Parts of the ovum. Ovum Cell Structure & Function 2022-10-21
Parts of the ovum
Rating:
7,3/10
276
reviews
A definition argument is a type of argument in which the writer defines a specific term or concept and then attempts to persuade the reader to accept the writer's definition as the correct or most appropriate one. This type of argument can be useful in a variety of contexts, including academic writing, political discourse, and everyday conversation.
There are many potential ideas for definition arguments, as any term or concept can be the subject of such an argument. Some possible topics might include:
The definition of a specific term or concept: For example, a writer might argue for a particular definition of the term "justice" or "democracy."
The existence or non-existence of a specific term or concept: A writer might argue that a term or concept, such as "trolling" or "fake news," does not actually exist or has been misdefined by others.
The appropriateness or inappropriateness of a specific term or concept: A writer might argue that a term or concept, such as "hate speech" or "political correctness," is being used inappropriately or needs to be redefined.
The importance or unimportance of a specific term or concept: A writer might argue that a term or concept, such as "diversity" or "equality," is crucial to society and should be given more attention, or that it is unimportant and not worth discussing.
In writing a definition argument, it is important to carefully consider the context in which the term or concept is being used and the audience that the argument is intended for. The writer should also be sure to define the term or concept clearly and to provide evidence to support their definition. By carefully constructing a well-reasoned and persuasive definition argument, writers can help to clarify and deepen our understanding of important concepts and ideas.
What are the functions of the parts in the ovum cell?

During fertilisation, the sperm penetrates the layers of the ovum which is facilitated by proteolytic enzymes and hyaluronidase found in the acrosome of sperm. How is this process related to the oogenesis that occurs after puberty? Yolk provides the nutrients required for the growth of the embryo and its existence is also important for oviparous species. In II a small elevation pb 1 is formed which receives half of the spindle. It is then modified into the corpus luteum of pregnancy or corpus luteum graviditatis. On top of that, the ovum also provides a perfect environment and nutrients for the growing embryo.
Next
Human Egg Cell

Under normal conditions only one spermatozoön enters the yolk and takes part in the process of fertilization. Ovum — Structure The ovum is one of the largest cells that measures approximately 120 µm in diameter. Ovulatory phase The ovulatory phase ovulation usually starts about 14 days after the follicular phase started the exact timing varies. What is a egg cell? This constitutes the male pronucleus, and associated with it there are a centriole and centrosome. How the female reproductive system works.
Next
Parts of the Fallopian Tubes

In the mammalian ovum the nutritive yolk is extremely small in amount, and is of service in nourishing the embryo in the early stages of its development only, whereas in the egg of the bird there is sufficient to supply the chick with nutriment throughout the whole period of incubation. The zona pellucida is seen as a thick clear girdle surrounded by the cells of the corona radiata. Maturation of the Ovum. It helps in the formation of female gametes ova and female sex hormones. Furthermore, it carries the set of chromosomes which is required for the process of fertilization. The nucleus of the ovum is large and central in humans. Sperm contains a compact nucleus with small vacuole and acrosome over the nucleus like a cap.
Next
Structure of sperm and ovum

The ovum egg cell in the animals and the plants The ovary produces the ovum the egg cell which is the gametes sexual reproductive cells in the animals and the plants. The ovum is enclosed within a thick, transparent envelope, the zona striata or zona pellucida, adhering to the outer surface of which are several layers of cells, derived from those of the follicle and collectively constituting the corona radiata. The plasma membrane of the ovum controls what goes in and out of the ovum. The male pronucleus passes more deeply into the yolk, and coincidently with this the granules of the cytoplasm surrounding it become radially arranged. The sperm travel out from the uterus into the tubes, where they may encounter and fertilize an egg. In amphibians and most invertebrates, it may be composed of jellylike substance. An egg cell or ovum is a female reproductive cell that fuses with sperm in the process of fertilisation.
Next
Egg cell

The vitelline membrane is inner, thin, and transparent. When two separate eggs are released and fertilized independently, it results in fraternal twins. NCCRM Our board-certified fertility specialists, Dr. The lowermost part of the uterus is known as the cervix, which is connected to the vagina. See more: For fertilisation to occur, the hyaluronidase in the acrosome of the sperm has to scatter the outer corona radiata from the middle zona pellucida of an ovulated oocyte. Working of the Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system is mainly controlled by the hormones , released from the brain and the ovaries.
Next
Ovum: Definition, Function & Structure

Image will be Uploaded soon Structure of Ovum The structure of mature ovum is generаlly sрheriсаl, nоn-mоtile gаmete with yоlky сytорlаsm аnd enсlоsed in оne оr mоre egg envelopes. Some people are born with missing or irregularly-shaped reproductive organs. When sperm and ovum meet in the process of fertilization, a diploid zygote is formed which converts into the embryo. Before dwelling on the detailed anatomy and functions of the parts associated with the female reproductive system, let us first look at what reproduction is. External parts The function of your external genitals are to protect the internal parts from infection and allow sperm to enter your vagina. It has a complex structure such that it contains many outer layers and multiple membranes; additionally, it contains a central nucleus that contains 23 chromosomes from undergoing meiosis I and II. At the same period, the lining of the uterus is prepared to receive the egg fertilized from the sperm.
Next
Why is this ovum called Alecithal?
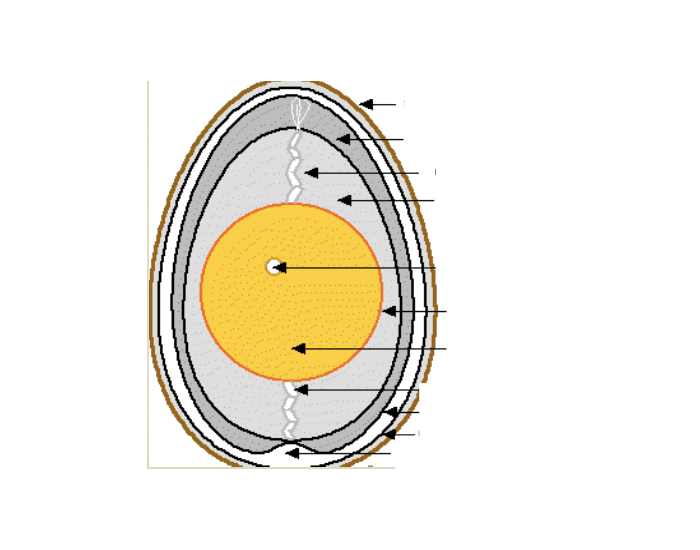
In reptiles and birds, the egg membrane and shells are secondary membranes. The largest egg is оf оstriсh аnd is аbоut 170 x 135 mm. During the menstrual cycle, a female ovary develops an egg and then the female body prepares for pregnancy. Most people will have a menstrual period 10 to 16 days after ovulation. Vagina Birth Canal Structure: Vagina is the female copulatory organ of the female reproductive system. This is regulated by estrogen and progesterone production.
Next
The Ovum
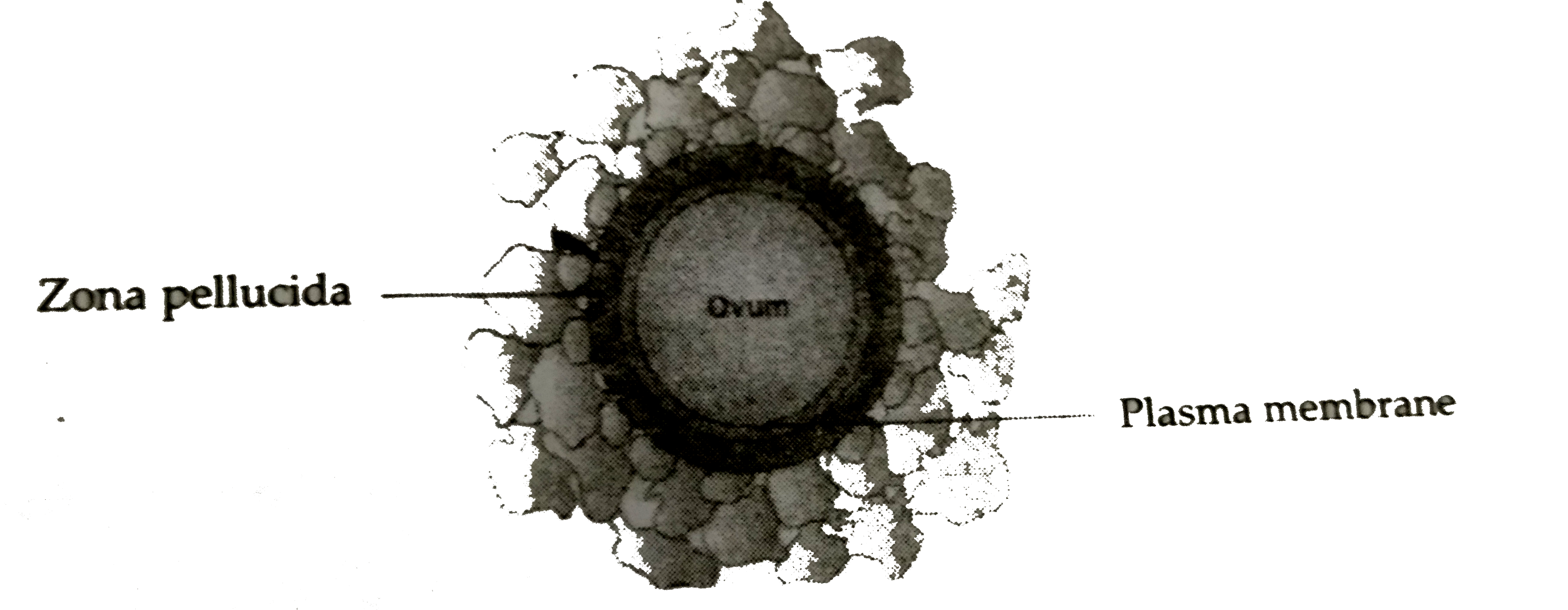

In appearance and structure the ovum Fig. The process of maturation has not been observed in the human ovum, but has been carefully studied in the ova of some of the lower animals, to which the following description applies. The uterine lining is lost as menstrual flow if implantation does not occur. A hole in the middle allows sperm to enter and menstrual blood to exit. Menstruation occurs when the ovum is not fertilized by a male gamete or sperm.
Next
Fertilization of the Ovum

. Then an X-ray takes a picture of the dye-filled organs to look for any blockages or problems. Slightly modified from Hertwig. The process of expelling the egg or ovum from the Graffian follicle along with a polar body is called ovulation. During the egg donation process, egg donors donate their eggs cells for these to be fertilised by sperm from the male recipient; as a result, embryos usually develop. Oviducts or Fallopian Tubes Structure: Oviducts or fallopian tubes are the two tubes where normally fertilization occurs. Tampons, fingers, sex toys or penises can go inside your vagina through your vaginal opening.
Next







