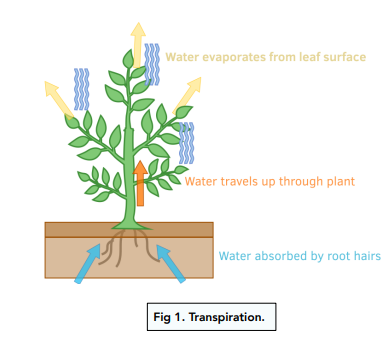
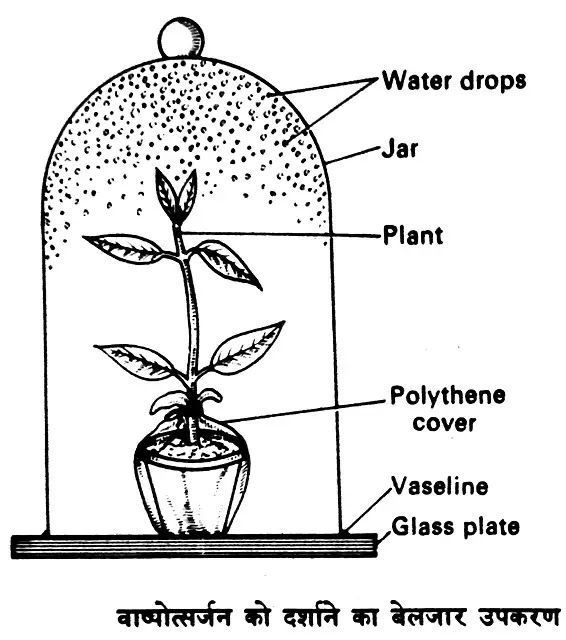
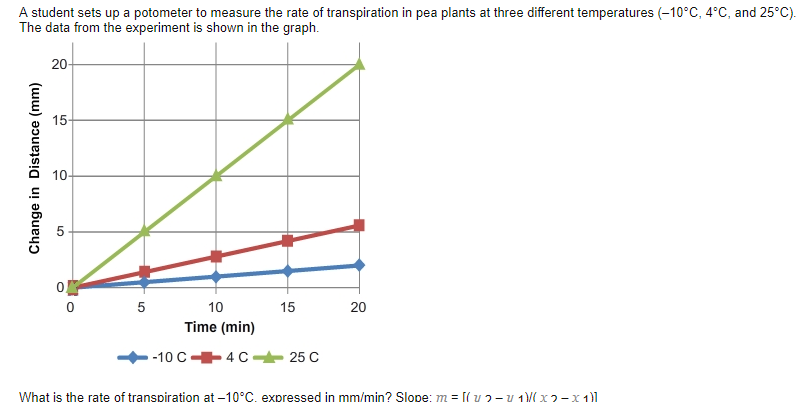
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost from a plant through the evaporation of water from the surface of the leaves. It is an important process for plants, as it helps to regulate their internal temperature and provide water to the plant through the xylem tissue. The rate of transpiration is influenced by a variety of factors, including the humidity and temperature of the air, the amount of light available to the plant, and the size and structure of the plant's leaves.
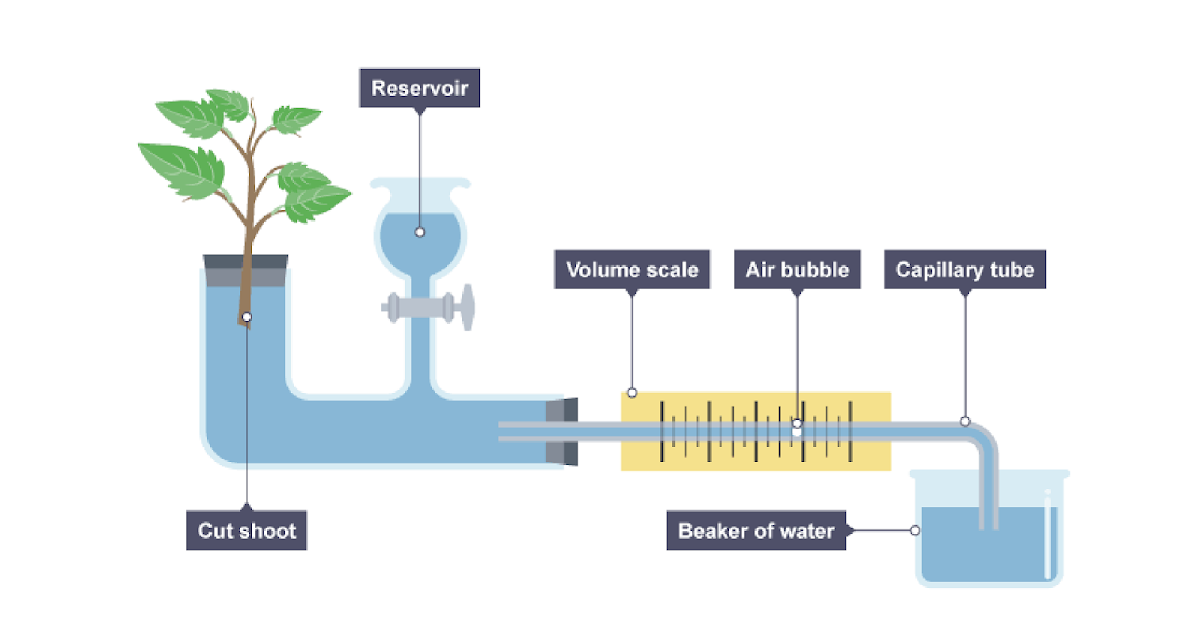
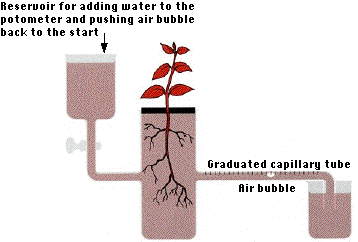
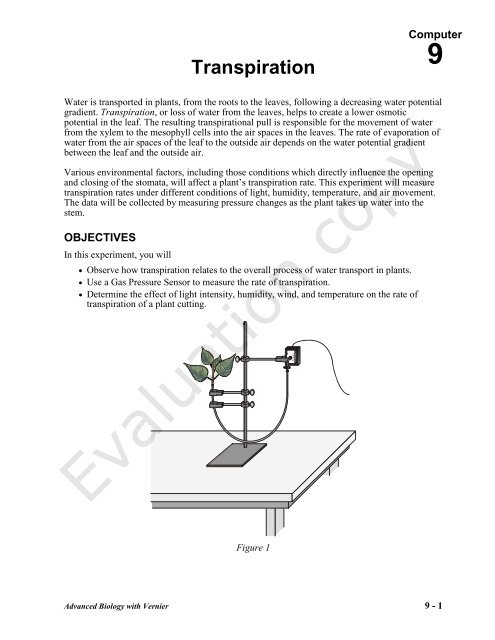
One way to measure the rate of transpiration in a plant is to perform an experiment using a potometer. A potometer is a device that measures the rate of water movement through a plant. It consists of a tube that is connected to a plant, with a reservoir of water at one end and a measurement scale at the other end. The plant is placed in a controlled environment, and the amount of water lost through transpiration is measured over a period of time.
To perform this experiment, the first step is to choose a plant and prepare it for the potometer. The plant should be healthy and undamaged, and it should have leaves that are fully expanded and not wilted. Next, the potometer is set up according to the manufacturer's instructions. This typically involves filling the reservoir with water and attaching the plant to the potometer using a rubber band or similar method.
Once the potometer is set up, the experiment can begin. The plant is placed in a controlled environment, such as a greenhouse or growth chamber, and the temperature and humidity of the air are carefully regulated. The amount of light the plant receives is also controlled, as this can have a significant impact on the rate of transpiration. The plant is left in the controlled environment for a set period of time, typically several hours or a full day, and the amount of water lost through transpiration is measured at regular intervals.
After the experiment is complete, the results can be analyzed to determine the rate of transpiration. This is typically done by calculating the amount of water lost per unit of time, such as milliliters per hour. The results can then be compared to other plants or to the same plant under different conditions to determine the factors that influence the rate of transpiration.
In conclusion, the rate of transpiration in a plant can be measured using a potometer. This experiment allows scientists to study the factors that influence the rate of transpiration and to understand how plants regulate their internal temperature and water balance. By understanding the process of transpiration, scientists can develop ways to improve the growth and health of plants, which has important implications for agriculture and the environment.