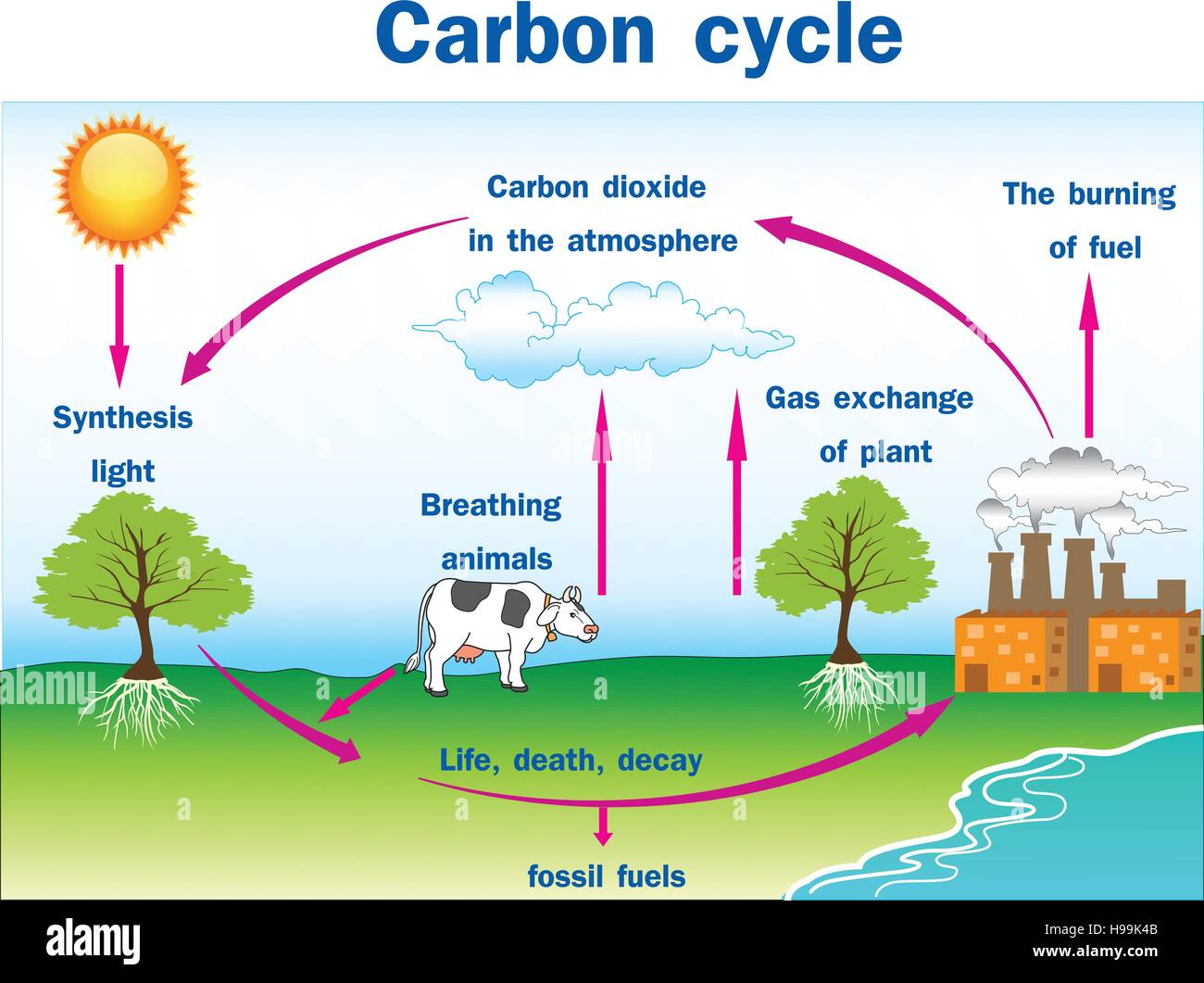
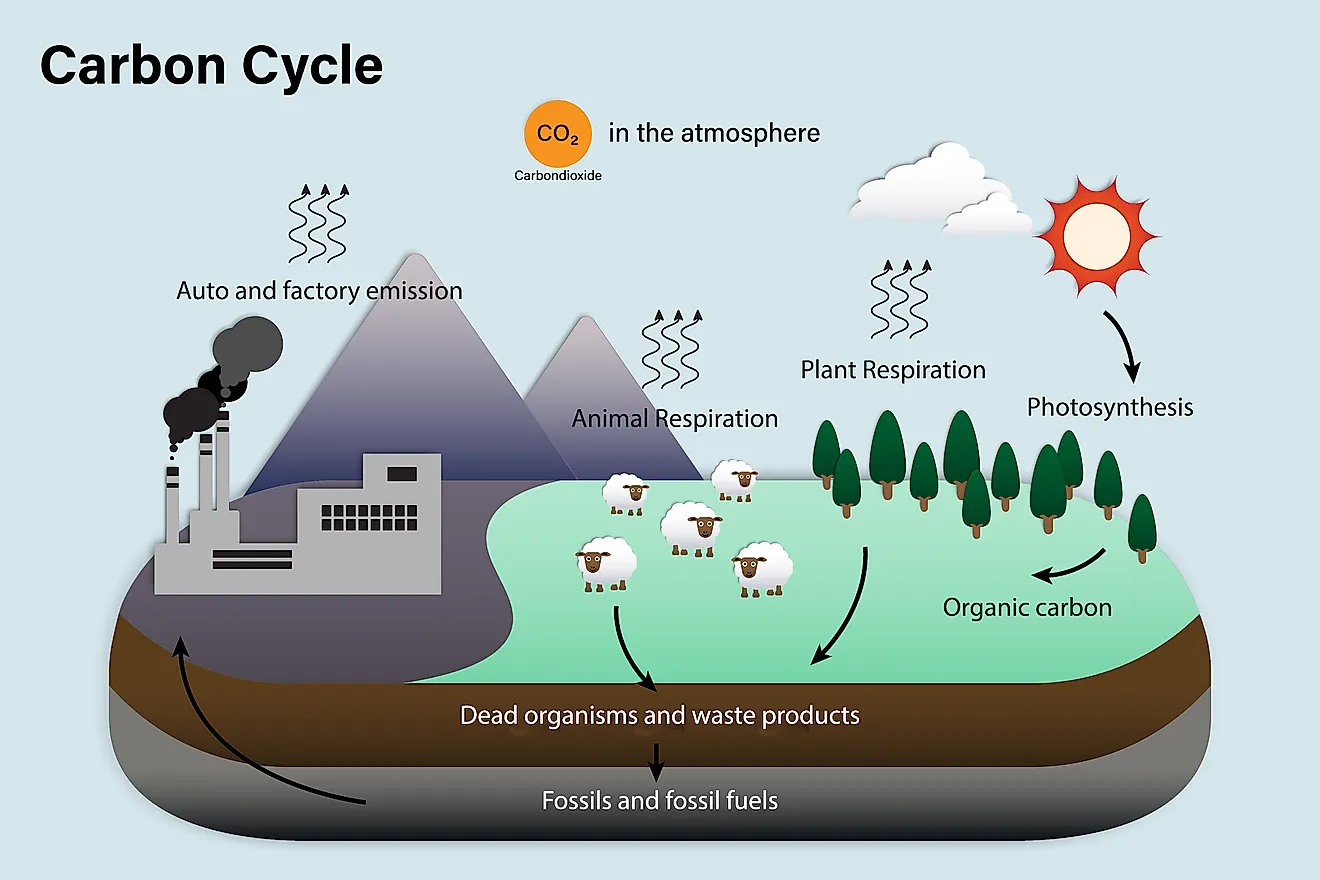
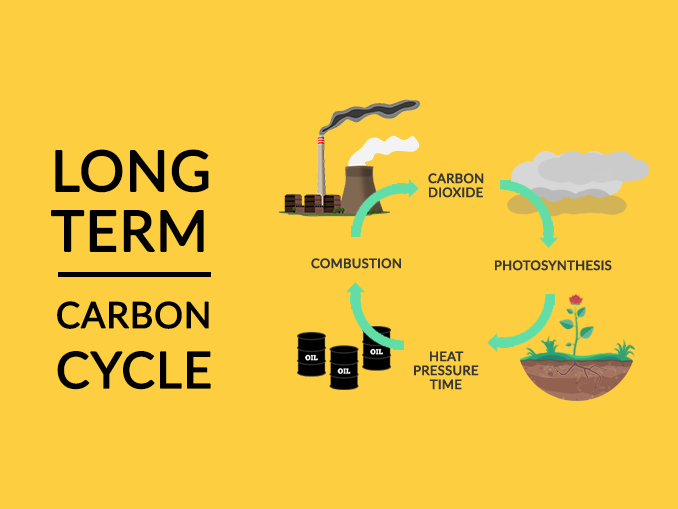
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is continuously circulated through the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land. It is a vital part of the planet's ecosystem and plays a key role in regulating the Earth's climate.
Carbon is a chemical element that is present in all living things. It is a building block for many of the molecules that make up the structure of plants, animals, and other organisms. Carbon can be found in several forms, including as a gas in the atmosphere, dissolved in the oceans, and stored in plants and animals.
The carbon cycle begins with the process of photosynthesis, which occurs in plants. During photosynthesis, plants use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into glucose, a simple sugar. The glucose is used by the plant as a source of energy and also serves as a building block for other molecules, such as cellulose and lignin, which make up the plant's cell walls and support structure.
As plants grow and mature, they take in CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in their cells. When plants die, their carbon is released back into the atmosphere through decomposition, a process in which microorganisms break down the plant matter into smaller molecules, releasing CO2 in the process.
The carbon cycle also involves the movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, and land. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can be absorbed by the oceans, where it is converted into a form that can be used by marine organisms. These organisms, such as phytoplankton, use CO2 to build their own tissues and produce oxygen as a byproduct. When these organisms die, their carbon is either released back into the atmosphere or sinks to the bottom of the ocean, where it can be stored for long periods of time.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, can disrupt the carbon cycle by releasing large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. This can contribute to the greenhouse effect, in which the Earth's atmosphere traps more heat, leading to an increase in global temperatures.
In conclusion, the carbon cycle is a complex and vital process that plays a crucial role in the Earth's ecosystem and climate. It involves the movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, and land, and is essential for the growth and survival of plants and animals. Understanding the carbon cycle is important for helping to mitigate the effects of human activities on the planet and to address issues such as climate change.