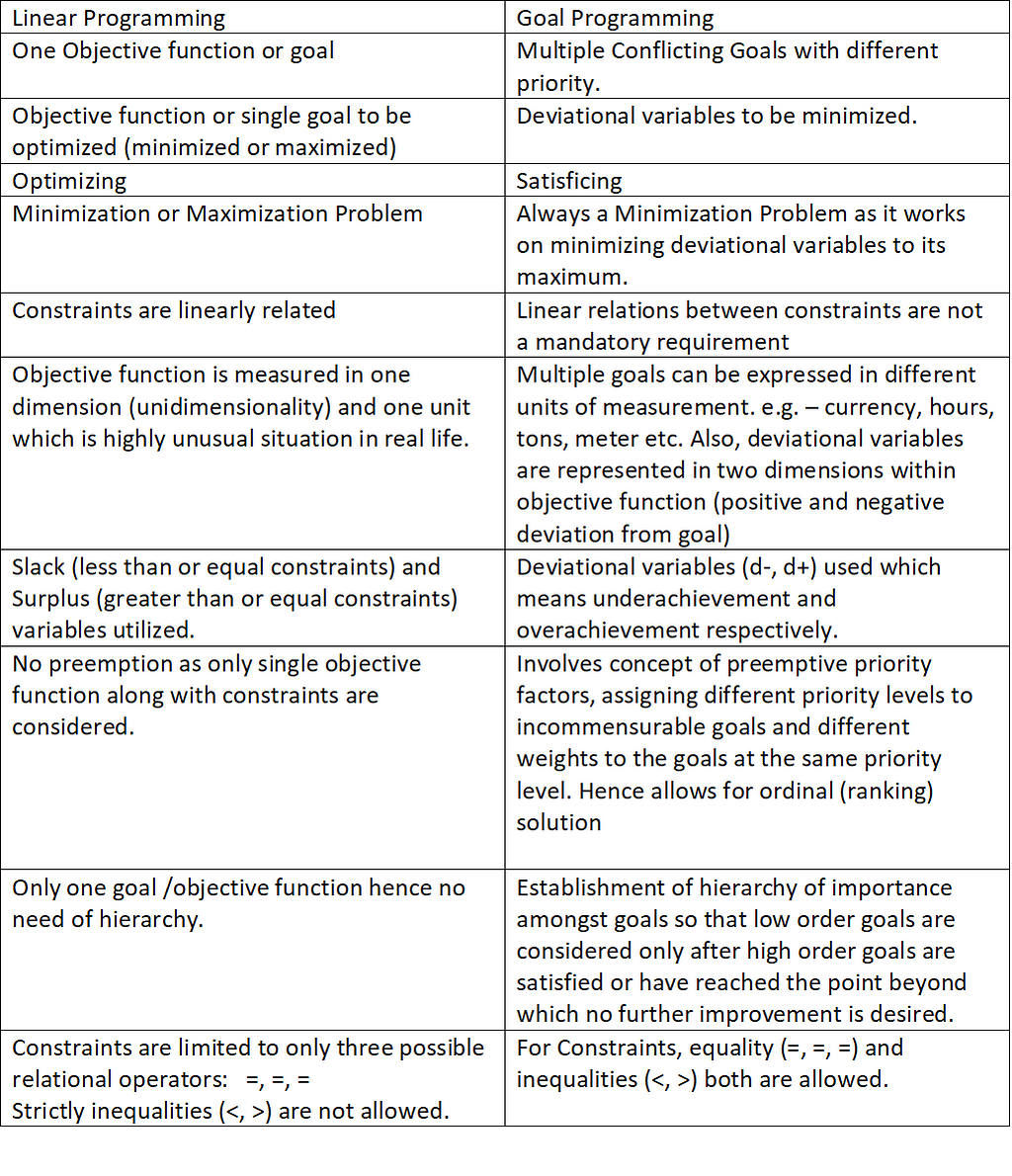
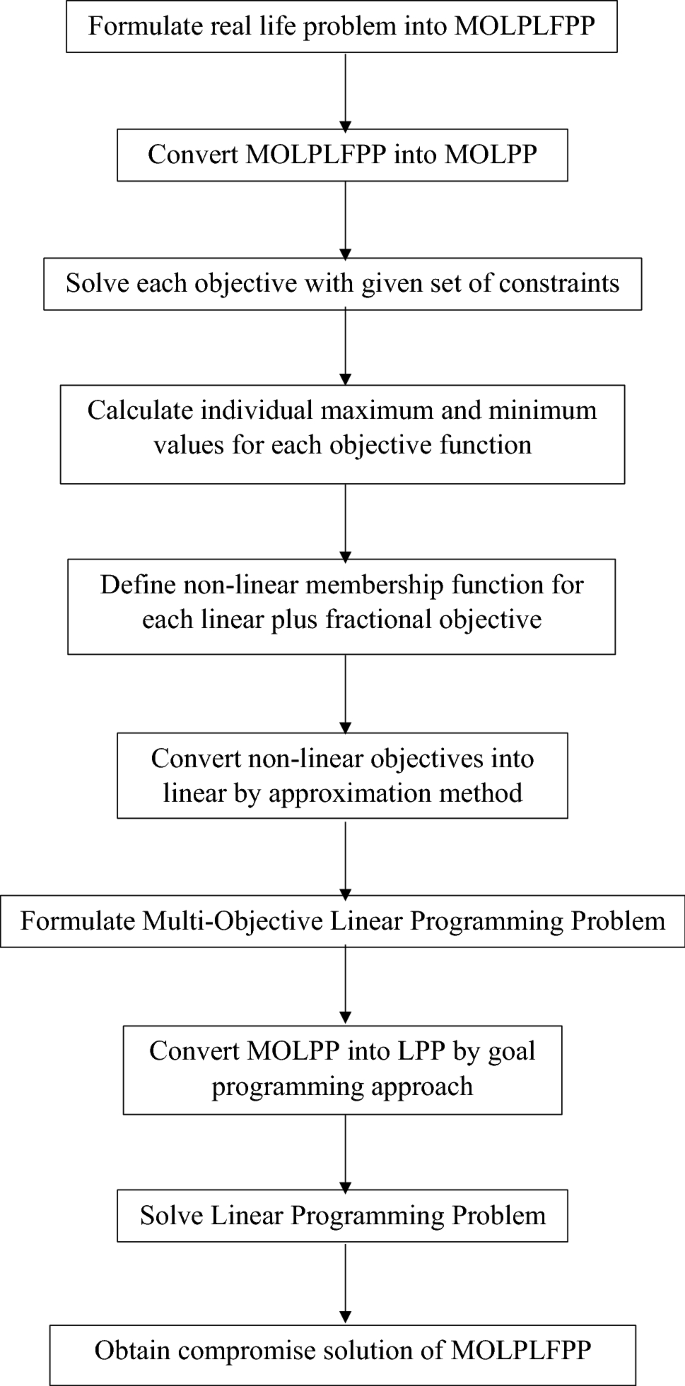
Linear programming is a mathematical optimization technique that is used to find the optimal solution to a problem involving linear constraints and an objective function. The primary objective of linear programming is to maximize or minimize the value of the objective function, subject to a set of constraints.
One of the main objectives of linear programming is to find the most efficient allocation of resources. For example, a company may want to maximize its profits by producing and selling various products. However, there may be limitations on the availability of resources such as raw materials, labor, and equipment. Linear programming can be used to determine the optimal combination of products to produce, given these resource constraints, in order to maximize profits.
Another objective of linear programming is to find the optimal solution to a problem involving multiple conflicting objectives. For example, a transportation company may want to minimize costs while maximizing customer satisfaction. Linear programming can be used to find the optimal routes and schedules for the company's vehicles that meet both of these objectives.
In addition to maximizing profits and minimizing costs, linear programming can be used to achieve other objectives such as minimizing waste or reducing environmental impacts. For example, a company may want to minimize the amount of waste produced in its manufacturing process in order to reduce its environmental footprint. Linear programming can be used to determine the most efficient use of resources in order to minimize waste.
Overall, the main objective of linear programming is to find the optimal solution to a problem involving linear constraints and an objective function. This can be used to maximize profits, minimize costs, or achieve other objectives such as minimizing waste or reducing environmental impacts.
Learning Objectives
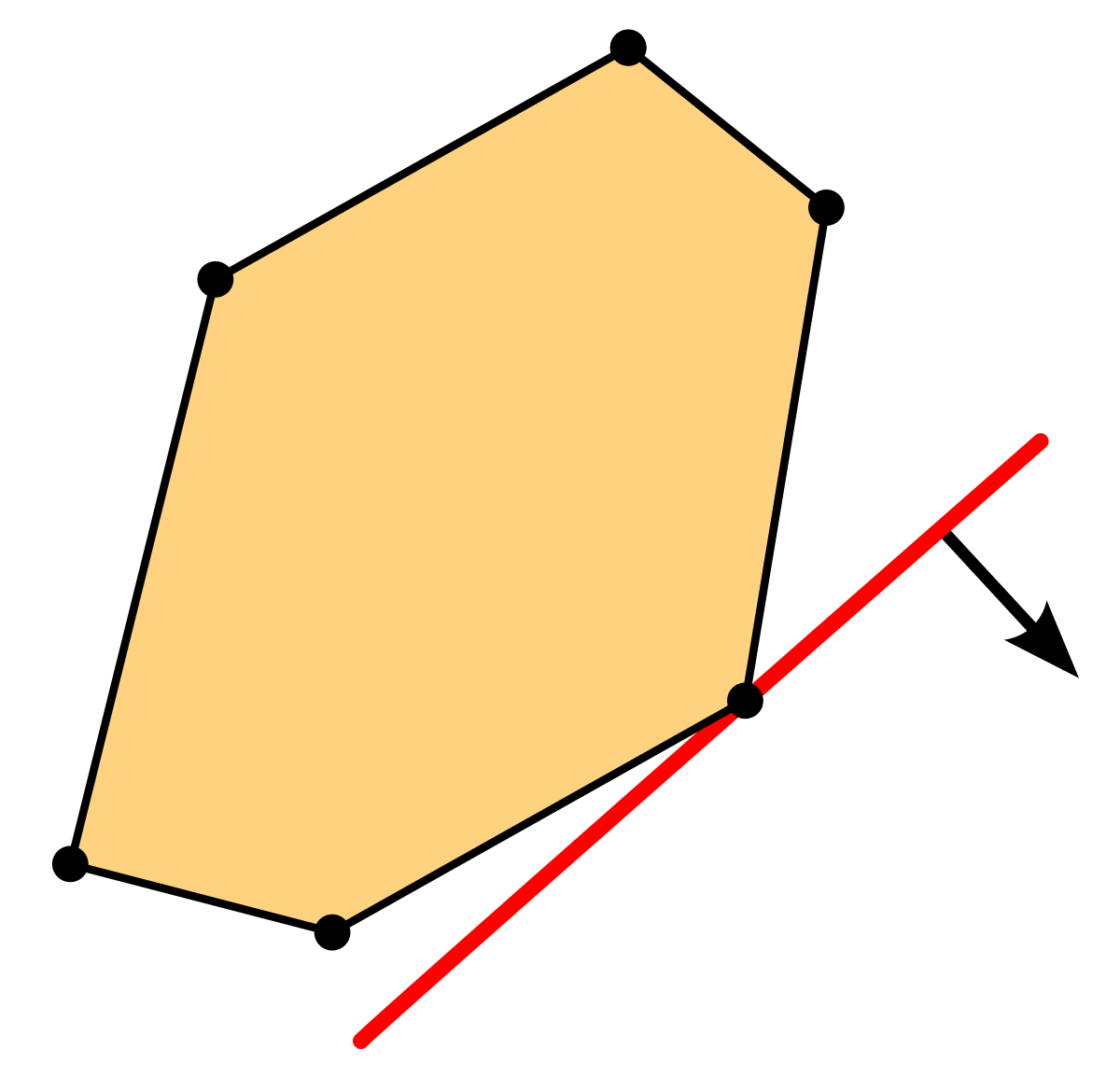
If the problem has two decision variables, a graphical method is the best method to find the optimal solution. The optimal value for an objective will often be in a corner of this feasible region, as this will be the maximal or minimal feasible value for the objective. A fan costs him Rs. It is part of a vital area of mathematics known as optimisation techniques. One must admit, though, that there are obvious traces of GP and LP in MOLP. Linear Programming In Mathematics, linear programming is a method of optimising operations with some constraints. Linear programming has been applied in a variety of industries to address a variety of problems.
What is linear programming?

Typically, the goal of linear programming is to maximize or minimize specified objectives, such as profit or cost. Variables are numerical or Boolean values, such as quantity of product to be produced or whether a distribution center is open. Both products require one day for quality assurance. According to the existing definition, goal programming can be viewed as a modification of linear programming, which provides the environment for accomplishing more complex goals and taking care of more processes than LP does. The objective in resource allo- cation may be either cost minimization or profit maximization.
What is the objective function in linear programming?

In the CompCorp problem, we wish to maximize the profit, P P P. To begin solving the problem, let us restate the information in mathematical form. Linear Programing Linear programing is a mathematical process that has been developed to help management in decision-making and it has become one of the most widely used and best known tools of management science. This technique has been useful for guiding quantitative decisions in business planning, in industrial engineering, and—to a lesser extent—in the social and physical sciences. It usually involves a system of linear inequalities, called constraints , but in the end, we want to either maximize something like profit or minimize something like cost. Mostly it is done by breading the graph, but a point can be identified by solving simultaneous equation relating to two lines which intersect to form a point on graph. Â Let us see an example here and understand the concept of linear programming in a better way.
Linear webapi.bu.edu

What is linear programming explain with an example? There should be means to detect such sets and not to solve them at all. Also known as the GP-OBS model, the above-mentioned approach towards setting goals and implementing them incorporates the use of graphical methods and involves complex mathematic calculations. It relies upon three different concepts: variables, objectives, and constraints. For our immediate purpose, linear programming can be defined as a method to allocate limited resources to competing activities in an optimal manner. Define each decision variable. Needless to say, shortly after being introduced into the realm of management, LP wore out its welcome. In this article, let us discuss the definition of linear programming, its components, and different methods to solve linear programming problems.