Project management theory. Communication Theories Applied on Project Management 2022-11-04
Project management theory
Rating:
7,4/10
465
reviews
Project management theory is the study of how to plan, organize, and control resources in order to successfully complete a project. It is a broad field that encompasses a variety of approaches and techniques, including agile, Waterfall, and Lean.
One popular approach to project management is agile, which is characterized by a focus on adaptability and flexibility. Agile projects are organized into short cycles, known as sprints, which allow the team to rapidly respond to changes and pivot as needed. Agile emphasizes collaboration and continuous improvement, with a focus on delivering value to the customer as quickly as possible.
Another common approach to project management is the Waterfall method, which is characterized by a linear and sequential approach to project delivery. Waterfall projects follow a set of predefined stages, with each stage building upon the previous one. This approach is well-suited to projects with clear and well-defined requirements, as it allows for thorough planning and a high level of control over the project.
Lean is another approach to project management that is focused on maximizing value and minimizing waste. Lean projects aim to eliminate unnecessary activities and focus on delivering value to the customer as efficiently as possible. This approach is often used in manufacturing, but it can also be applied to other types of projects, such as software development or product design.
Regardless of the approach used, effective project management requires a clear understanding of the project goals, a well-defined plan for achieving those goals, and strong communication and collaboration among team members. It also requires the ability to identify and mitigate risks, as well as the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
In summary, project management theory is the study of how to effectively plan, execute, and control projects in order to achieve their goals. It encompasses a variety of approaches and techniques, including agile, Waterfall, and Lean, and is critical for the successful completion of any project.
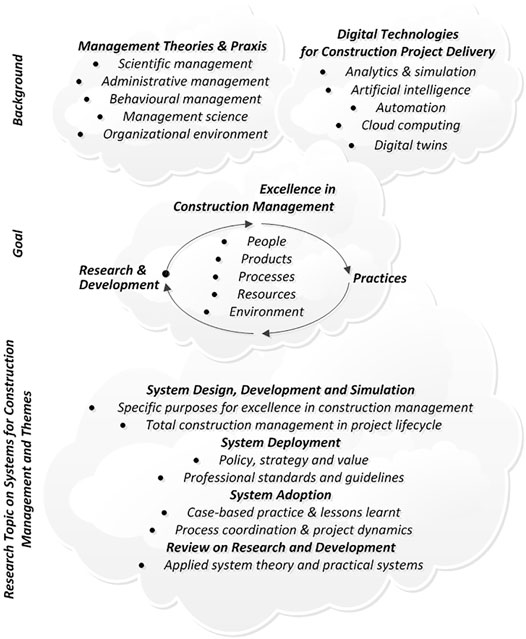
Project Management Theories
At each stage of the project, it is required to follow a management process which comprises planning, control, organise and implement the process PMBOK® Guide, 4th Ed 2008, p. It is rarely explained that the ubiquitous estimate at completion EAC assumes a linear cumulative labor curve. Quality entails meeting settled commitments that can be used to move the project to the next level. According to this theory, a group goes through five essential stages of forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Working in the team helped us learn from one another so that we functioned effectively.
Next
Communication Theories Applied on Project Management
Project Management: Theory and Practice, Third Edition gives students a broad and real flavor of project management. We derive a fundamental relation between the project network structure and the labor rate profile, which then becomes a legitimate project observable. However, why should such a narrow i. Projects within the context of product development are temporary, divine, unique, and transient. It also provides insights into many areas of project management. However, nothing about the PNR model is specifically tied to software projects.
Next
Project Management Theory and Practice, Third Edition
This signifies that a decision or action by one of the elements in the system will affect all other related elements, subsystem and ultimately the overall system. In the end, the project ended with customer termination. The theory presented here is no more complex than the PNR curve, which is widely used for estimation and tracking. Sudden changes in plans can disorient some team members, causing them to not function as properly as usual. Therefore, for this particular network structure, the average number of nodes, or activities, is constant over time. Each member of the team practiced effective communication and displayed the essential skills of careful listening, decision making, conflict management, problem-solving, and leadership Smith 2002, p. A tool for managing projects: An analytic parameterization of the S-curve.
Next
Theory of Project Management
The estimate at completion EAC is a good example: EAC is ubiquitous in the literature but that it assumes a cumulative labor cost profile that is linear over time is rarely explained. A more sophisticated model should be based on the scientific method. Its drivers are factors related to project size, project variety, project interdependence and project context. In section 3, we show that that the PNR model establishes that the labor cost is, indeed, an observable in the formal sense. Project managers should keep this theory in mind during the planning stage.
Next
Project Management Theory and Practice
Then, in the literature review, both Linear and CAS framework will be defined and elucidated in detail. Evidently, the non-systemic techniques including risk evaluation and management were incapable to encapsulate what need to be managed. Parr's elegant and compelling model blazed a trail toward an understanding of the importance of the network structure and its relation to observable project parameters. Typically, activities in the early stages of the project open up new areas for subsequent work, and so the earlier a node appears in the project, the more likely it is to have descendants. This model is not specific to software projects because the relations between the nodes are simply finish-to-start constraints.
Next
Project Management: Theory and Practice

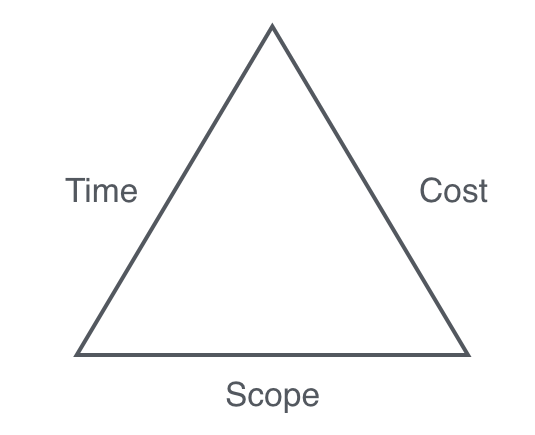
TOC owes its provenance to Eli Goldratt. First, we require a definition of the observables associated with a project and likely candidates are the cost and schedule. Parr 1980 developed what might be described as the first foundational theory of software development. As a member of the team, I learned that teamwork dynamics differ distinctly from individual work. If the branching ratio is k and the probability of a leaf node is p t , after the completion of a node, the number of new, visible activities is: After the completion of a leaf node, the number of visible activities declines by 1, with probability p t. Project success was associated with achieving the project goals in which linked to the Iron Triangle — Cost, Time and Quality Atkinson R, 1999, p.
Next
Concepts of Project Management Theories

The labor rate falls at the end of the project because the team runs out of activities to work on. Interestingly, the cumulative labor profile that emerged was S-shaped and so represents a significant improvement in the theoretical modeling of projects, which to date has been almost entirely based on linear theories. When resources are applied in this optimal way, activities will be completed at a rate proportional to V k t , which implies, Boehm, B. Figure 1: Thermodynamics allows for the efficient control of engines, which is described by the second law. To obtain useful analytic results, the discrete model is converted to its continuous-time analog and the method for solving the resulting equations is given in the Appendix. The four phases of the project life cycle are concept, planning, implementation and closure.
Next
Project management theory
In the PNR model, a project is the completion of a fixed number of activities, and n t denotes the cost of the activities completed at time, t, with the total cost of the project denoted by N. Therefore, without loss of generality, we can interpret the number of activities, N, as the total cost. In sum, these dimensions demonstrate how CAS diverges from linear systems. It will be difficult to achieve Groupthink since the cohesiveness within the members has to be high. Once the project began, the actual costs jagged line quickly deviated significantly from the plan and a new PNR curve was fit to the actual, emerging data. Groupthink To achieve maximum results, a group needs to have one mind. International Journal of Project Management, 24, 136—144.
Next

The mythical man-month: Essays on software engineering. In numerous kinds of literature Aritua et al 2009 , Dooley K 1997 and Lansing J. Network diagrams may contain other types of constraints e. The processes were determined by the communication, cooperation and coordination of the teams that participated in the PD process PMI, 2008. Our theory should also support rational control of projects during execution by determining the impact of proposed network changes on the system's observables.
Next








