Monopolistic competition refers to a market structure in which there are many firms producing slightly differentiated products. These firms have some market power, meaning they can influence the price of their product, but they face competition from other firms offering similar products. In this type of market, firms must consider both the demand for their product and the actions of their competitors when determining their price and output.
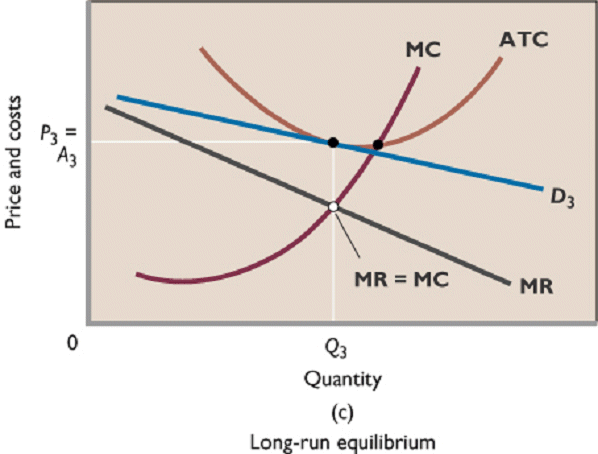
The demand curve for a firm under monopolistic competition is downward sloping, as in a perfectly competitive market, but it is not perfectly elastic. This means that the firm can charge a higher price and still sell some quantity of its product, but it will face a decrease in demand as the price increases. The degree of inelasticity of demand will depend on the level of differentiation of the firm's product and the availability of substitutes.
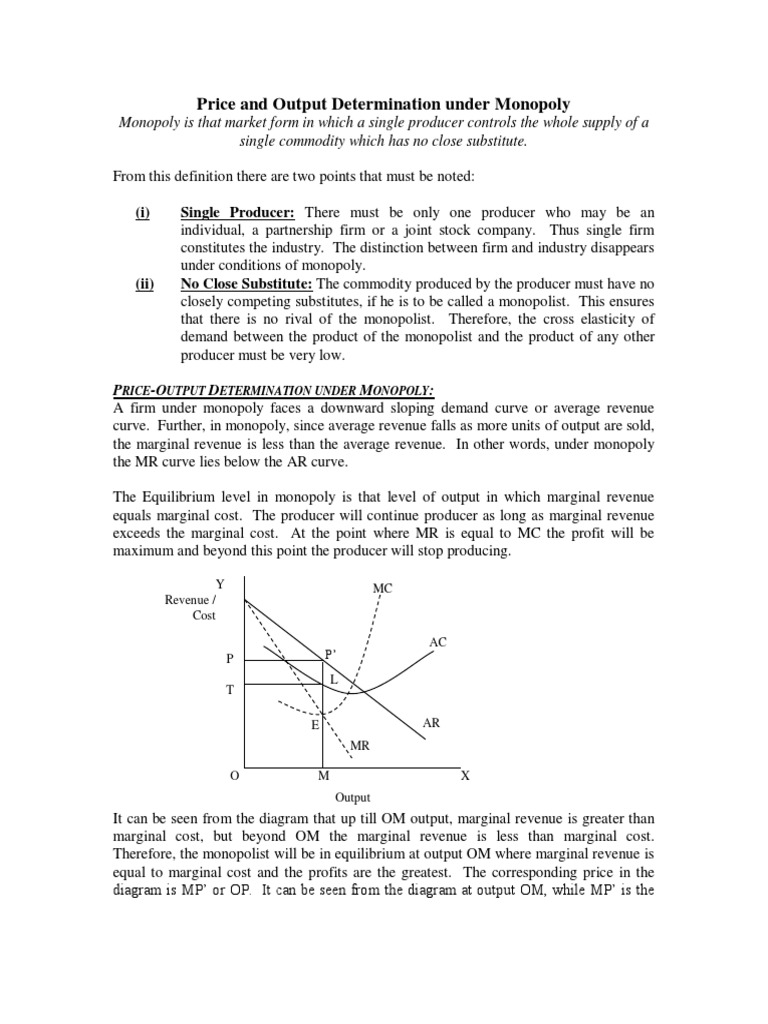
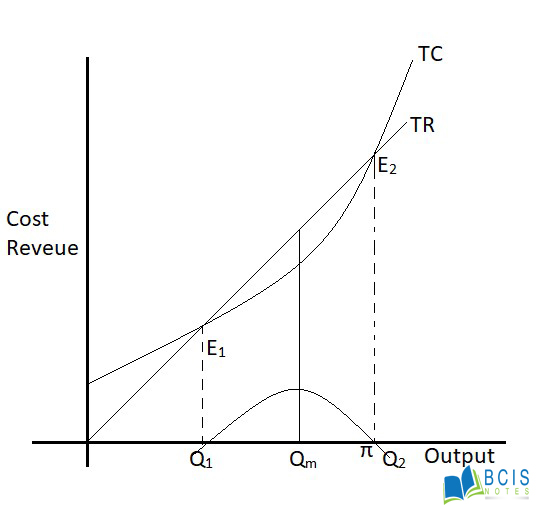
The firm's marginal cost curve will also play a role in determining its price and output. The marginal cost is the cost of producing one additional unit of the product, and it will typically increase as the firm increases its output. The firm will choose to produce at the level of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, as this will maximize its profit.
Under monopolistic competition, firms will not necessarily produce at the lowest point on their average total cost curve as they do in perfect competition. This is because firms will often choose to produce at a higher level of output and charge a higher price in order to increase their profits. This is known as excess capacity.
The level of differentiation of the firm's product, as well as the intensity of competition, will influence the firm's ability to charge a higher price. If a firm's product is highly differentiated, it may be able to charge a higher price due to its perceived value to consumers. On the other hand, if the intensity of competition is high, the firm may be unable to charge a higher price and may need to lower its price in order to remain competitive.
In summary, under monopolistic competition, firms must consider both demand and the actions of their competitors when determining their price and output. The demand for their product, their marginal cost, and the level of differentiation of their product all play a role in this decision. Firms may choose to produce at a level of output above the lowest point on their average total cost curve in order to increase their profits.