Prenatal development is the process of growth and development that occurs in an individual from conception until birth. It is a complex and dynamic process that involves the development of various body systems and organs, as well as the formation of numerous structures and functions that are necessary for life outside the womb. Understanding the stages of prenatal development can provide insight into the remarkable transformations that take place during this critical period of development.
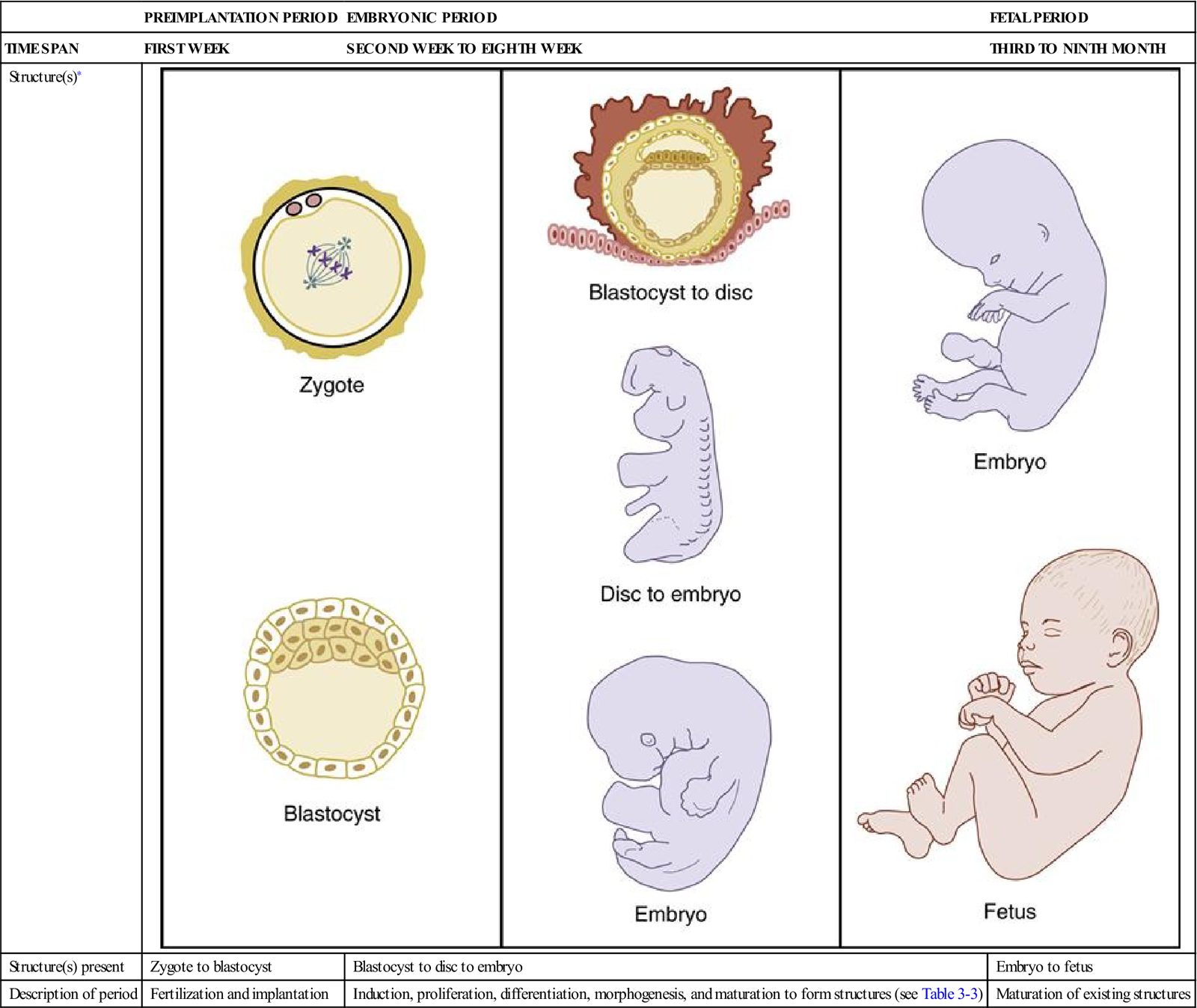
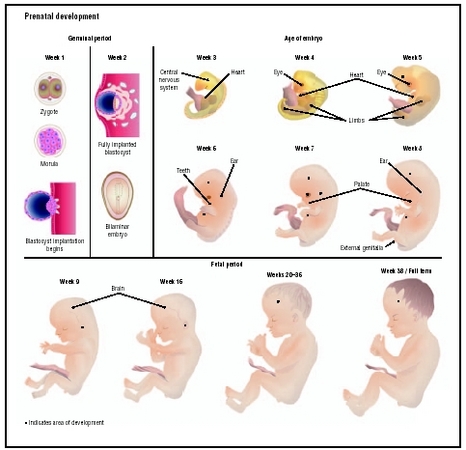
The process of prenatal development begins with fertilization, which occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg. This process results in the formation of a zygote, which is a single cell that contains the genetic material from both the sperm and the egg. The zygote begins to divide and grow as it travels down the fallopian tube and into the uterus, where it implants itself into the uterine lining.
During the first week of development, the zygote becomes a ball of cells known as a blastocyst. The blastocyst consists of an outer layer of cells, called the trophoblast, and an inner group of cells, called the inner cell mass. The trophoblast will eventually develop into the placenta, while the inner cell mass will give rise to the embryo.
During the second week of development, the blastocyst implants itself into the uterine lining and begins to produce hormones that prevent the woman's body from ovulating again. At this stage, the blastocyst is also forming the three primary germ layers that will give rise to all of the body's organs and tissues. These germ layers are called the ectoderm, the mesoderm, and the endoderm.
The ectoderm will give rise to the nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, as well as the skin, hair, and nails. The mesoderm will give rise to the circulatory system, including the heart and blood vessels, as well as the muscles, bones, and connective tissue. The endoderm will give rise to the digestive system, including the liver, pancreas, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
During the third week of development, the embryo begins to take on a more recognizable form, with the head and spinal cord becoming visible. The heart begins to form and begins to beat, and the beginnings of the brain, eyes, and ears can also be seen. At this stage, the embryo is about the size of a grain of rice.
During the fourth week of development, the embryo's major body systems and organs continue to develop. The arms and legs begin to form, and the eyes and ears continue to develop. The embryo is now about the size of a bean.
During the fifth week of development, the embryo's fingers and toes begin to form, and the nose, mouth, and chin become more defined. The embryo is now about the size of a small raspberry.
During the sixth week of development, the embryo's face becomes more distinct, with the ears moving to their final position on the head. The embryo's internal organs, including the liver and pancreas, continue to develop, and the beginnings of the reproductive system can also be seen. The embryo is now about the size of a small cherry.
During the seventh week of development, the embryo's arms and legs continue to grow, and the hands and feet become more distinct. The embryo's face becomes more human-like, with the eyes moving closer together and the nose and mouth becoming more prominent. The embryo is now about the size of a small blueberry.
During the eighth week of development, the embryo's external genitalia begin to form, and the bones in the arms and legs begin to harden. The embryo is now about