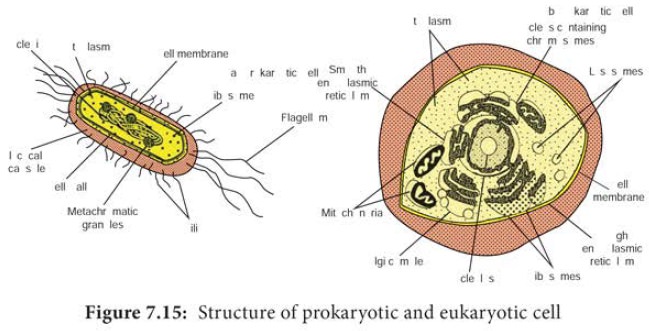
Eukaryotic Cell: What Is It, Difference from Prokaryotic Cells, and More

Scientists have long noticed that bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are similar in size. A number of approaches have been used to find the first eukaryote and their closest relatives. These structures are composed of structures called centrioles that are composed largely of α-tubulin, β-tubulin, and other proteins. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts. Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are plant cell organelles that carry out photosynthesis. We call the space between the two membranes the intermembrane space, and the space inside the inner membrane the mitochondrial matrix. Chloroplasts also have their own genome, which is contained on a single circular chromosome.
Cytoskeletal Structures of Eukaryotic Cell

When the cell is in the growth and maintenance phases of its life cycle, proteins attach to chromosomes, and they resemble an unwound, jumbled bunch of threads. There are various checkpoints between each stage. We will first look at types of plant cells and then cat types of animal cells in direct comparison. Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system. It is driven by cell division, which produces identical copies of cells. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 125. American Journal of Botany.