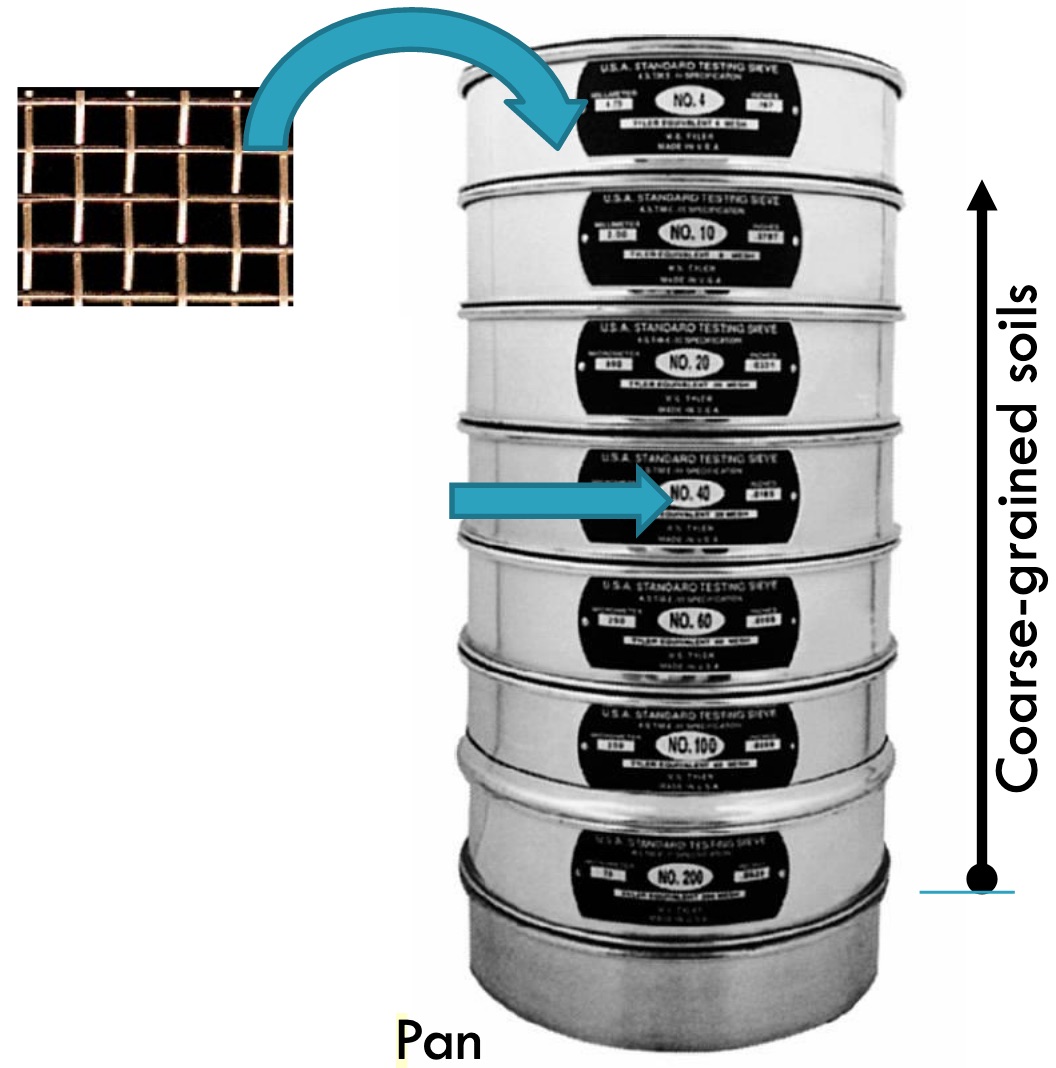
A sieve analysis is a laboratory technique used to separate and classify particles according to size. This technique is commonly used in the field of geology, as well as in industries such as construction, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals.
The basic principle of sieve analysis is simple: a sample of finely ground material is placed on a series of sieves with progressively smaller mesh sizes. The sieves are stacked on top of each other, with the coarsest mesh at the top and the finest at the bottom. The sample is then agitated, either manually or mechanically, causing the particles to fall through the sieves.
One of the main advantages of sieve analysis is that it is a relatively quick and easy way to measure the size distribution of a sample. It can be performed in a laboratory setting or on site, and the results are usually available within a few hours. Sieve analysis is also relatively low cost, making it a popular choice for many industries.
There are several factors that can affect the accuracy of a sieve analysis, including the quality of the sieves, the size and shape of the particles, and the method of agitation. It is important to carefully control these variables to ensure the reliability of the results.
Sieve analysis is often used in conjunction with other techniques, such as laser diffraction or microscopy, to provide a more complete picture of the particle size distribution of a sample. It is also often used to determine the particle size distribution of a sample for use in quality control or for research purposes.
In summary, sieve analysis is a widely used technique for separating and classifying particles according to size. It is simple, quick, and cost-effective, making it an important tool in a variety of industries and applications.