Quantitative easing is a monetary policy used by central banks to stimulate economic growth by increasing the money supply in the economy. It was first implemented by the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, during the Great Recession of 2007-2009 under the presidency of Barack Obama.
During the Great Recession, the economy was facing a severe downturn as a result of the housing market crash and the subprime mortgage crisis. The Federal Reserve responded by lowering interest rates to near zero in an attempt to stimulate borrowing and spending. However, this policy alone was not sufficient to boost the economy, and the Federal Reserve turned to quantitative easing as an additional tool to stimulate growth.
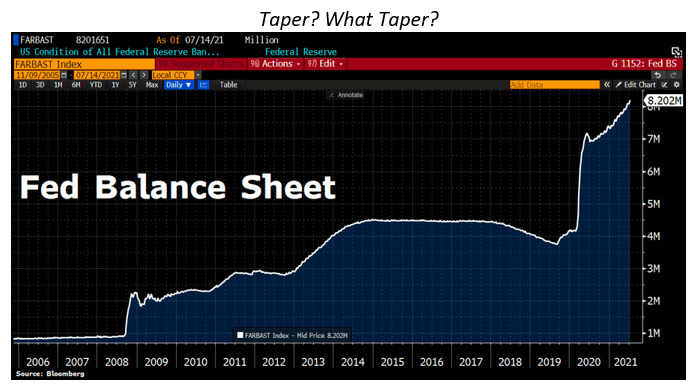
Under quantitative easing, the Federal Reserve purchased large quantities of government bonds and other securities in the open market, effectively increasing the money supply in the economy. The idea behind this policy is that by increasing the money supply, the Federal Reserve can encourage banks to lend more, leading to increased borrowing and spending. This in turn can stimulate economic growth and help to address deflation, or falling prices.
Quantitative easing was implemented in three rounds by the Federal Reserve under the Obama administration: QE1, QE2, and QE3. Each round involved the purchase of a specific amount of securities, with the goal of increasing the money supply and boosting economic growth.
While quantitative easing was successful in providing a boost to the economy during the Great Recession, it also came with some potential risks and drawbacks. For example, some critics argued that quantitative easing could lead to higher inflation, as the increase in the money supply could drive up prices. Others argued that it could lead to asset price bubbles, as the increased demand for securities could drive up their prices beyond their fundamental value.
Overall, quantitative easing was a key tool used by the Federal Reserve under the Obama administration to stimulate economic growth during the Great Recession. While it was effective in boosting the economy, it also came with some potential risks and drawbacks that should be considered when implementing this policy.