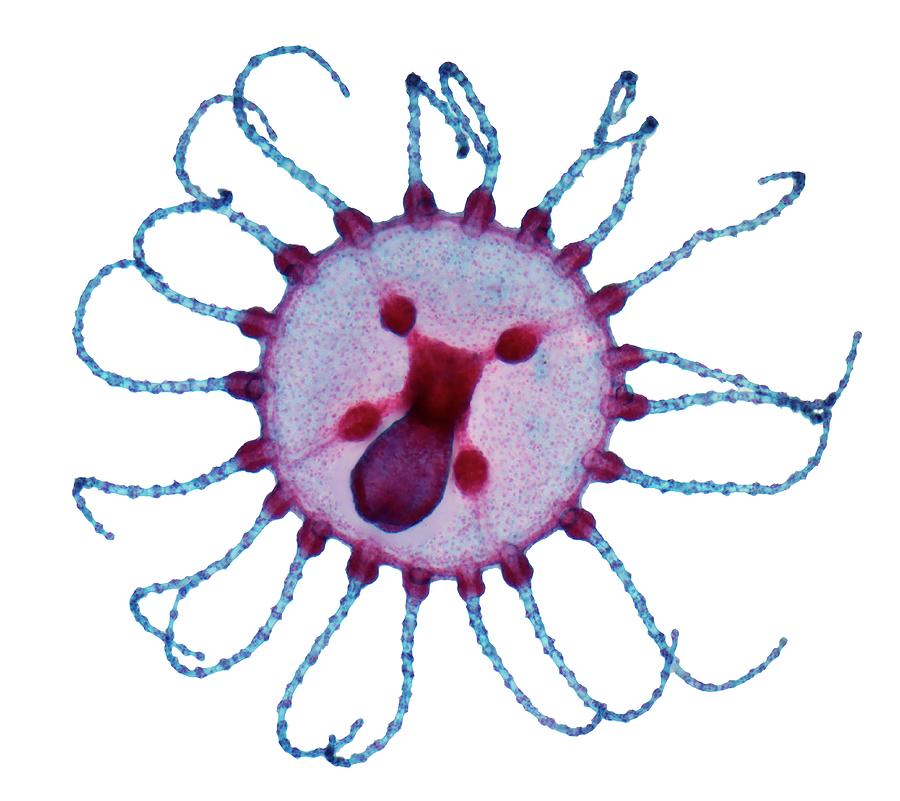
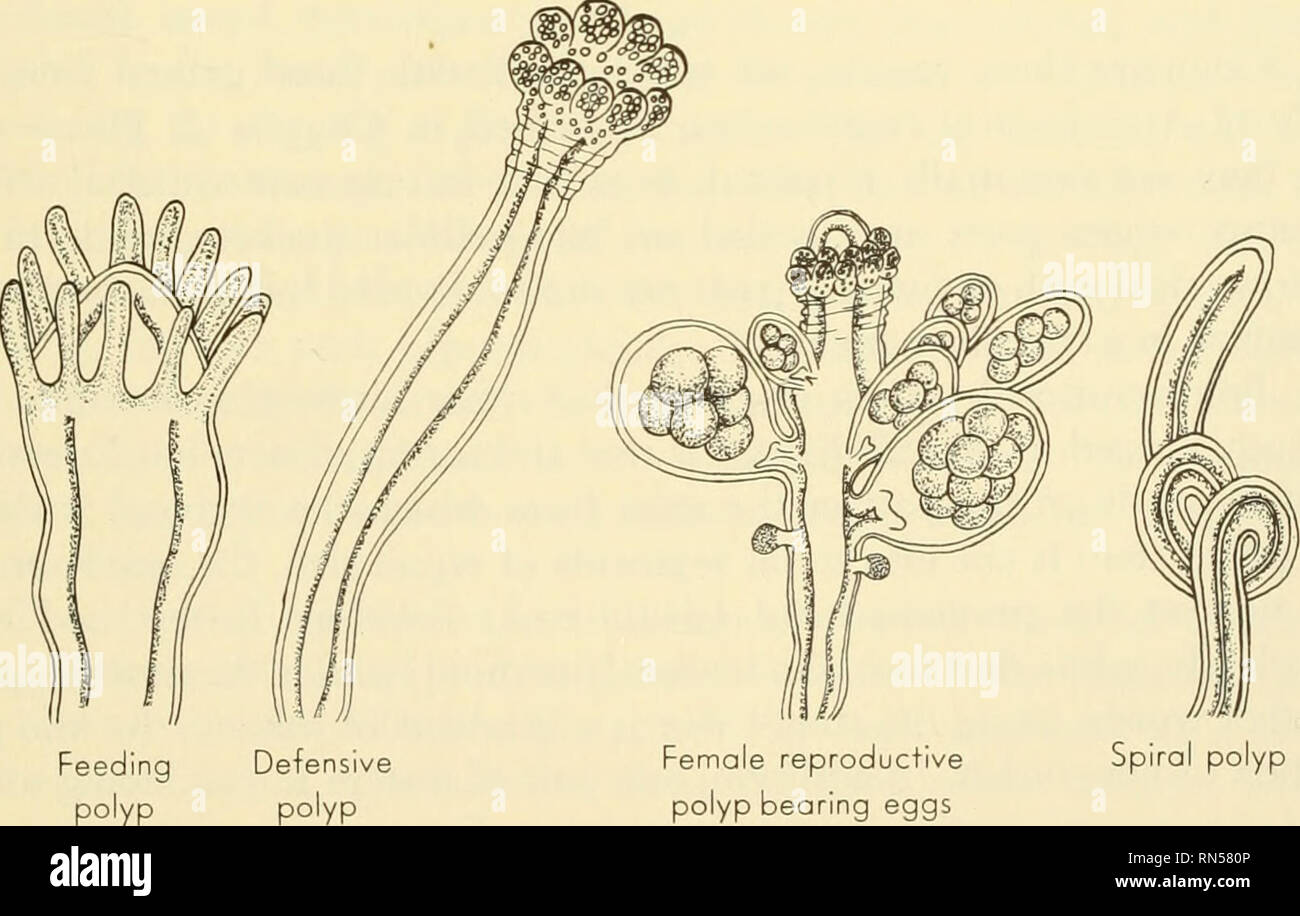
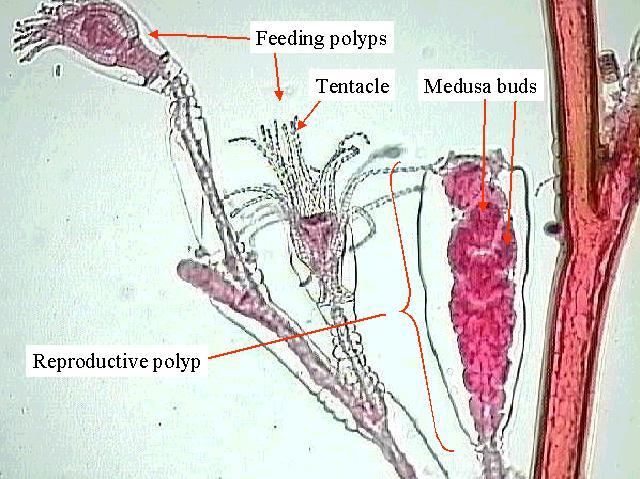
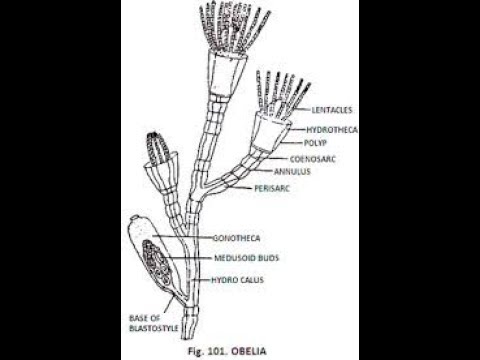
Obelia is a colonial hydroid that belongs to the family of Hydrozoa. It is a small, tube-like structure that is found in both freshwater and marine environments. The Obelia colony is made up of numerous tiny polyps, which are interconnected to form a branching structure. Each polyp is responsible for carrying out specific functions within the colony.
Obelia colonies can be found in a variety of habitats, including coral reefs, rocky shores, and kelp forests. They are commonly found in shallow waters and are known to attach themselves to rocks, shells, and other hard surfaces. Obelia colonies can range in size from a few centimeters to several meters, depending on the species and the habitat in which it is found.
The Obelia colony is made up of both sexual and asexual polyps. Asexual polyps are responsible for reproducing and building the colony, while sexual polyps produce eggs and sperm. The eggs and sperm are released into the water, where they fuse to form a new Obelia colony.
Obelia colonies play a vital role in the marine ecosystem. They provide a habitat for a variety of small organisms, such as algae and small invertebrates. They also serve as a source of food for larger animals, including fish and birds.
Despite their importance in the ecosystem, Obelia colonies are facing numerous threats. Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change are all factors that can negatively impact the survival of Obelia colonies.
In conclusion, the Obelia colony is a fascinating and important part of the marine ecosystem. It is made up of numerous interconnected polyps that carry out various functions within the colony. Obelia colonies provide a habitat for small organisms and serve as a source of food for larger animals. However, they are facing numerous threats, including pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. It is important that we work to protect and preserve Obelia colonies for the benefit of the ecosystem and future generations.