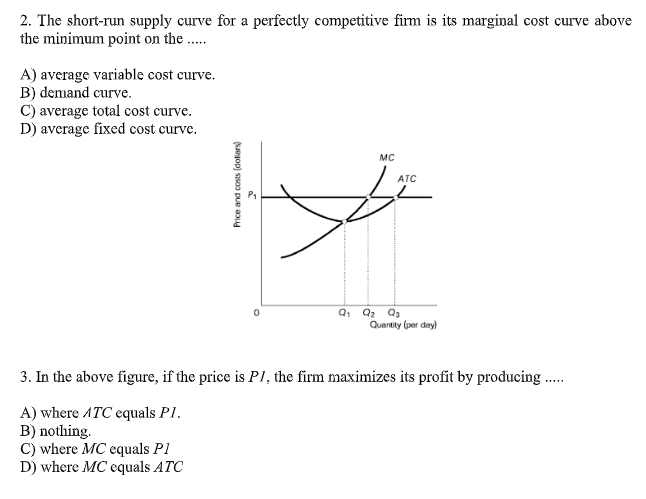
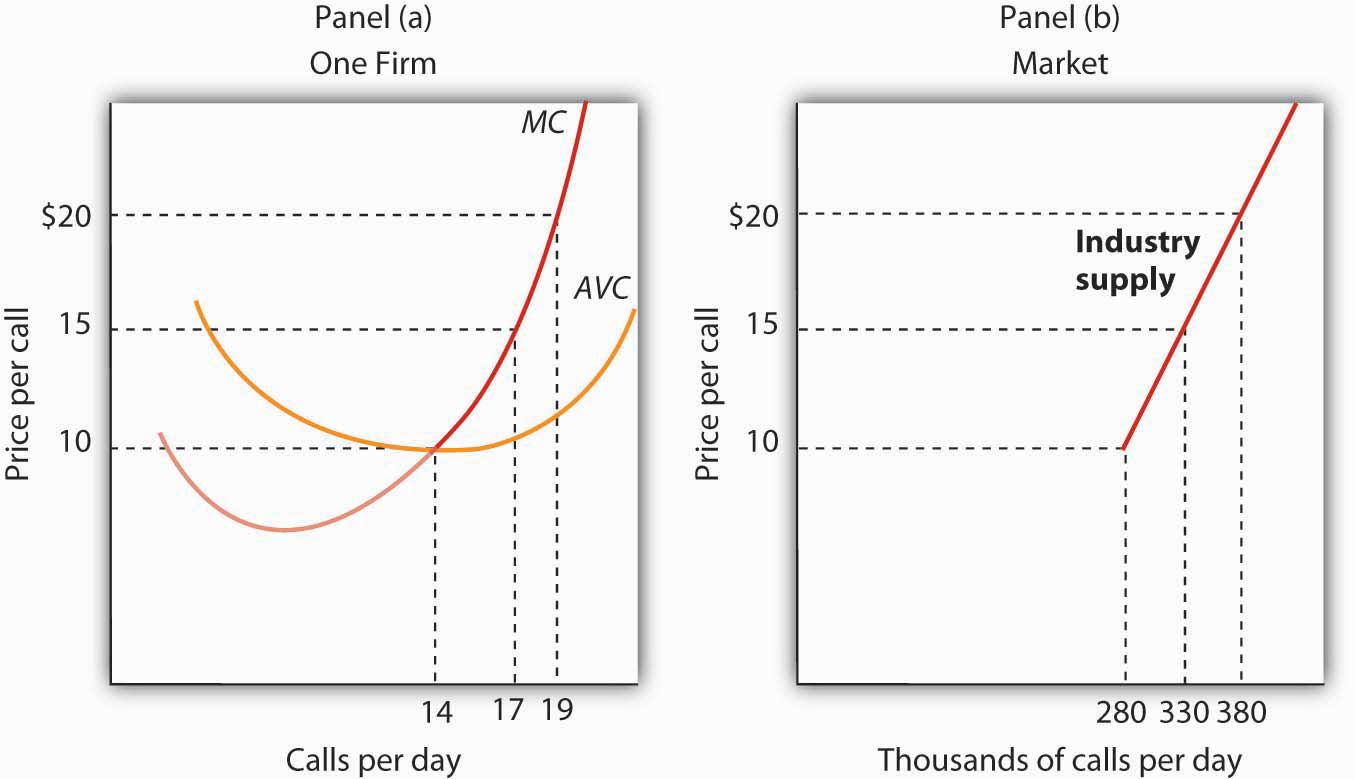
In economics, the short run is a period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed, while others are variable. The short run supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply at that price.
There are several factors that can shift the short run supply curve. An increase in the price of a good or service will typically lead to an increase in the quantity supplied, as firms will be able to charge higher prices and earn higher profits. This is known as the law of supply. On the other hand, an increase in the cost of production, such as an increase in the price of raw materials or an increase in wages, will lead to a decrease in the quantity supplied, as firms will be less able to afford to produce as much.
Another factor that can shift the short run supply curve is changes in technology. If a firm is able to adopt new technologies that increase productivity, it will be able to produce more at a given price, leading to an increase in the quantity supplied. Similarly, if a firm is faced with a decrease in technology, it will be less able to produce as much and the quantity supplied will decrease.
The shape of the short run supply curve is typically upward sloping, reflecting the law of supply. However, the slope of the curve can vary depending on the specific circumstances of the firm. For example, if a firm is operating at full capacity, the slope of the supply curve may be relatively steep, as the firm will be unable to increase production without incurring additional costs. On the other hand, if a firm has excess capacity, the slope of the supply curve may be relatively flat, as the firm will be able to increase production without incurring significant additional costs.
In summary, the short run supply curve represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply at that price in the short run. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including changes in price, changes in costs, and changes in technology. The shape of the curve can vary depending on the specific circumstances of the firm, with a steeper slope indicating that the firm is operating at full capacity and a flatter slope indicating that the firm has excess capacity.
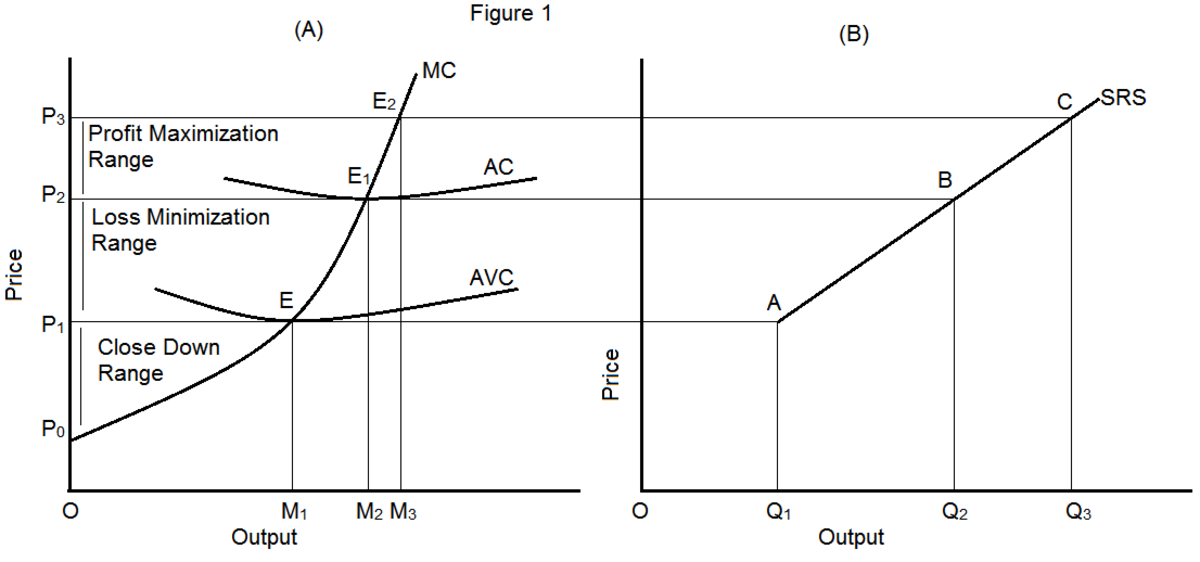
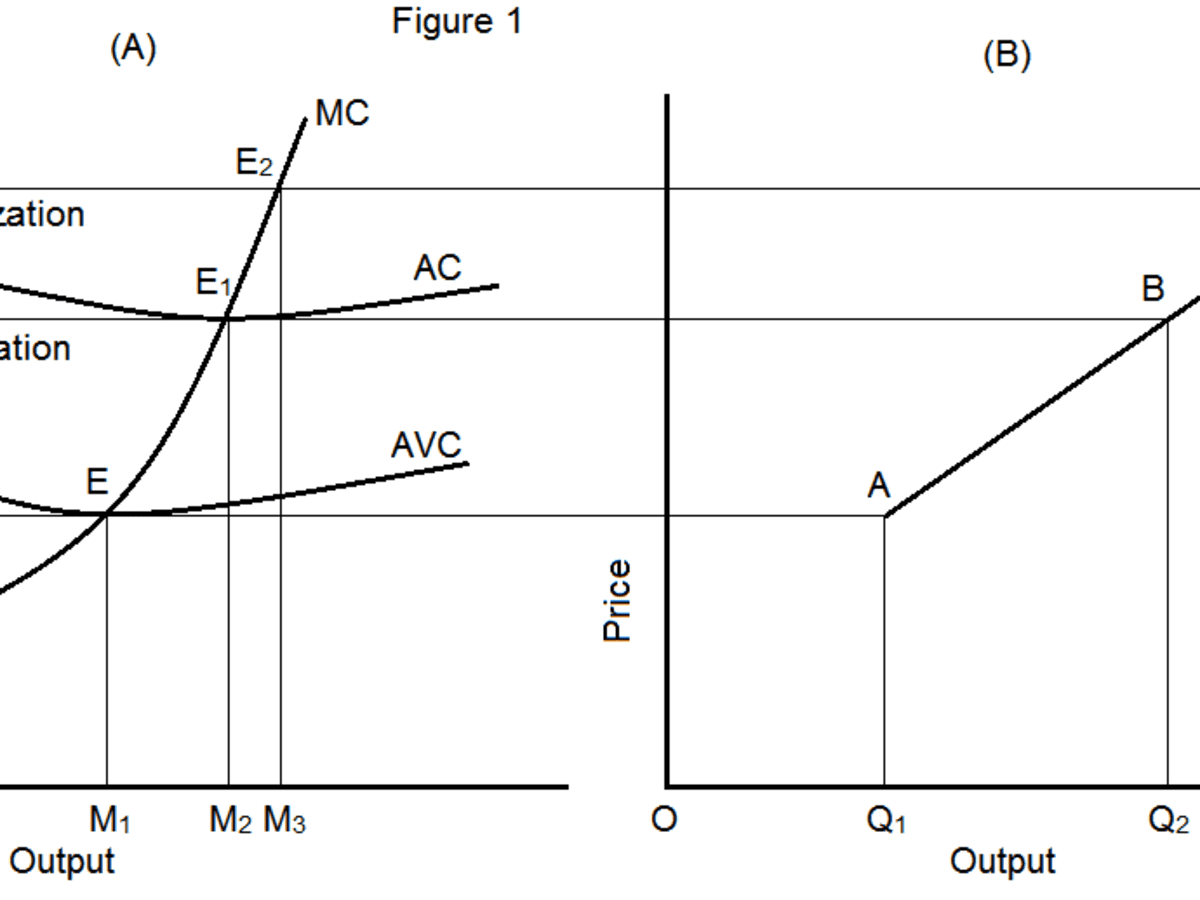
Short Run Supply Curve of a Firm

An increase in the total aggregate price level is related to the rise in the total quantity of aggregate output supplied. In simple terms, at least one of the resources, costs, or other factors remain fixed in the short run. As a general rule, a firm will shut down production whenever its average variable costs exceed its marginal revenue at the profit maximizing level of output. Short-run aggregate supply is a key economic indicator that can track the balance of price levels and the quantity of goods and services supplied. Example 2 In 2018, increased Due to the rise in raw materials costs, the company increased its product prices by 12% in 2021 to cover the losses.
The Short
This shift causes quantity to decrease from Y 1 to Y 2 and price to increase from P 1 to P 2 In general, a shift to the right of the SRAS curve lowers the overall prices and raises the output produced. Because the general level of prices does not affect the capacity of the economy to create goods and services over the long run, the aggregate supply curve, in the long run, is vertical. The SRAS curve has a positive slope, increasing in quantity as price increases. A rise in productivity gives the firm the ability to produce more while maintaining low or constant costs. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. Also, notice that we assume firms are getting at least some profits area A because in the short term only labour is variable, which means that there are no firms entering this market, even though profits exist.
Short Run Aggregate Supply Concept & Curve
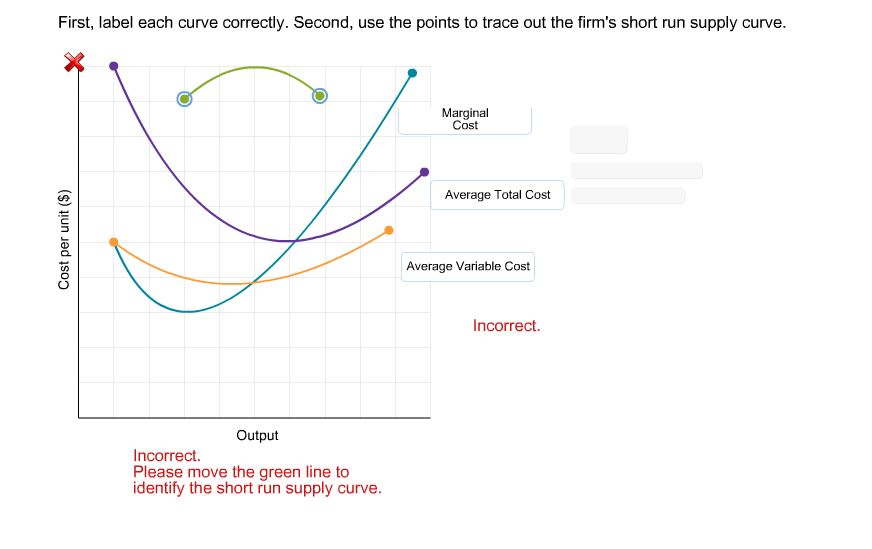
Short Run Supply Curve of a Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve for an enterprise. This will increase the cost firms face, shifting the SRAS to the left. This amounts to saying that the demand curve or the AR curve that coincides with the MR curve becomes perfectly elastic. Common long-term determinants can also cause short-term shifts, such as amount of capital available, the size of the labor force, technology improvements, cost of raw materials, energy prices and education and training of the workforce. Why is long run supply curve elastic? Even in situations with no formal contracts, there are often informal agreements between management and employees. This curve corresponds to SMC curve above the AVC curve of panel a. As a result, the short-run aggregate supply shifted to the left, resulting in higher prices.
What is the long term supply?

On the other hand, if there is a deadline of seven months for bulk manufacturing, the manufacturer will likely get one or more machinery to speed up the production. Firms experience constant returns to scale when the long-run average cost curve is flat. What is LRAS and sras? It means that an increase in the total aggregate price level is related to the rise in the total quantity of aggregate output supplied, all other things being equal; conversely, a decrease in the whole aggregate price level is related to a reduction in the total quantity of aggregate output supplied, all other things being equal. However, the market fluctuations in the short run can devastate livelihoods, so sticky wages are a necessary element. It's an upward-sloping curve that shows the positive relationship between the aggregate price level and the number of goods and services firms are willing to supply. The new profits of each firm, C, is determined by both the new quantity produced and the drop in marginal and average costs.