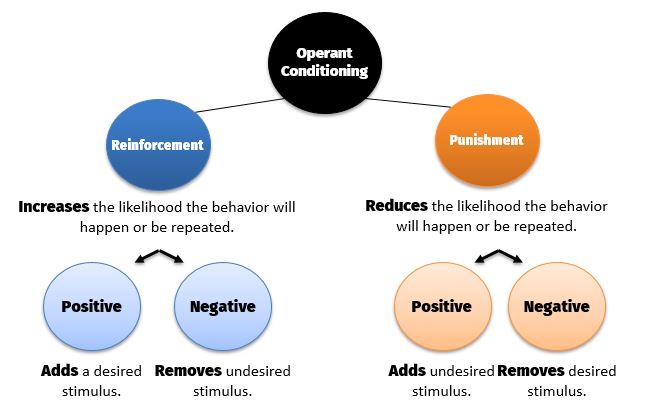
Operant conditioning is a type of learning that occurs when an animal or human learns to associate a particular behavior with a particular consequence. This type of learning was first described by psychologist B.F. Skinner in the 1930s, and it has since become an important area of study within the field of psychology.
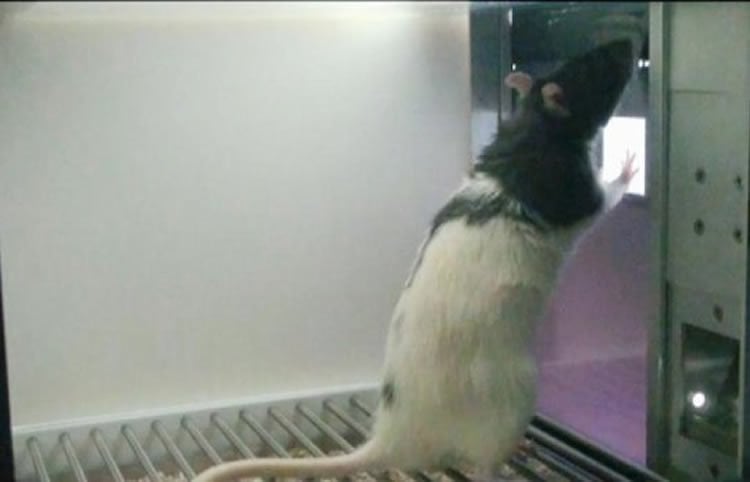
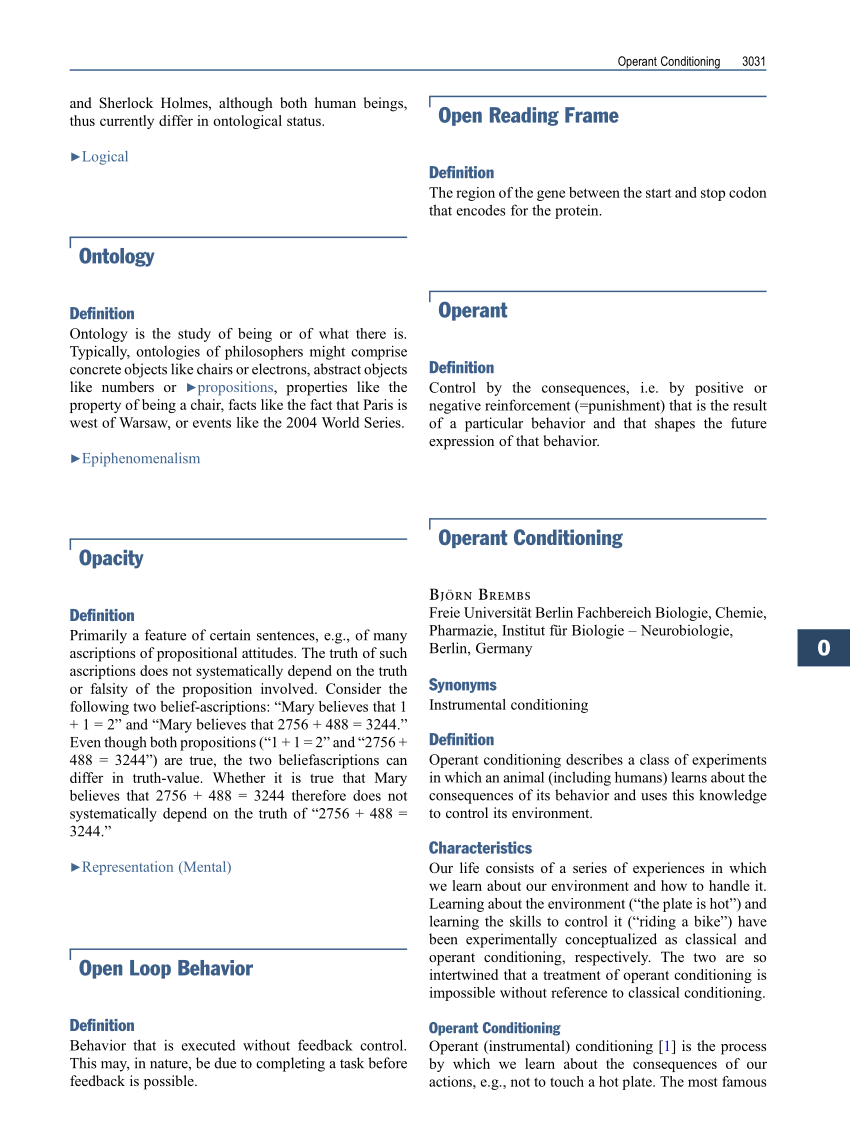
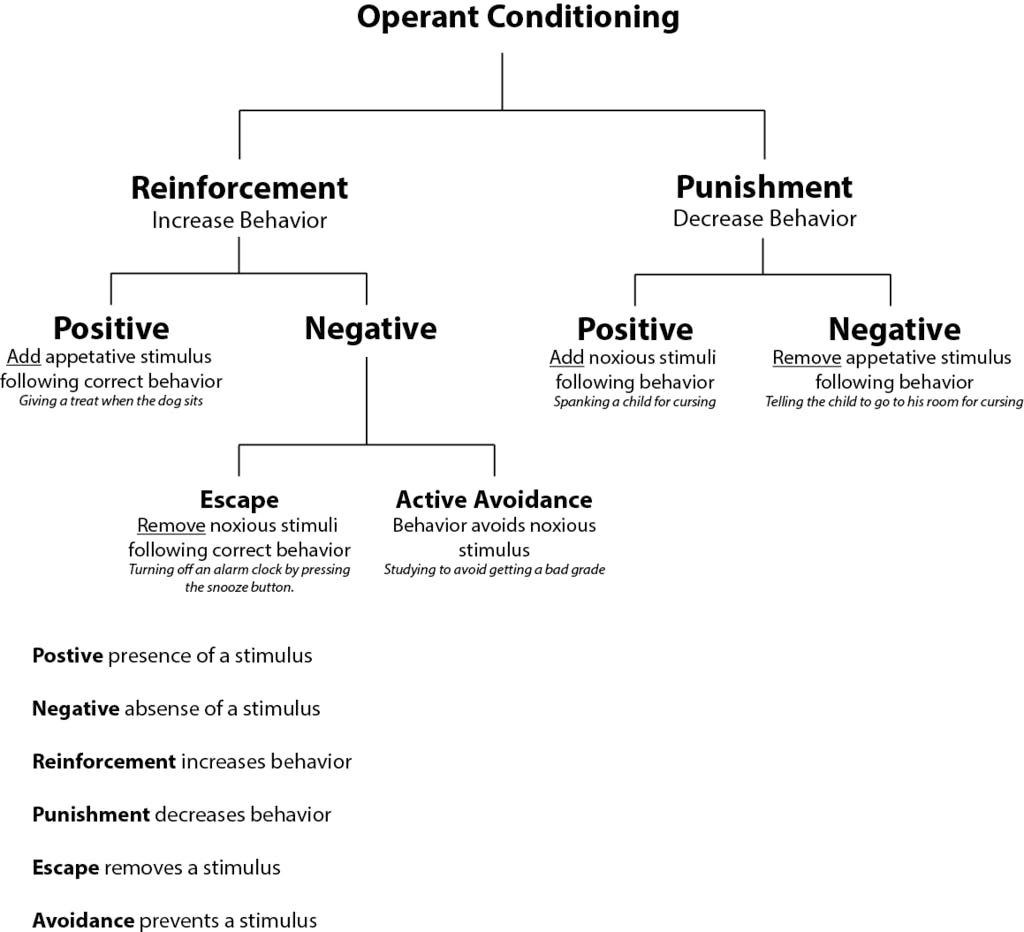
In operant conditioning, an animal or human learns to associate a particular behavior with a particular consequence, such as receiving a reward or punishment. For example, if a rat receives a food pellet every time it presses a lever, it will eventually learn to press the lever more often in order to obtain the reward. Similarly, if a child is scolded every time they misbehave, they may learn to avoid misbehaving in order to avoid the punishment.
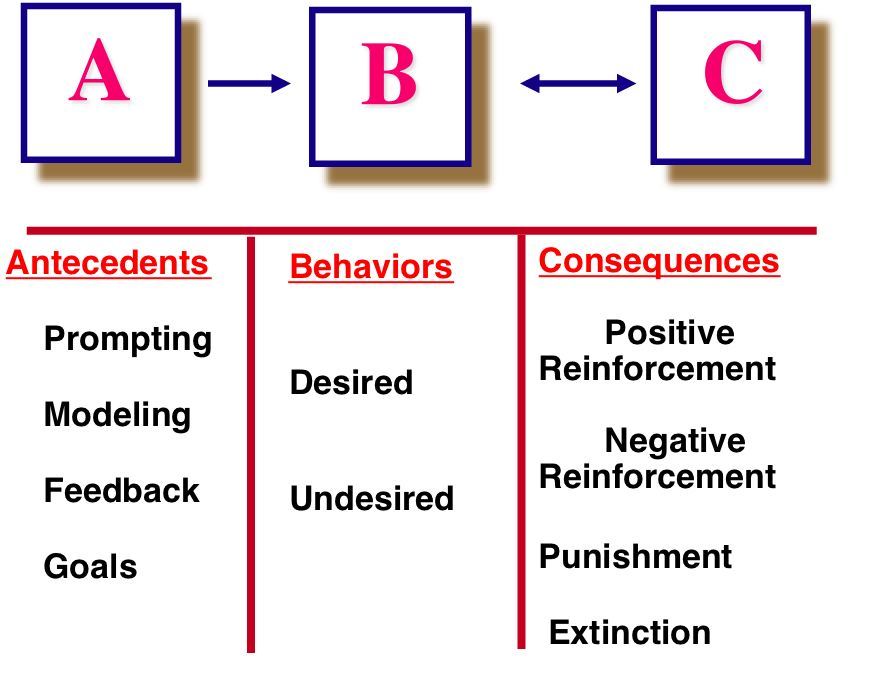
One of the key features of operant conditioning is that it involves the use of reinforcement, which is a technique used to increase the likelihood that a particular behavior will be repeated. There are two main types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, which involves the addition of a desirable consequence following a behavior, and negative reinforcement, which involves the removal of an undesirable consequence following a behavior.
One of the most well-known examples of operant conditioning is the use of a Skinner box, which is a laboratory apparatus used to study the principles of operant conditioning in animals. The box contains a lever that the animal can press, and pressing the lever is reinforced with a food pellet or other reward. By studying the animal's behavior in the Skinner box, researchers can learn about how operant conditioning works and how it can be used to shape animal behavior.
There are many practical applications of operant conditioning research, including the use of reinforcement to train animals for specific tasks, such as assistance dogs for people with disabilities. Operant conditioning has also been used to study human behavior, such as how people learn to perform new tasks or how they develop habits.
In conclusion, operant conditioning is an important area of study within psychology that involves the association of a particular behavior with a particular consequence. It has many practical applications, including the training of animals for specific tasks and the study of human behavior. Understanding operant conditioning can help us to better understand how we learn and how we can shape our own behaviors.