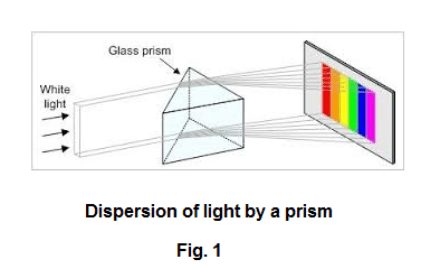
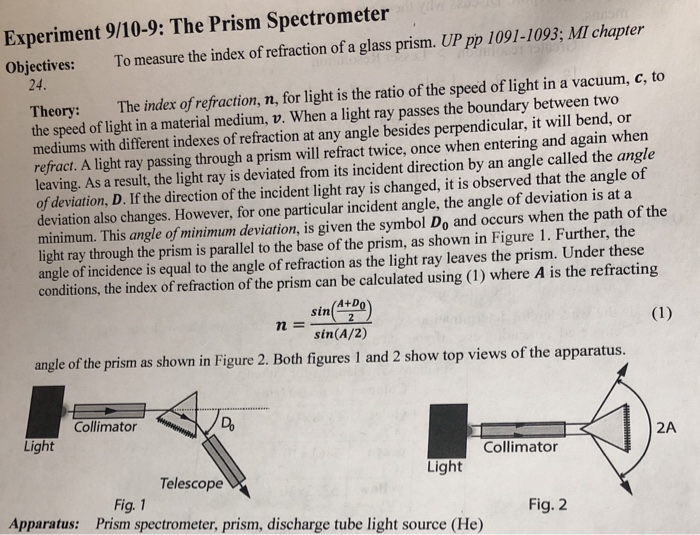
A prism spectrometer is a scientific instrument used to analyze the composition of a sample by separating the light it emits or reflects into its component wavelengths. This is done by passing the light through a prism, which refracts (or bends) the light at different angles based on its wavelength. The resulting spectrum of wavelengths can then be measured and analyzed to determine the relative amounts of various substances present in the sample.
The theory behind the operation of a prism spectrometer is based on the principles of refraction and dispersion. When light passes through a medium with a different refractive index, it will bend at an angle determined by Snell's Law. This phenomenon is used in the prism to separate the different wavelengths of light, with longer wavelengths bending less and shorter wavelengths bending more.
The amount of bending, or refraction, that occurs also depends on the shape of the prism and the angle at which the light enters it. By carefully designing the shape and angles of the prism, it is possible to achieve a wide range of dispersion, or separation of the wavelengths. This allows for the analysis of a wide range of samples, from gases and liquids to solid materials.
One of the key advantages of a prism spectrometer is its ability to produce a continuous spectrum, rather than a discrete set of lines or bands. This allows for more precise measurement of the relative amounts of various substances present in the sample, as well as the detection of trace elements that may not be visible in other types of spectrometers.
There are several types of prism spectrometers, including the normal incidence spectrometer, the immersion spectrometer, and the grating spectrometer. Each of these designs has its own advantages and limitations, and is used in different applications depending on the needs of the experiment.
In conclusion, the prism spectrometer is a powerful tool for analyzing the composition of a sample by separating the light it emits or reflects into its component wavelengths. Its ability to produce a continuous spectrum allows for more precise measurement and detection of trace elements, and it has a wide range of applications in scientific research and industry.
Prism Spectrometers, Two Typical Spectrometers Used in Spaceborne Hyperspectral Imagers
In fact, compounds like steroids are modified As mentioned, negative ions can be produced by electron capture, and in negative chemical ionization a buffer gas such as methane can slow down the electrons in the electron beam allowing them to be captured by the analyte molecules. However, similar to EI, samples must be thermally stable since vaporization within the CI source occurs through heating. The increased frequency improves accuracy as it allows for more measurements to average. This chapter will focus on the principles of operation and current performance capabilities of mass analyzers, while briefly touching on ion detectors and the concept of vacuum in a mass spectrometer. A disadvantage of both ESI and APCI is that they can generate background ions from solvents.
Spectrophotometer

As a result, you have measured the curve of index of refraction as a function of wavelength. A sample is introduced into the mass spectrometer and is then ionized. Notice that there are two windows in which you can read an angle. If at all possible, we should try to use set it so that this window is to the left of the telescope as we are looking over the barrel toward the lamp because this will make reading our angle easiest. Tandem mass analysis is used to sequence peptides, and structurally characterize carbohydrates, small oligo-nucleotides, and lipids. White light is made up of all the colors of the rainbow red, yellow, green, blue, and violet. D is minimum when the angles of the incoming and outgoing rays make equal angles with the prism surfaces.
Theory of the Prism Spectrometer

Become familiar with the spectrometer a Identify each component: the black table, the prism table, the collimator, and the telescope b Note the clamping screws and the fine adjustment screws for the telescope and the black table. A cadmium lamp provides a few discrete wavelengths and for each wavelength the minimum deviation angle will be different. The energies of the prominent γ rays from nuclei listed in Table 2. Electrospray Ionization ESI The idea of electrospray, while not new, has been rejuvenated with its recent application to biomolecules. Journal of Chemical Physics. Namely, 600cornu quartz prism and 300Littrow Prism.
Mass Spectrometry: Basics
Chemical Ionization CI Chemical Ionization CI is applied to samples similar to those analyzed by EI and is primarily used to enhance the abundance of the molecular ion. This approach, while less sensitive, can be effective for otherwise insoluble compounds. First, we introduce a coordinate break in our lens file and set the Tilt About X to 33. Upon photoionization of the dopant, charge transfer occurs to the analyte. In addition, the modified-Dyson design utilizes two thin lenses, instead of one very thick Dyson lens.