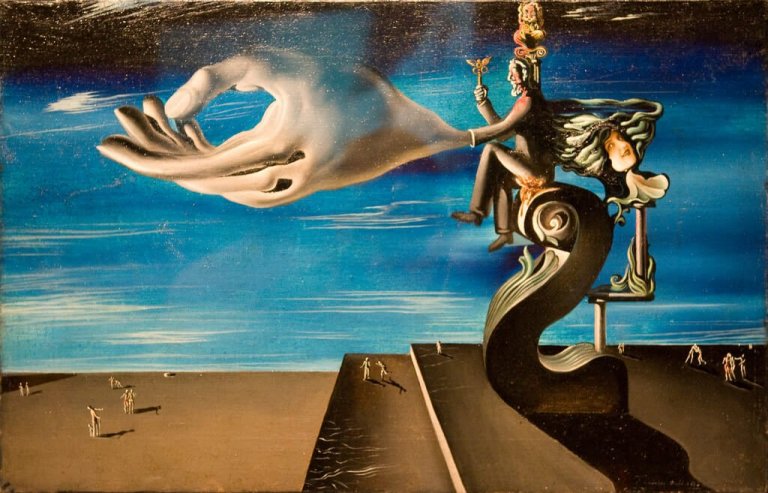
The psychoanalytic approach to art is a perspective that sees artistic creation as a means of expressing and resolving unconscious conflicts and desires. This approach, which originated with the work of Sigmund Freud and was further developed by his followers, seeks to understand the psychological motivations and meanings behind artistic production.
According to the psychoanalytic view, art serves as a way for individuals to express their unconscious thoughts and feelings in a socially acceptable manner. It allows the artist to give form to their innermost desires and conflicts, and to work through them in a creative way. In this sense, art can be seen as a form of therapy, helping the artist to resolve their inner turmoil and achieve greater psychological integration.
One of the key concepts in the psychoanalytic approach to art is the idea of sublimation. Sublimation is the process by which an individual's unconscious desires and impulses are channeled into a socially acceptable form of expression, such as art. This allows the individual to satisfy their desires in a way that does not conflict with their personal values or social norms.
For example, an artist who has aggressive or sexual impulses may sublimate these feelings into their artwork, creating pieces that are violent or sexually charged. Similarly, an artist who has feelings of inadequacy or self-doubt may create works that explore themes of identity and self-worth. In both cases, the art serves as a means of expressing and resolving these unconscious conflicts.
The psychoanalytic approach to art also emphasizes the role of the artist's unconscious mind in the creative process. According to this perspective, the artist's unconscious mind plays a central role in the selection and organization of material, as well as in the overall form and meaning of the artwork. This means that even the artist may not be fully aware of the unconscious motivations and meanings behind their art.
One way to understand the unconscious meanings in an artwork is through the use of psychoanalysis, which is a method of exploring the unconscious mind through techniques such as free association and dream interpretation. By analyzing an artist's unconscious thoughts and feelings, it is possible to gain insights into the psychological motivations and meanings behind their artwork.
In conclusion, the psychoanalytic approach to art sees artistic creation as a means of expressing and resolving unconscious conflicts and desires. It emphasizes the role of the unconscious mind in the creative process and suggests that art can serve as a form of therapy, helping the artist to resolve their inner turmoil and achieve greater psychological integration. This approach offers valuable insights into the psychological motivations and meanings behind artistic production.
Psychoanalytic Criticism, Creativity, and the Artist (Book Review)

Dynamic the theory of conflict 3. The text explains the subconscious mind and the theory of the dynamic unconscious that directs the human mind. Symbolism Indirect and figurative representation of an unconscious idea, conflict or wish. Moreover, many French novelists like Marshall, Maupassant etc. According to Freud, dreams offer a good indication of how the subconscious mind is processing information and emotion, which might not be accessible to the conscious mind. Motion is life, immobility is death; therefore, while beauty brings life, the peace it offers is death.
Psychoanalysis and Art: A Link to the Unconscious

While historically mountain scenery was not regarded as beautiful, perhaps, as Sachs 1951 suggests, because they aroused anxiety in the presence of which beauty could not dwell, with the concept of the sublime, anxiety waned and the landscapes acquired beauty. With growth comes a capacity to restore, a relinquishment of the depressive anxieties, and an integration and enrichment of the ego by assimilation of the loved objects. Research on psychodynamic treatment of some populations shows mixed results. These practices involved automatic drawing, the process of creating marks and images without conscious intention, or as Surrealist principal Landscape, Andre Breton, 1933 Surrealist painter Eine Kleine Nachtmusik 1943 , named for a chamber music composition by Eine Kleine Nachtmusik is a symbolic tableau of youth, featuring the supernatural elements of nightmares and Gothic fiction that Tanning remembered from her childhood. In other words, art would be a way of following our impulses through a vehicle that society does accept.
Psychoanalytic and Jungian approaches to art therapy

Automatists and Veristic Surrealists Earlier surrealists, such as Joan Miro of Spain and Man Ray of the U. Interpersonal theory was first introduced by Harry Stack Sullivan, MD, and developed further by Frieda Fromm-Reichmann, Clara Thompson, Erich Fromm, and others who contributed to the founding of the William Alanson White Institute and Interpersonal Psychoanalysis in general. Unconscious processes can therefore be evaluated from each of these six points of view. However, building on his claims that the patients reported infantile sexual abuse experiences, Freud subsequently contended that his clinical findings in the mid-1890s provided evidence of the occurrence of unconscious fantasies, supposedly to cover up memories of infantile masturbation. Many psychoanalysts who work with children have studied the actual effects of child abuse, which include ego and object relations deficits and severe neurotic conflicts.
The Impact of Psychoanalysis on Art

The latent content takes time to coalesce and percolate in the conscious mind. The International Psychoanalytical Association accredits psychoanalytic training centers throughout the rest of the world, including countries such as Serbia, France, Germany, Austria, Italy, Switzerland, and many others, as well as about six institutes directly in the U. Like cultural critics and literary scholars, Ricoeur contended, psychoanalysts spend their time interpreting the nuances of language. Being a great intuitive teacher of mankind, by his ingenious and deep insight he realised that wherever man goes and wherever he stays, certain kinds of human conflicts are inevitable to prevail. He met with his patients wherever they were, such as when he used free association — where clients would say whatever came to mind without self-censorship.