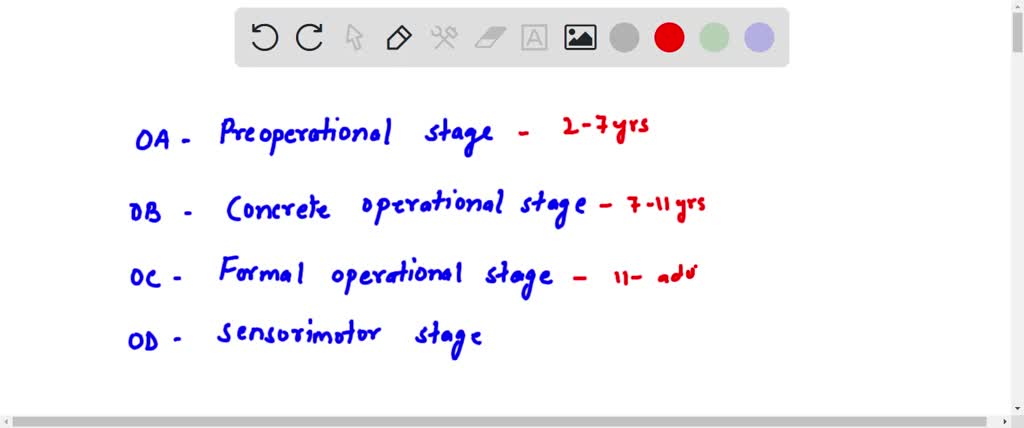
Jean Piaget's formal operational stage is the fourth and final stage of cognitive development in his theory of cognitive development. This stage typically begins around the age of 11 or 12 and continues until the individual reaches adulthood. During this stage, individuals develop the ability to think abstractly and logically, and they are able to engage in deductive reasoning.
During the formal operational stage, individuals develop the ability to use logical and systematic thinking to solve problems and understand complex concepts. They are able to think hypothetically and are able to consider multiple possibilities when solving problems. They are also able to understand and use formal mathematical operations, such as algebra and geometry.
One of the key characteristics of the formal operational stage is the ability to think about abstract concepts and ideas, rather than just concrete objects or experiences. This allows individuals to consider abstract ideas, such as justice, fairness, and morality, and to use logical reasoning to evaluate and analyze these concepts.
Another important characteristic of the formal operational stage is the ability to think about and manipulate ideas in a systematic way. This means that individuals are able to create and test hypotheses, and to use scientific methods to understand and explain phenomena. They are also able to use logic and evidence to support their arguments and to evaluate the validity of others' arguments.
While the formal operational stage marks a significant milestone in cognitive development, it is important to note that not all individuals reach this stage at the same age, and some may never fully reach it. Factors such as education, culture, and life experiences can all influence an individual's development and their ability to reach the formal operational stage.
Overall, the formal operational stage represents a major shift in cognitive development and marks a significant milestone in an individual's ability to think abstractly, logically, and systematically. It is a crucial stage in the development of higher-order thinking skills and the ability to understand and engage with complex concepts and ideas.
Piaget Stages of Development: What Are They and How Are They Used?

More recent work from a newer dynamic systems approach has strongly challenged some of the basic presumptions of the "core knowledge" school that Piaget suggested. Do All Children Reach the Formal Operational Stage? Following on from an elevated understanding of categories, the formal operational stage enables children to manipulate and combine different categories systematically to solve problems. Biologie et connaissance: Essai sur les relations entre les régulations organiques et les processus cognitifs. Some of its ideas are helpful to provide a frame of reference, but it should not be considered completely reliable. How can caregivers use schemas? Yet in some cases, children may be able to learn advanced ideas even with brief instruction. Once a child reaches this stage, their method of acquiring knowledge does not change, it only involves building upon knowledge. In addition, it described the processes of biological maturation.
Piaget's Formal Operational Stage

These new cognitive skills increase the child's understanding of the physical world. For example, there might be changes in shape or form for instance, liquids are reshaped as they are transferred from one vessel to another, and similarly humans change in their characteristics as they grow older , in size a toddler does not walk and run without falling, but after 7 yrs of age, the child's sensorimotor anatomy is well developed and now acquires skill faster , or in placement or location in space and time e. What problems can they solve? The type of symbolic play in which children engage is connected with their level of creativity and ability to connect with others. The process is somewhat subjective because we tend to modify experiences and information slightly to fit in with our preexisting beliefs. In this stage, there are still limitations, such as egocentrism and precausal thinking. The operative and figurative aspects of knowledge in Piaget's theory.
Formal Operational Stage: How Parents Support Cognitive Development

As kids interact with the world around them, they continually add new knowledge, build upon existing knowledge, and adapt previously held ideas to accommodate new information. Conclusion Both Piaget and Erikson have theories that have a profound impact on how we understand child development. Early Childhood Education Journal. In fact, one very influential book of his The Origins of Intelligence in Children , 1952 , contained conclusions based on findings involving only three children-his own. This kind of hypothetical reasoning allows them to function better in the world, understanding the consequences of their actions and being able to problem-solve.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/preteenpresent-ec67c687df594cadb327c2e4f74246a6.jpg)