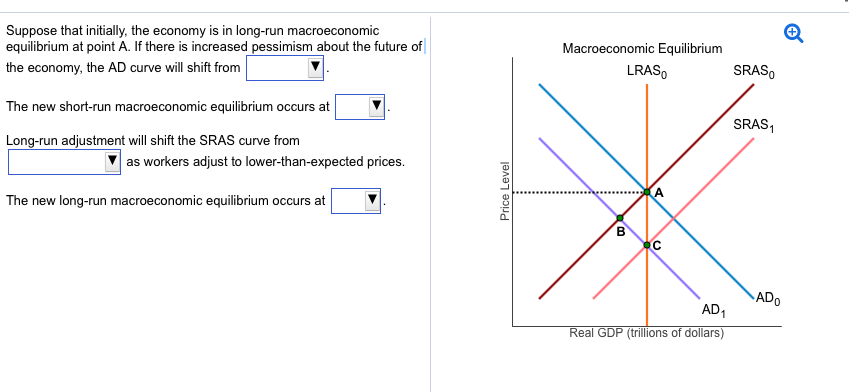
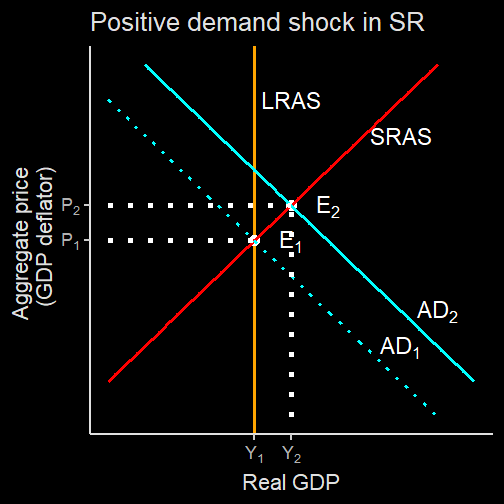
Short run macroeconomic equilibrium is a state in which the economy is in balance, with the demand for goods and services being equal to the supply of those goods and services. This is a dynamic process, as the economy is constantly changing and adjusting to new factors such as changes in consumer spending, changes in the money supply, and shifts in international trade. In the short run, the economy is primarily driven by aggregate demand, which is the total amount of goods and services demanded by households, firms, and the government.
To understand short run macroeconomic equilibrium, it is important to understand the role of the aggregate demand curve. The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between the price level (measured by the consumer price index) and the quantity of goods and services demanded. When the price level increases, the quantity of goods and services demanded decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is based on the law of demand, which states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases.
In the short run, the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping, which means that as the price level increases, the quantity of goods and services demanded decreases. This is because households and firms are willing to purchase fewer goods and services when prices are high, as they can only afford to buy so much at a given price level.
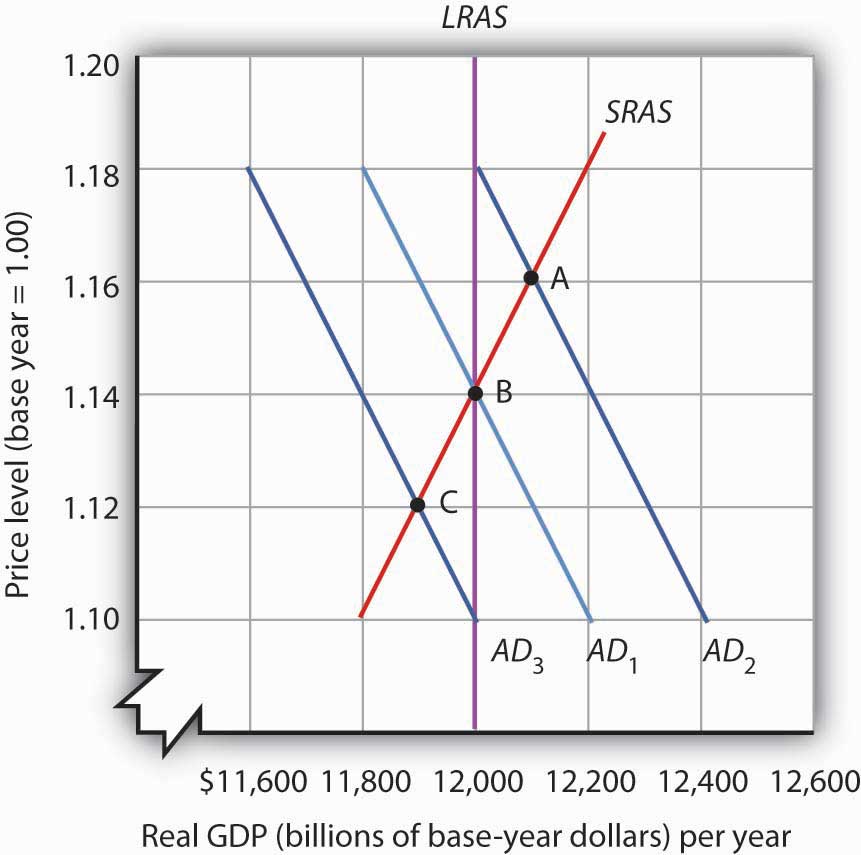
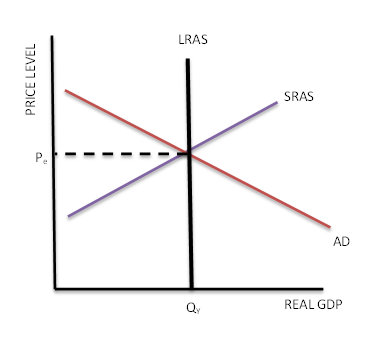
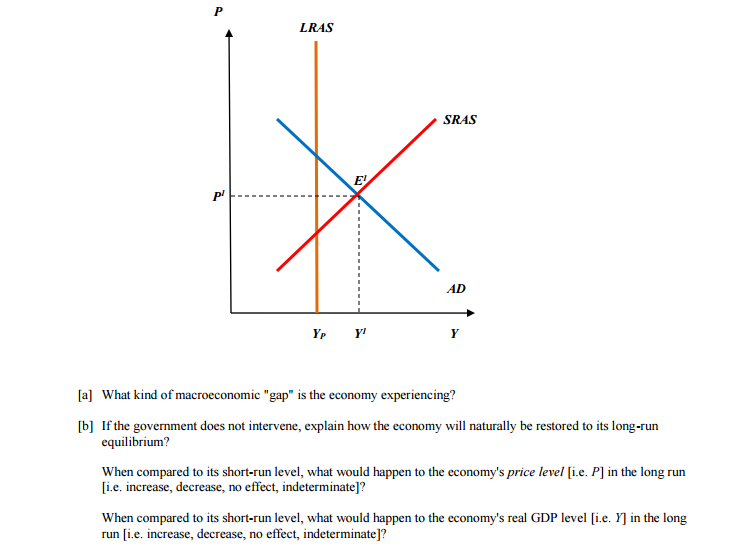
The short run macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when the aggregate demand curve intersects the aggregate supply curve. The aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing to produce. When the price level increases, firms are willing to produce more goods and services, as they can sell them at higher prices and increase their profits. Conversely, when the price level decreases, firms are willing to produce fewer goods and services, as they can only sell them at lower prices and their profits will decrease.
In the short run, the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping, which means that as the price level increases, the quantity of goods and services supplied increases. This is because firms are able to increase production by using their existing resources more efficiently or by hiring more workers.
The intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve determines the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of goods and services produced in the economy. At this point, the economy is in balance, with the demand for goods and services being equal to the supply of those goods and services.
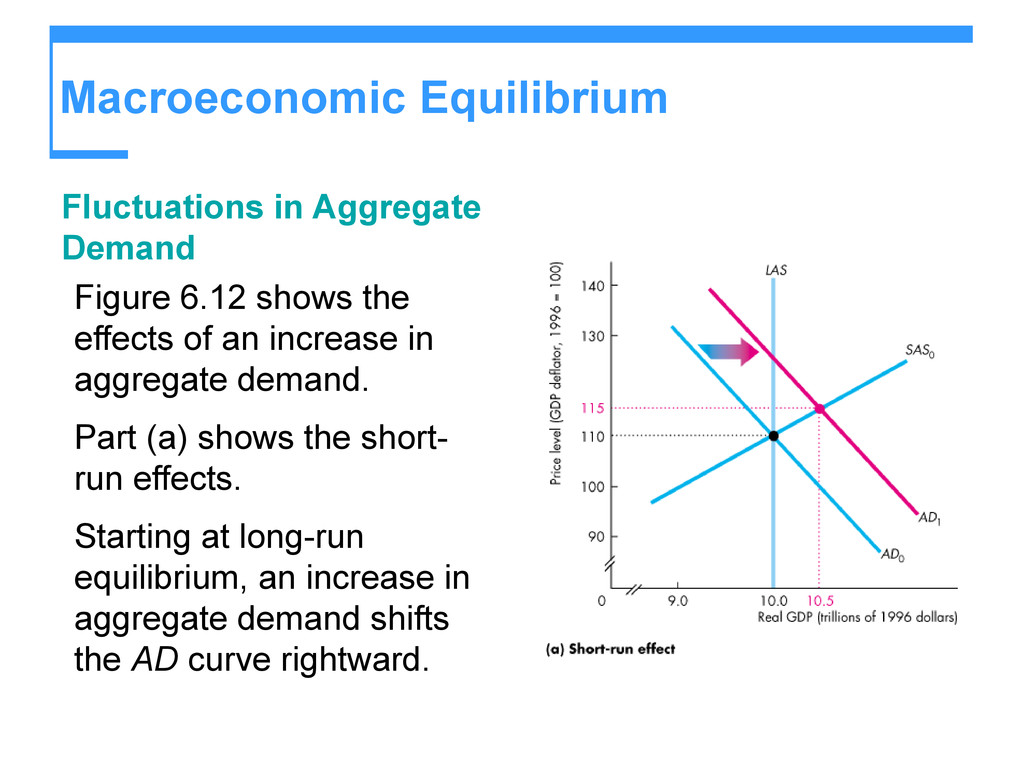
There are several factors that can cause the aggregate demand curve to shift, including changes in consumer spending, changes in the money supply, and shifts in international trade. For example, if consumer spending increases, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right, leading to an increase in the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of goods and services produced. Conversely, if consumer spending decreases, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the left, leading to a decrease in the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of goods and services produced.
In the short run, changes in the money supply can also affect the aggregate demand curve. If the money supply increases, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right, leading to an increase in the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of goods and services produced. Conversely, if the money supply decreases, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the left, leading to a decrease in the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of goods and services produced.
Shifts in international trade can also affect the short run macroeconomic equilibrium. If the economy becomes more open to international trade, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right, leading to an increase in the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of goods and services produced. Conversely, if the economy becomes less open to international trade, the aggregate demand curve will shift