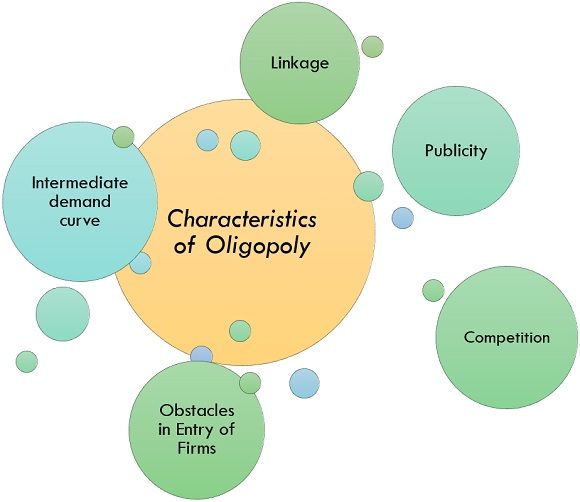
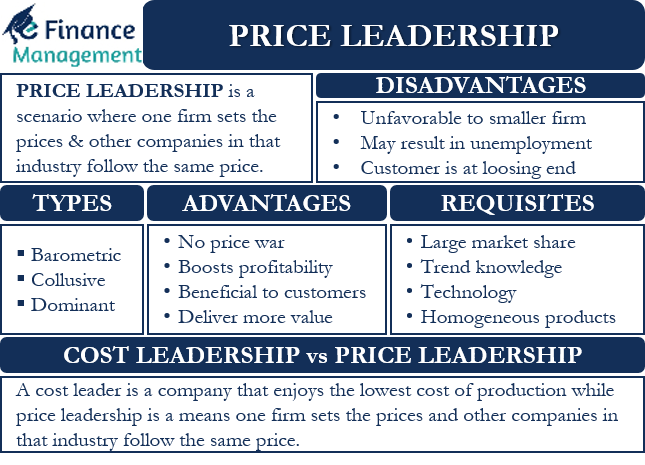
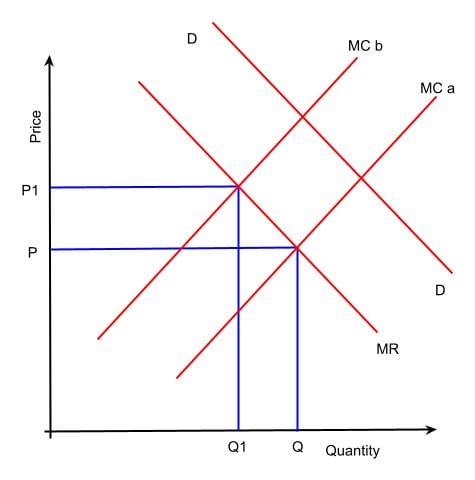
In an oligopoly market, a small number of firms dominate the industry and have the ability to influence the prices of their products. One way that firms in an oligopoly can exercise this influence is through price leadership, in which one firm takes the lead in setting prices and the other firms follow suit.
There are several reasons why firms may engage in price leadership. One reason is to avoid price wars, which can lead to reduced profits for all firms in the industry. By establishing a leader who sets prices, the other firms can avoid the costs of constantly adjusting their prices in response to competitors. Price leadership can also help firms coordinate their pricing strategies and avoid the temptation to engage in predatory pricing, in which a firm sets prices low in an attempt to drive out competitors.
There are several types of price leadership that can occur in an oligopoly market. In exclusive price leadership, one firm takes the lead in setting prices and the other firms in the industry are not allowed to deviate from those prices. This type of price leadership is more common in industries with high barriers to entry, such as industries with high fixed costs or industries that are regulated by the government.
In contrast, in inclusive price leadership, all firms in the industry are allowed to set their own prices, but they are expected to follow the lead of the dominant firm. This type of price leadership is more common in industries with low barriers to entry, such as industries with low fixed costs or industries that are not regulated by the government.
There are several factors that can affect the effectiveness of price leadership in an oligopoly market. One factor is the degree of differentiation among the products offered by the firms in the industry. If the products are highly differentiated, it may be more difficult for the firms to coordinate their pricing strategies. Another factor is the degree of collusion among the firms. If the firms are able to collude and coordinate their pricing strategies, price leadership is more likely to be effective. However, if the firms are unable to collude or if there is suspicion of collusion, price leadership may be less effective.
Overall, price leadership is a common strategy that firms in an oligopoly market may use to exert influence over prices and coordinate their pricing strategies. While it can be an effective way to avoid price wars and predatory pricing, it is not without its challenges, as the effectiveness of price leadership can be affected by various factors such as differentiation among products and the degree of collusion among firms.