Price determination under perfect competition refers to the process by which prices are set in a market characterized by a large number of small firms, all producing homogeneous products and facing perfectly elastic demand. In such a market, no single firm has the ability to influence the market price, as they are too small relative to the size of the market. Instead, the market price is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves.
In perfect competition, firms are price takers, meaning they must accept the market price as determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. They have no choice but to sell their product at the market price, as they cannot influence the price due to their small size. However, firms are still able to choose their level of output, as long as they are able to cover their average total costs at the market price.
Firms in a perfectly competitive market are motivated to produce and sell as much as possible, as long as they are able to cover their costs. This is because they are earning a normal profit, meaning they are earning just enough to cover their opportunity cost of production. If a firm were to produce less than the optimal level, they would be earning less than a normal profit, as they would not be covering all of their costs. On the other hand, if a firm were to produce more than the optimal level, they would be earning more than a normal profit, as they would be able to sell their excess output at the market price.
However, it is important to note that the market price in a perfectly competitive market is not always equal to the firms' marginal cost. In the short run, when a firm has fixed costs, the market price may be above the firm's marginal cost, allowing the firm to earn a positive economic profit. However, in the long run, when all costs are variable and firms can enter and exit the market freely, the market price will tend towards the firms' marginal cost. This is because in the long run, firms will enter the market as long as they can earn a normal profit, increasing the supply of the product and driving down the price. Conversely, firms will exit the market if they are unable to cover their costs, decreasing the supply of the product and driving up the price.
In summary, price determination under perfect competition is driven by the forces of supply and demand, with the market price being determined at the intersection of the two curves. Firms in such a market are price takers and are motivated to produce and sell as much as possible as long as they are able to cover their costs. In the long run, the market price will tend towards the firms' marginal cost.
Economics Notes For Class 12 Price Determination Under Perfect Competition

It intersects supply curve at point E. Its supply can be increased out of the given stock such commodities are cloth, wheat, tea, etc. The industry supplies 0M 2 quantity at this equilibrium price. ADVERTISEMENTS: a Market Period: In a market period, the time span is so short that no firm can increase its output. For example, if there is no fixed price of gold, various sellers will sell the gold at the cheapest rate and hence the overall value of gold will fall. Since both buyers and sellers in perfectly competitive market set quantity in response to price, in such a market price plays the key role of an equilibrating variable.
Price determination under perfect competition market

These three situations can be illustrated with the help of three diagrams as w e In these diagrams, AC is average cost curve. In this way, the firm has normal earnings. In this way, unsatisfied buyers will compete with each other to have the limited supply. On the contrary, if demand decreases demand curve will shift to left of the original demand curve DD. The demand curve DD and supply curve SS, intersect each other, and we get Equilibrium Price aLongside Equilibrium quantity. They strictly follow the Price structure, as stated by the industry. The firm will have to sell all its output at OP price.
Price and output determination

Its average cost AC will be BQ because AR is higher than AC. In the Figure, long run supply LRS curve has a positive slope. The new equilibrium price is 0P 2, which is higher than the original equilibrium price 0P 0. In other words, the number is stable when all firms are at equilibrium, making normal profits. For example, if the demand is high and supply is low, then the Price will increase. In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been theoretically demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every product or service, including labour, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. ADVERTISEMENTS: The first, if price is very high the seller will be prepared to sell the whole stock.
Price Determination Under Perfect Competition

It is the point of equilibrium. Thus, in the short run, larger quantity of the commodity is sold and price is not quite so high as it was in the market period. In this diagram, quantities of demand and supply have been shown on x-axis and price on y-axis. From the above discussion, it is clear that as demand increases, the long run normal price increases, remains the same or decreases depending upon whether the industry in question is an increasing cost, constant cost or decreasing cost industry. Every organization has a fixed stock of products to be sold thus supply curve is perfectly inelastic in a very short period of time. EMC curve at the point of equilibrium, the firm will suffer loss.
Price Determination under Perfect Competition (With Diagram)
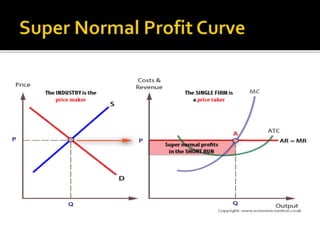
Now, we will explore more on the topic of how Prices are determined under Perfect Competition. According to these economists, the cost of production is the determinant of price. Nor can the price fall below the minimum average cost, since in that situation the firms will be incurring losses and, in the long-run, if these losses persist, some of them will leave the industry, and thereby the price will rise to the level of minimum average cost so that in the long run firms are earning only normal profits. Thus, the slope of supply curve will be different accordingly. All firms are at break-even because of the loss of profits.








