Plant cells are the fundamental unit of life in plants and are the building blocks for all plant tissues and organs. Like animal cells, plant cells contain a variety of organelles that perform specific functions that are essential for the cell's survival and growth. In this essay, we will explore the different plant organelles and their functions in detail.
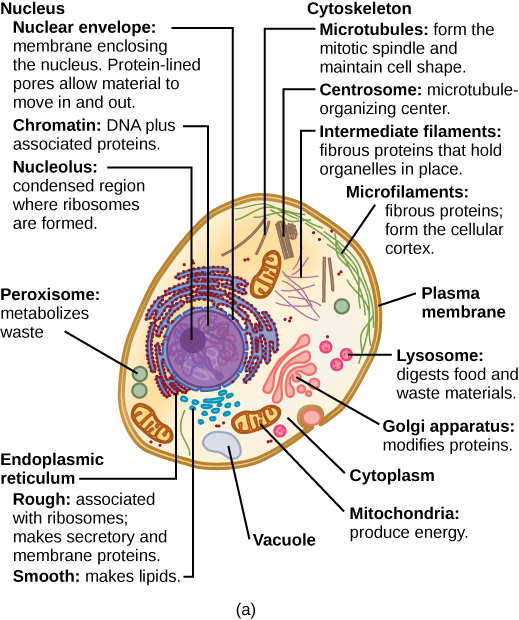
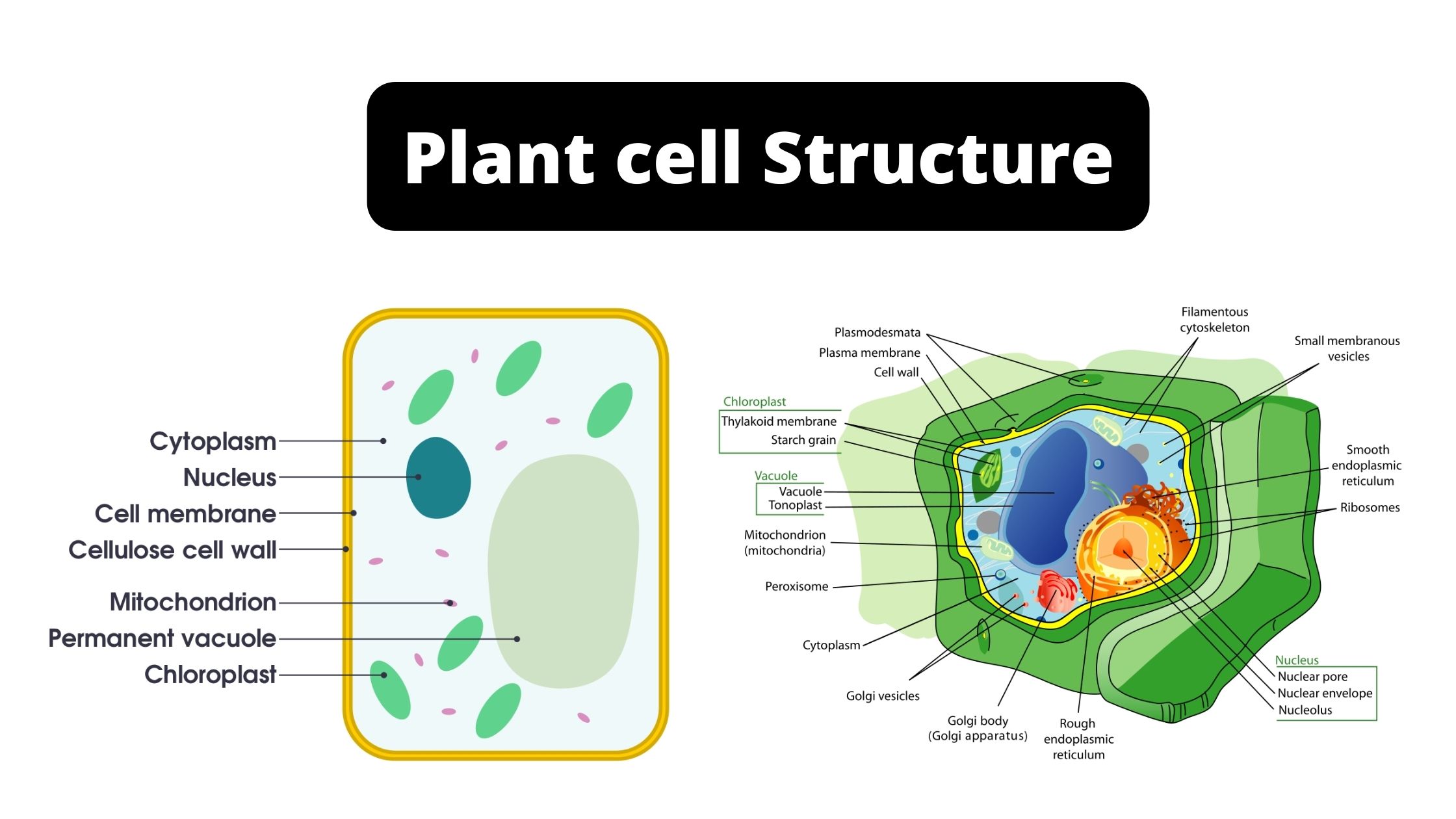
The cell wall is a protective layer that surrounds the cell membrane in plant cells. It is made up of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate, and other substances such as pectin, lignin, and proteins. The cell wall provides support and protection to the cell, helping the plant to maintain its shape and resist external forces such as wind and gravity. It also helps to prevent the cell from bursting due to the high turgor pressure inside the cell.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment. It is made up of lipids and proteins and acts as a selective barrier, allowing some substances to pass through while preventing others from entering the cell. The cell membrane is also involved in communication with other cells, as it contains receptors that can detect signals from the environment and transmit them to the inside of the cell.
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. It is made up of water, salts, and organic molecules such as enzymes, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. The cytoplasm is where most of the cell's chemical reactions take place, and it is also the site of energy production.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. It is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope, which is made up of two membranes. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA, which is organized into chromosomes and carries the genetic instructions that are needed to build and maintain the cell. The nucleus also contains small, spherical structures called nucleoli, which are involved in the synthesis of ribosomes, the organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle that is involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids. It is made up of a network of flattened sacs and tubes that are connected to the nucleus and the Golgi apparatus. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is studded with ribosomes, which are involved in the synthesis of proteins. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) does not contain ribosomes and is involved in the synthesis and modification of lipids and carbohydrates.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle that is involved in the sorting, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids. It is made up of flattened stacks of membranous sacs that are connected to the endoplasmic reticulum and the cell membrane. The Golgi apparatus modifies the proteins and lipids that are produced by the endoplasmic reticulum, adding carbohydrate or protein groups to them to give them specific functions. It then sorts the modified molecules into vesicles, which are transported to different parts of the cell or to the cell surface for secretion.
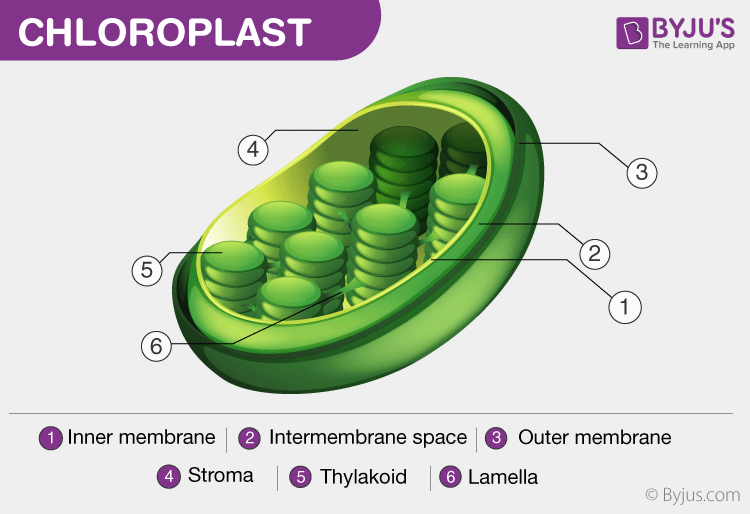
The mitochondria are organelles that are responsible for producing the energy that the cell needs to carry out its functions. They are made up of two membranes, the inner and the outer membrane, and contain their own DNA and ribosomes. The mitochondria produce energy by breaking down glucose and other organic molecules in a process called respiration. The energy is stored in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is used