Self-determination theory (SDT) is a psychological theory that explains the psychological and behavioral factors that contribute to an individual's motivation and well-being. According to this theory, people have a fundamental need for autonomy, competence, and relatedness, and when these needs are met, they are more likely to experience positive outcomes such as well-being, motivation, and engagement. On the other hand, when these needs are not met, people may experience negative outcomes such as demotivation, disengagement, and even mental health issues.
One example of self-determination theory in action is the concept of intrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation refers to the desire to engage in an activity for its own sake, rather than for the sake of external rewards or punishments. Research has shown that people who are intrinsically motivated are more likely to be engaged, persistent, and successful in their pursuits, as compared to those who are motivated by external rewards or punishments.
For example, consider a student who is intrinsically motivated to learn. This student may be more likely to put in extra effort, seek out additional resources and opportunities to learn, and be more engaged in the learning process. On the other hand, a student who is motivated by external rewards or punishments, such as grades or praise, may be less likely to engage in learning for its own sake, and may be more focused on achieving the external reward rather than on learning itself.
Another example of self-determination theory in action is the concept of autonomy support. Autonomy support refers to the extent to which an individual is allowed to make decisions and have control over their own actions and environment. Research has shown that people who feel that they have autonomy and control over their own lives are more likely to be motivated and engaged, as compared to those who feel that they have no control or agency.
For example, consider a manager who provides autonomy support to their team members. This manager may allow team members to choose their own projects, set their own schedules, and make decisions about how to complete their work. As a result, team members may feel more motivated and engaged, as they feel that they have control over their own work and are able to make decisions that align with their own values and interests. On the other hand, a manager who does not provide autonomy support may create a feeling of helplessness and demotivation among team members, as they feel that they have no control over their own work or decision-making processes.
In conclusion, self-determination theory provides a framework for understanding the psychological and behavioral factors that contribute to an individual's motivation and well-being. By focusing on the needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness, we can better understand how to create conditions that foster motivation and well-being, and avoid conditions that lead to demotivation and negative outcomes.
Free Self
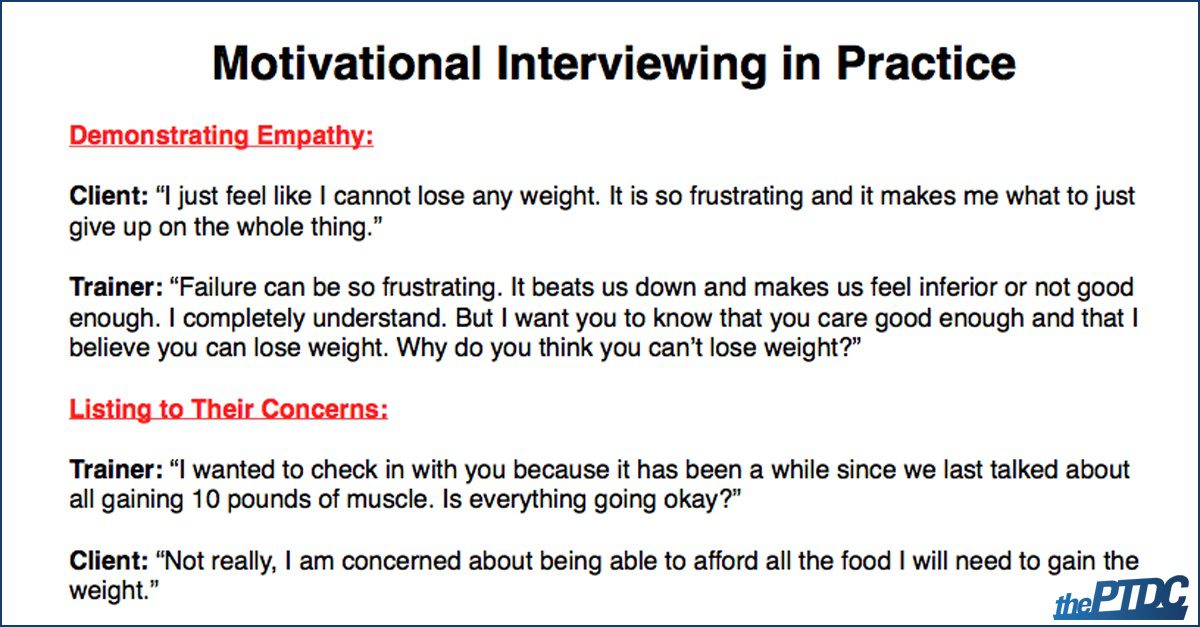
For example, if you believe that the world will never vote you into political office, you are unlikely to do anything to start your campaign. Engage with them, be creative, try new things, be open-minded, ask for feedback from coaches and administration, and have fun doing it! The incentive theory looks at rewards and punishment. Motivational dynamics of eating regulation: a self-determination theory perspective. Who Created Self Determination Theory? Concerning this theory, McKenna 2000 explains that intrinsic motivations are those motivational drivers that are based on satisfaction of taking action for its shake. Reinforcement reflected a discrepancy principle, when behavior is continually mediated by the activity of dopamine neurons elicited by continuous correction error between predictions and outcomes. It also looks at the processes and structures related to the three innate psychological needs of autonomy, competence, and interpersonal relatedness. It can also be fueled by deeply held values or interest and enjoyment of the behavior itself.
Self Determination Theory and How It Explains Motivation

Since these needs are fulfilled just because of the nature of a competitive setting, self determined behavior is easily enhanced, leading to highly motivated individuals. Similarly, with the lack of control mechanisms, self-determination can lead to bad choices or bad behavior Stainton, 2000. Psychological Needs Self-determination theory suggests that all humans have three basic psychological needs—autonomy, competence, and relatedness—that underlie growth and development. The theory discusses and assesses three forms of causality orientations. Using self-determination theory to explain sport persistence and dropout in adolescent athletes. This is through highlighting on social development, personal growth, and enhancement of individual well-being. Positive feedback for tasks they have accomplished makes them feel more competent.
Self Determination Theory of Motivation, Explained! (2023)

Which goals are you determined to achieve? These choices may be a different movement, loading structure, exercise order, physiological emphasis, etc. This need fulfillment is essential for self determined behavior, which helps increase and sustain motivation levels. If an athlete has to go up to the coach and request an alternate, it no longer feels like a choice for that athlete but more like a modification. He may still do the job, but his lack of intrinsic motivation Our psychological health is examined with a lot of factors, one of them being our motivation levels towards our roles and jobs in life. Aspirations or life goals are what people use to guide their own behavior. Self Determination, other than being a huge influence in our motivation, also helps us feel more aware of our sense of self. Self-theories: Their role in motivation, personality, and development.
Self Determination Theory (Definition + Examples)

Intrinsic motivation merely drives them to do a better job than what they would do without any such motivation. Omaha, NE: Bartholomew Strength. In conclusion, it can then be said that while SDT does raise a lot of good points on how to create and sustain motivation, it may be best to incorporate it with other theories of motivation. I decided to pause the lift and give the entire team a couple of coaching cues, and while doing so, I happened to be demonstrating on the platform of our strongest group of guys. Being aware of your strengths, weaknesses, needs, and desires will help you set new goals and find the motivation to achieve them. We know that autonomous motivation and controlled motivation lead to very different outcomes, with autonomous motivation yielding greater psychological health, more effective performance, and greater long-term persistence 2. Particularly, at initial stages, individuals may learn to introject a behavior that they had earlier intrinsically motivated to pursue.






