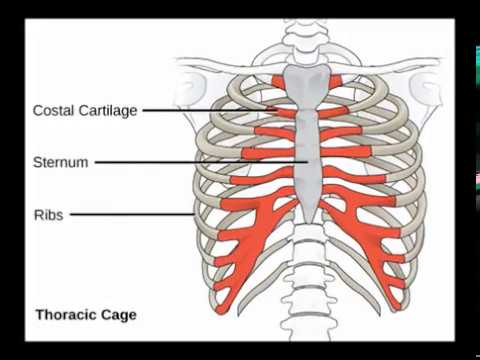
The sternum, also known as the breastbone, is a flat bone located in the center of the chest and forms the front of the rib cage. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and plays an important role in protecting the vital organs located within the thoracic cavity, such as the heart and lungs.
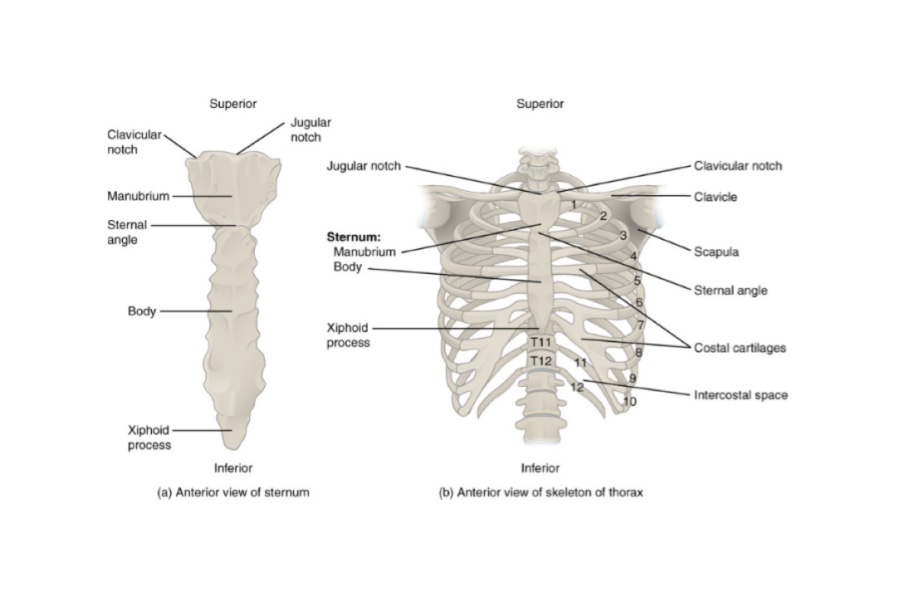
The sternum is divided into three parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The manubrium is the uppermost part of the sternum and is the widest and most rounded. It connects to the clavicles (collarbones) and the first pair of ribs. The body of the sternum is the longest and narrowest part and connects to the second through seventh pairs of ribs. The xiphoid process is the smallest and most pointed part of the sternum and is located at the bottom. It serves as a site of attachment for muscles and ligaments.
In addition to its structural role, the sternum also has several important landmarks that are used in medical procedures and examinations. The suprasternal notch, located between the manubrium and the body, is a depression that can be palpated (felt) through the skin and is used to locate the pulse of the internal jugular vein. The sternal angle, where the manubrium and body of the sternum meet, is a key reference point in anatomy and is used to measure the size of the thoracic cavity and the position of the ribs.
Despite its importance, the sternum is susceptible to injury and can be fractured or dislocated in accidents or during certain medical procedures. Treatment of sternal injuries may involve immobilization with a chest brace or surgery to repair or stabilize the bone.
In conclusion, the sternum is a crucial bone located in the center of the chest that provides structural support and protection for the organs within the thoracic cavity. It is divided into three parts and has several important landmarks used in medical procedures and examinations. While it is vulnerable to injury, treatment options are available to repair or stabilize the bone.
Sternum: Anatomy, parts, pain and diagram
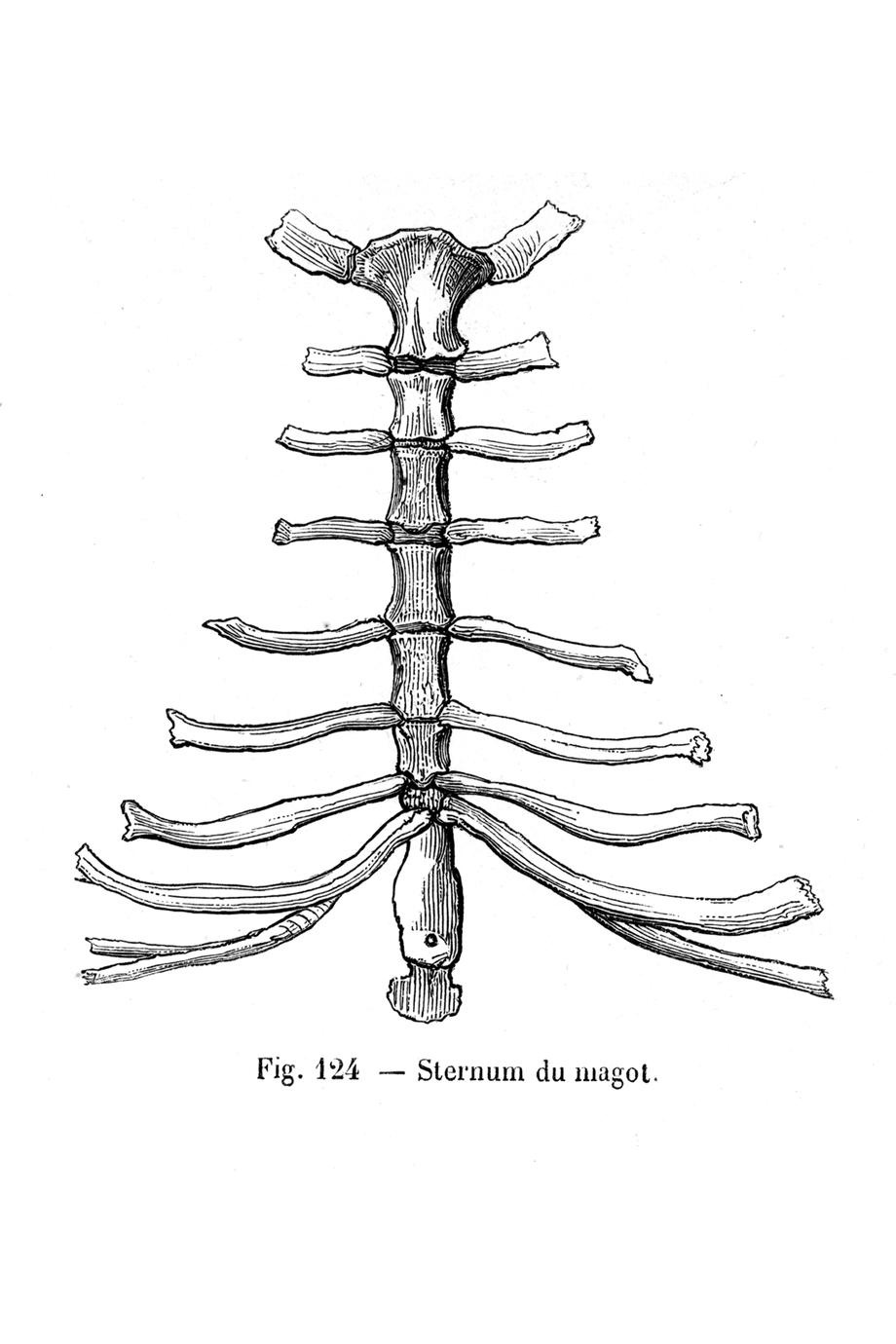
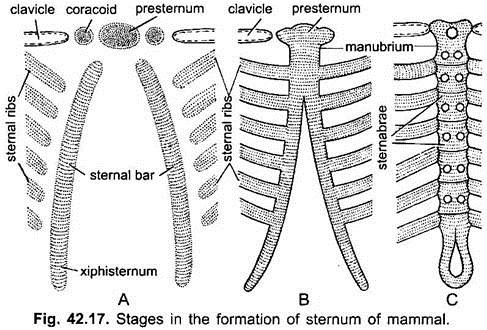
It has become segmented secondarily and has three regions- an anterior presternum manubrium , middle mesosternum consisting of five pieces or sternebrae, the fifth is very small, and a posterior region called metasternum xiphisternum , which is long and has a terminal expanded xiphoid cartilage. Mammalia: The sternum is made of a series of bones fixed together and arranged in a row lying mid-ventrally in the thorax. Some of the anterior parasternals fuse to form a sternum, such a sternum is called an archisternum. The central part of the bars joining the ribs becomes the mesosternum, while its free posterior end is the xiphisternum, later the cartilage ossifies. The vital organs can be compromised. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. Some tetrapoda such as Proteus, Amphiuma, caecilians, snakes, turtles and limbless lizards have no sternum.
Sternum
At the superior border of the bone is the jugular notch or suprasternal notch, fibres of interclavicular ligaments are attached here. In amniotes but not in amphibians it also articulates with ribs to form a thoracic basket which is protective and aids in breathing. The smallest and most inferior region of the sternum, the xiphoid process, begins life as a region of flexible hyaline cartilage attached to the end of the body of the sternum. Last medically reviewed on April 27, 2020 Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. In addition, the powerful pectoralis major muscles that adduct and flex the humerus at the shoulder attach to the anterior surface of the body of the sternum and manubrium. It typically involves rest and pain relief while you heal. It provides both support and protection for your torso.
Sternum of Mammal (With Diagram)
Several muscles that move the arms, head, and neck have their origins on the sternum. Other conditions can also cause pain in the area of your sternum. The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, is a long, narrow flat bone that serves as the keystone of the rib cage and stabilizes the thoracic skeleton. The clavicles meet the manubrium at the concave clavicular notches to form the sternoclavicular joint, the only point of skeletal attachment between the pectoral girdle of the shoulder and the axial skeleton of the thorax. Severe injuries may need surgery. Over-the-counter pain medication may also help with pain and swelling. It forms a T-shaped girder to bear the weight of the heavy abdominal viscera.
Sternum Area, Anatomy & Pictures
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/59/hhX1gkhVmmrvZoY1uiAesA_anatomy-of-sternum_english.jpg)
The sternal fibers of sternal angle of louis , it is where the second pair of costal cartilage attaches to the sternum and at the level of the inferior border of T4, is also clinically known as the Angle of Louis. Bats have carinate sternum. Our mission is to provide an online platform to help students to discuss anything and everything about Zoology. Kenhub does not provide medical advice. The lower border is narrower, is quite rough, and articulates with the body with a thin layer of cartilage in between.
Sternum Diagram Vectores Libres de Derechos
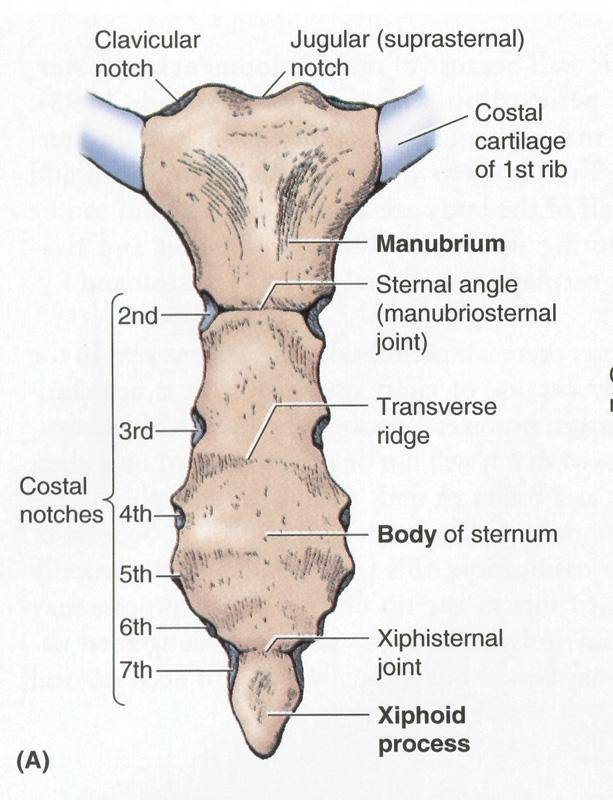
The origin of a sternum is obscure. It has facets on its each lateral border for articulation with the costal cartilage of the 3rd to 7th ribs along with the part of second costal cartilage. Best suited to muscle strains in the arms or legs, this involves elevating the injury above the level of the heart to help fluid drain away from the injury. Bone marrow biopsy The sternum is used as the site for bone marrow biopsy in obese or overweight patients, where access to the Pectus excavatum Pectus excavatum is a condition also known as funnel chest, where the sternum and superior ribs grow abnormally, created a sunken chest appearance. It connects to the third through seventh ribs directly and the eighth through tenth ribs indirectly.


:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/corpus-sterni/RNlEWxo6XbdJ9CGRNlaLQ_Corpus_sterni_01.png)


:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/59/hhX1gkhVmmrvZoY1uiAesA_anatomy-of-sternum_english.jpg)
