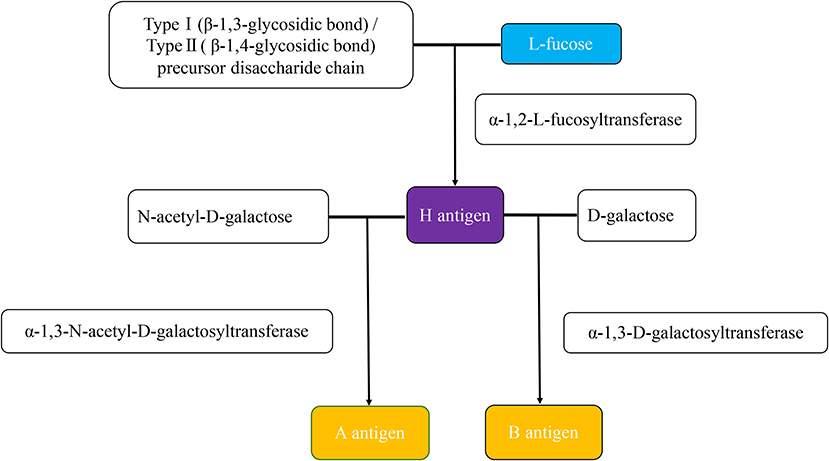
Reverse blood typing is a laboratory procedure used to determine the blood type of a person when the individual's blood is not available for testing. This is often necessary in cases where a patient has a transfusion or transplant and the donor's blood type is unknown. Reverse blood typing can also be used to identify the blood type of a newborn when the mother's blood type is not known.
The reverse blood typing procedure involves testing the recipient's blood to determine which blood type it is compatible with. This is done by mixing the recipient's blood with different blood type antigens and observing for any reactions. If the recipient's blood reacts with a particular blood type antigen, it means that the recipient is not compatible with that blood type.
To begin the reverse blood typing procedure, a small sample of the recipient's blood is collected and placed in a tube. The blood is then mixed with a series of antigens from different blood types, including A, B, AB, and O. The tube is then incubated for a specific period of time, during which any reactions between the recipient's blood and the antigens will occur.
After the incubation period, the blood is examined for any changes in color or appearance, which may indicate a reaction. If the recipient's blood reacts with a particular blood type antigen, it means that the recipient is not compatible with that blood type. If the recipient's blood does not react with any of the antigens, it means that the recipient is compatible with all blood types and is considered a "universal recipient."
Reverse blood typing is an important procedure in the field of transfusion medicine. It helps to ensure that patients receive the most compatible blood type, which can help to reduce the risk of transfusion reactions and other complications. It is also an important tool for identifying the blood type of newborns, as this information is crucial for ensuring that they receive the appropriate care and treatment.