Perfect competition and monopolistic competition are two different market structures that describe the level of competition that exists within an industry. While perfect competition is characterized by a large number of small firms, each producing a homogeneous product, monopolistic competition is characterized by a large number of firms, each producing a slightly differentiated product.
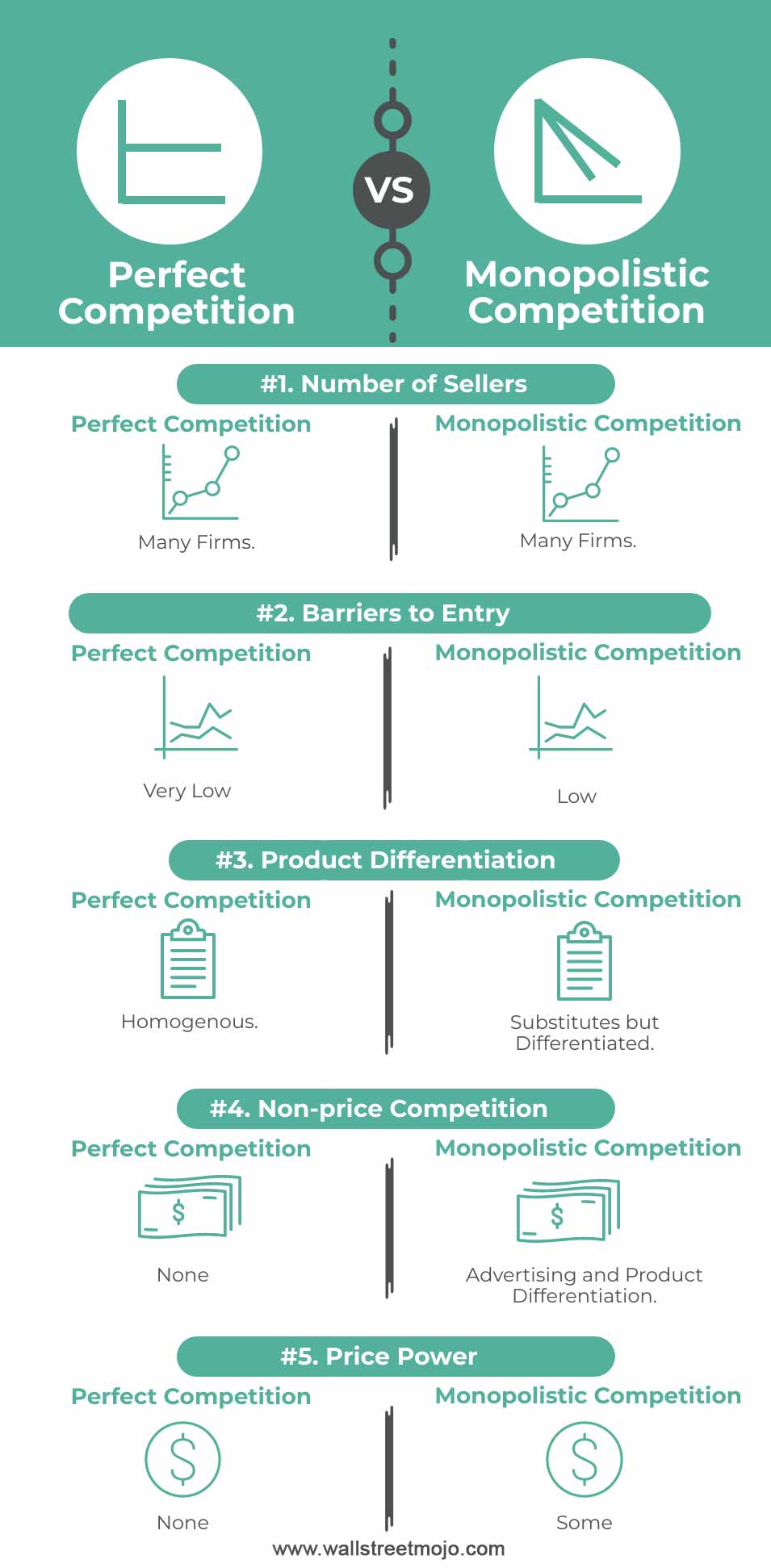
In perfect competition, there are many buyers and sellers in the market, and all firms are price takers. This means that each firm must accept the market price for its product and cannot influence the price through its own actions. Because there is such a large number of firms in the market, it is easy for new firms to enter, and existing firms have no barriers to exit. This constant entry and exit of firms helps to ensure that the market remains competitive.
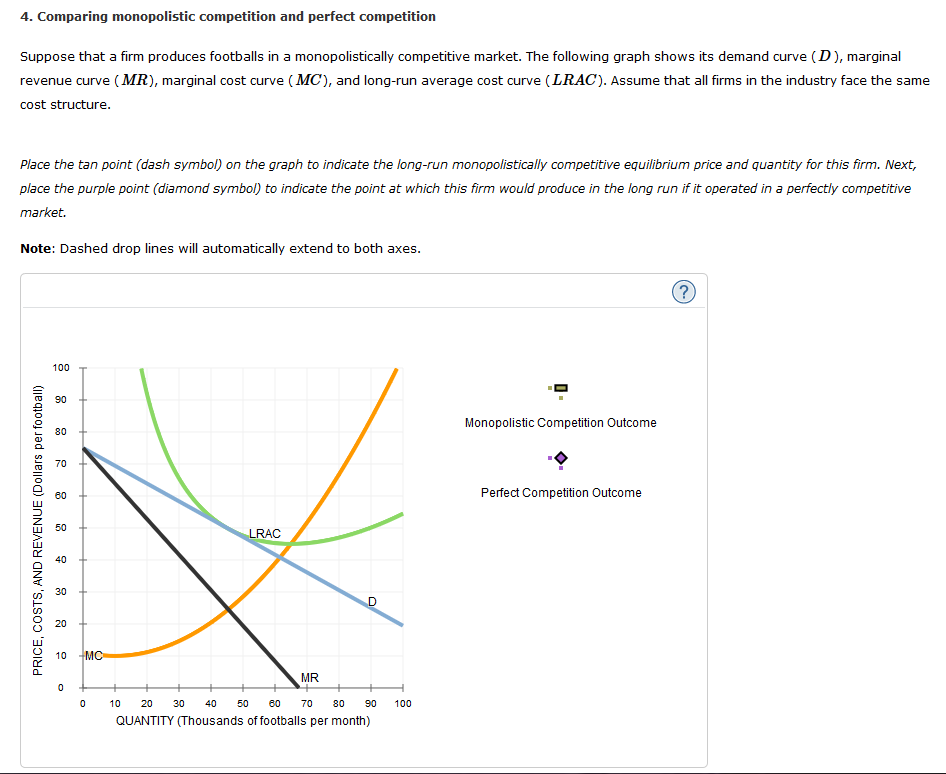
One of the key characteristics of perfect competition is that firms are profit maximizers. In order to maximize profits, firms will produce at the point where their marginal cost (the cost of producing one additional unit of the product) equals their marginal revenue (the increase in revenue that results from selling one additional unit of the product). This point is known as the profit-maximizing level of production.
In monopolistic competition, there are also many buyers and sellers in the market, but the products offered by each firm are slightly differentiated from one another. This means that each firm has some level of control over the price of its product, as consumers are willing to pay a slightly higher price for the unique features of the product. Because of this, firms in monopolistic competition are not pure price takers like firms in perfect competition.
In monopolistic competition, firms have some level of market power, which allows them to raise prices and earn economic profits. However, these profits are not as high as they would be in a monopoly, as there are still other firms in the market offering similar products. As a result, firms in monopolistic competition must constantly be innovating and differentiating their products in order to stay competitive and maintain their market power.
Overall, perfect competition and monopolistic competition are two different market structures that are characterized by different levels of competition. Perfect competition is characterized by a large number of firms producing a homogeneous product, while monopolistic competition is characterized by a large number of firms producing a slightly differentiated product. While both types of markets have their own unique characteristics, they both play an important role in the functioning of a market economy.
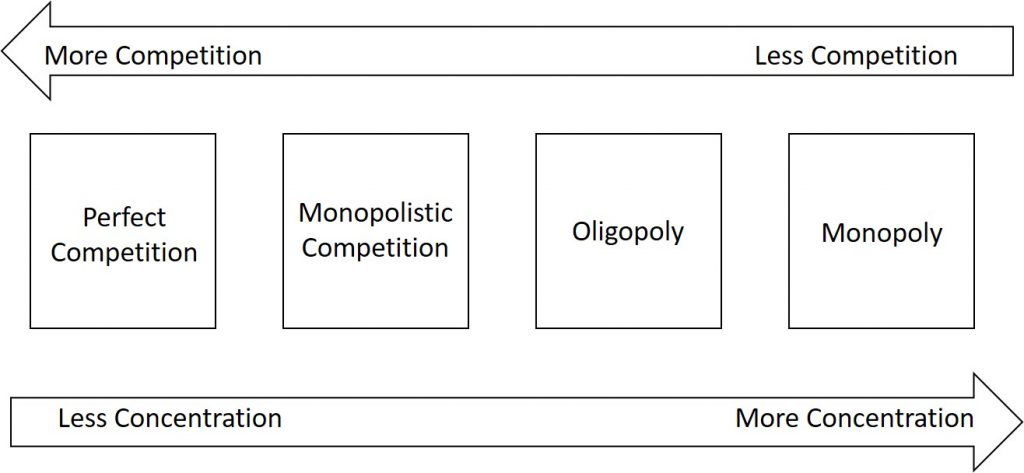
1.5 Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly, and Monopoly

For example, a market may be characterized by both perfect competition and monopolistic competition, depending on the specific goods or services being sold. Dissimilarities between Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition: ADVERTISEMENTS: There are, however, certain points of dissimilarities between perfect competition and monopolistic competition. Product Differentiation Companies can differentiate their products by using color, size, features, performance, and accessibility in the retail industry. If, at the point where the marginal cost meets average variable costs, prices can be captured above that point, then they can stay producing, otherwise they need to shut down. However, this can also lead to inefficiency, as firms may not be motivated to produce goods or services at the lowest possible cost in order to maintain their market power. Lastly, buyers, as well as sellers, have limited information in this structure. Deadweight Loss This says that if we were to compare two circumstances: one that is a monopoly and the other where competition exists.
Perfect and Monopolistic Competition
This website includes study notes, research papers, essays, articles and other allied information submitted by visitors like YOU. Hairdressers Although the premises and the location of a hairdresser play an important role in determining its place in the market, it is undoubtedly the skill of the hairdresser that sets a specific saloon apart from others. This example talks about farmers who produce food for the entire 7. Additionally, depending on the location, one restaurant may have more power over the others based on the number of customers. How is product differentiation accomplished? It is impossible to provide a complete set of examples that address every variation in every situation since there are thousands of such markets. This is deadweight loss.
Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly
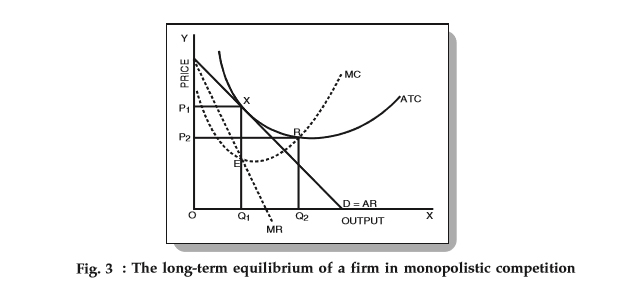
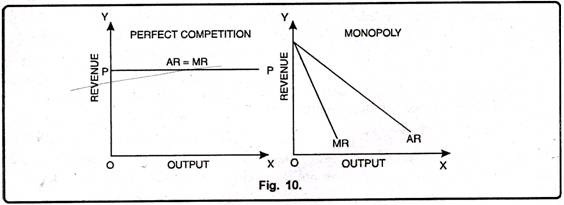
As large firms supplying a sizable portion of a market, these companies have some control over the prices they charge. Perfect competition is not realistic, it is a hypothetical situation, on the other hand, monopolistic competition is a practical scenario. The equilibrium of the competitive firm is established at E and that of the monopolistic competitive firm at E 1. That means higher the price, lower the demand. In a monopolistically competitive market, firms can differentiate their products in order to distinguish themselves from their competitors.
Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition

The change in overall revenue, or total revenue, is divided by the change quantity. However, a dominant seller is controlling the market regarding prices and quality of products. The equilibrium position of these market are reached in different circumstances and are based on revenues earned and cost incurred. A market is a special place where sellers and buyers meet for transactions; this may happen through a dealer or directly. Grocery Stores Grocery stores are nothing but monopolistic competition because each product offered in stores is identical; however, at a slightly different price. A Large Number of Sellers India, the largest producer of mangoes, has many mango cultivators.