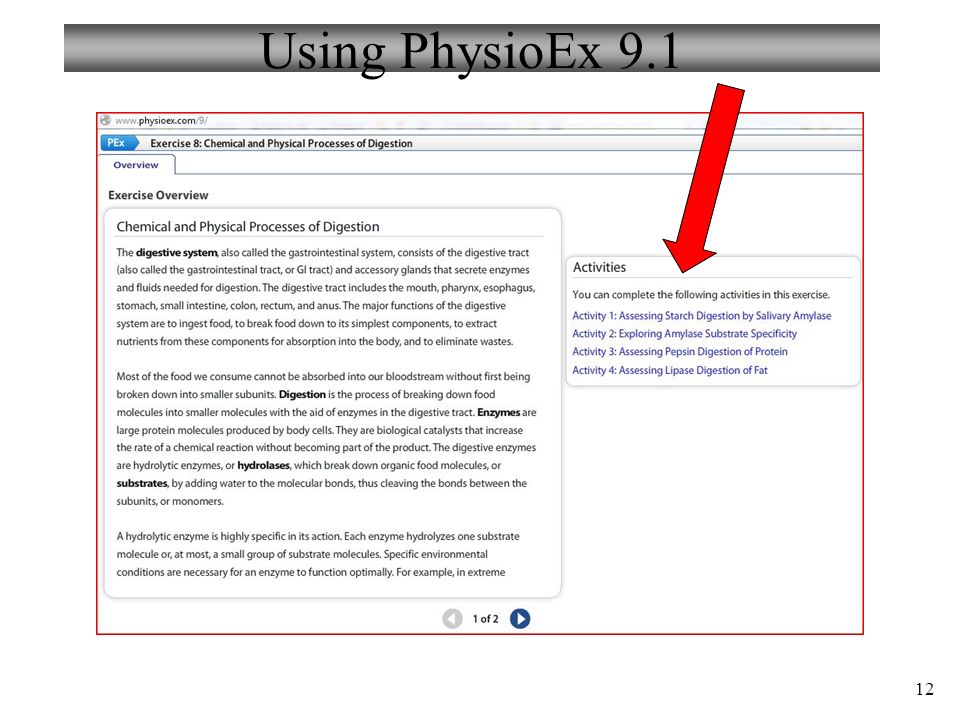
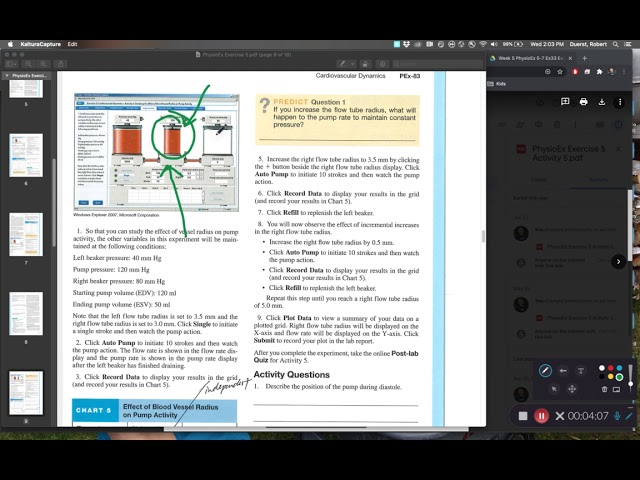
Physioex 9.1 is a computer-based simulation program designed to help students learn and understand human physiology. Exercise 9 is focused on the respiratory system and specifically on the mechanics of breathing. In this exercise, students are asked to complete a series of activities and answer questions related to the respiratory system and how it functions.
The first activity in exercise 9 asks students to observe and interpret graphs of respiratory volume and air flow as a person breathes in and out. This helps students understand how the volume of air in the lungs changes during the respiratory cycle and how this is related to the movement of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
The second activity focuses on the effects of different respiratory disorders on respiratory volumes and air flow. Students are asked to observe and interpret graphs of respiratory volume and air flow in individuals with asthma, emphysema, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This helps students understand how these disorders affect the mechanics of breathing and how they can lead to respiratory difficulties.
The third activity in exercise 9 asks students to examine the effects of different respiratory muscles on respiratory volumes and air flow. Students are asked to observe and interpret graphs of respiratory volume and air flow as different respiratory muscles are contracted and relaxed. This helps students understand how these muscles work together to control breathing and how they can be affected by different factors, such as exercise or disease.
The final activity in exercise 9 asks students to analyze the effects of altitude on respiratory volumes and air flow. Students are asked to observe and interpret graphs of respiratory volume and air flow as an individual ascends to high altitudes. This helps students understand how the respiratory system adjusts to changes in atmospheric pressure and how it can be affected by altitude.
Overall, exercise 9 of Physioex 9.1 helps students understand the mechanics of breathing and how different factors can affect the respiratory system. By completing the activities and answering the related questions, students can gain a better understanding of how the respiratory system works and how it can be affected by different disorders and environmental factors.