Neoclassical unemployment. Analyse The Neoclassical Concept Of Unemployment Economics Essay Essay Example 🎓 2022-10-12
Neoclassical unemployment
Rating:
6,7/10
413
reviews
Neoclassical unemployment, also known as structural unemployment, refers to a type of unemployment that occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills and characteristics of the unemployed workers and the requirements of the available job openings. This type of unemployment is not caused by a lack of overall demand for goods and services in the economy, but rather by a specific mismatch between the supply and demand of labor.
One of the main causes of neoclassical unemployment is technological change, which can lead to the obsolescence of certain skills and the demand for new ones. For example, the widespread adoption of computers and automation in the manufacturing sector has led to a decrease in the demand for workers with certain manual skills, while increasing the demand for workers with computer and technical skills. This shift in the demand for labor can lead to unemployment for workers who do not have the necessary skills to fill the available job openings.
Another cause of neoclassical unemployment is globalization, which can lead to the offshoring of jobs to countries with lower labor costs. This can result in unemployment for workers in the affected industries, as they may not have the skills or experience needed to compete with workers in other countries.
Government policies can also contribute to neoclassical unemployment. For example, strict labor regulations and high minimum wages can make it more difficult for businesses to hire workers, leading to unemployment for those who are unable to find jobs. Similarly, generous unemployment benefits can discourage workers from actively seeking employment, leading to a persistent state of unemployment.
To address neoclassical unemployment, policy makers can focus on providing education and training programs to help workers acquire the skills needed to fill the available job openings. They can also consider policies that make it easier for businesses to hire workers, such as reducing labor regulations and minimum wages.
In conclusion, neoclassical unemployment is a type of unemployment caused by a mismatch between the supply and demand of labor, rather than a lack of overall demand in the economy. It can be caused by technological change, globalization, and government policies, and can be addressed through education and training programs and policies that make it easier for businesses to hire workers.
Neoclassical Theory Of Unemployment

Instead, neoclassical economists believe that aggregate demand should be allowed to expand only to match the gradual shifts of aggregate supply to the right—keeping the price level much the same and inflationary pressures low. Abstract The last three recessions in the United States were followed by jobless recoveries: while labor productivity recovered, unemployment remained high. Physical capital per person refers to the amount and kind of machinery and equipment available to help people get work done. Second, neoclassical economists would predict price increases as firms sought to regain back their profits after paying workers a higher wage price effects. People allocate their incomes to maximize their levels of utility. By 1990, the economy recovered back to 4% unemployment, but at a lower inflation rate of 1%.
Next
Neoclassical Economics: What It Is and Why It's Important

Your graph will appear similar to Figure 2. Linking the level of wages to unemployment cannot by itself explain the maintenance of high levels of unemployment. Moreover, seemingly small disruptions in the supplies of primary commodities such as energy could be the source of fluctuations in aggregate employment and can exert surprisingly large effects on real output. This growth has fallen below its potential GDP and, at times, has exceeded its potential. This high demand for labor will drive up wages. The theory of negotiations Calmfors and Driffill 1988:16-61 is an effort of the modern neoclassical approach to explain why the labor market is not competitive and to understand the development of trade unions and collective bargaining in the developed capitalist countries.
Next
A Neoclassical Model of Unemployment and the Business Cycle

After all, neoclassical economists argue, it takes government statisticians months to produce even preliminary estimates of GDP so that politicians know whether a recession is occurring—and those preliminary estimates may be revised substantially later. Therefore, the decrease of the unemployment rate will come chiefly from the strengthening of effectual demand and non by cut downing rewards. The traditional neoclassical approach attempts to interpret unemployment as a phenomenon that is not related to development itself, but to external factors which it considers as a pre-given. In turn, the public may expect expansionary monetary policy, and lower interest rates, in the short run. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics BLS , the current unemployment rate is at 5. It believes that unemployment is due either to failure to reduce salaries or to the existence of imperfections in the labor market. As the macroeconomic equilibrium rises from E 0 to E 1 to E 2, the price level rises, but real GDP does not budge; nor does the rate of unemployment, which adjusts to its natural rate.
Next
Neoclassical Economics

The human capital of modern workers is far higher today because the education and skills of workers have risen dramatically. Overdependence on its mathematical approaches Neoclassical economics is criticized for its over-dependence on its mathematical approaches. Classical unemployment is one of the main types of unemployment. While a lower price level i. Therefore, the neoclassical attack to cut down unemployment leads to a dead end, since it regards unemployment as a secondary job, which itself does non necessitate systematic province intercession. In 2014, 40% of working-age Americans had a four-year college degree. Arestsis, P and Skott, P 1995 Conflict, wage relativities and hysterisis in the UK wage determination, Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, pp: 43.
Next
Analyse The Neoclassical Concept Of Unemployment Economics Essay

Suppose a decrease in aggregate demand causes the economy to go into recession with high unemployment. The study provides empirical evidence of human behaviors in an economy. After all, there will always be workers who are unemployed while looking for a job that is a better match for their skills. While others such as Evan and Macpherson, 2017 have starker findings : their model estimated that for each 10% increase in the California minimum wage, their findings implied that would reduce employment for all employees by 2%. Other theories, like adaptive expectations, suggest that adjustment to the neoclassical outcome takes a few years. Different from neoclassical approach argue that a change in price and quantity affect the economy relatively low, the Keynes macroeconomic approach states that price shifts are nominal thus bears some effects with the exclusion of price Screpanti, and Zamagni, 2005.
Next
Analyse The Neoclassical Concept Of Unemployment Economics Essay
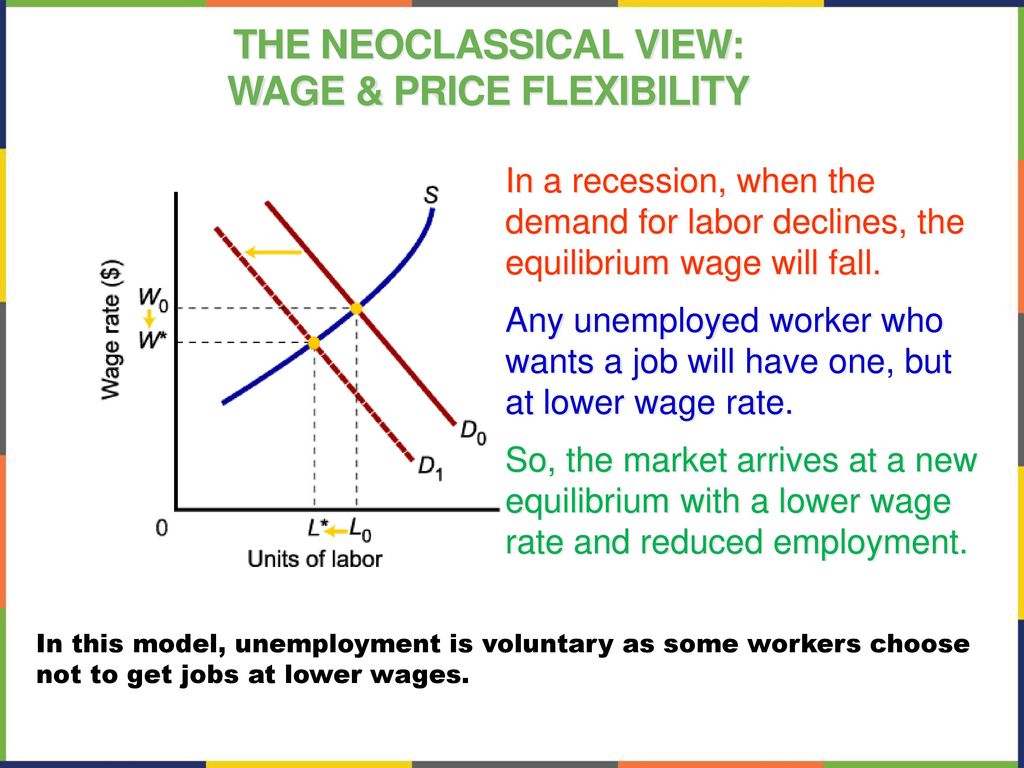
Industrial relations does not mean only the legal side of employment, as the neoclassical theory understands it, but a network of institutions that govern both the production and the reproduction process. An alternative approach to the duality in the labor market is the theory of Insiders — Outsiders Lindbeck and Snower, 1989. The eighties: the search for alternatives to fordism, Cepremap, No 8909, pp:55. Then in 2000, both unemployment and inflation increased to 5% and 4%, respectively. The term flexibility refers to the two main aspects of the organization of production. The United States experienced significant growth in the twentieth century due to phenomenal changes in infrastructure, equipment, and technological improvements in physical capital and human capital. As you can see the supply for labour outstrips the demand for it.
Next
Minimum Wage and Unemployment: Is it time to break up with Neoclassical Economics?

The technology available to modern workers is extraordinarily better than a century ago: cars, airplanes, electrical machinery, smartphones, computers, chemical and biological advances, materials science, health care—the list of technological advances could run on and on. When the Congressional Budget Office carried out its long-range economic forecasts in 2010, it assumed that from 2015 to 2020, after the recession has passed, the unemployment rate would be 5. It uses the methodological tools of microeconomic theory to analyse the labour market, i. One important side effect is that may be buried Involuntary Unemployment And Its Effects On The Economy Contrary to what some economists believe, involuntary unemployment is a very real and continuous presence in the economy, both past and present. The Keynesian attack, sing that the labour market is imperfect by nature, it considers that the employment policy is a consequence of this evident failure of the market to run.
Next
Analyse The Neoclassical Concept Of Unemployment Economics Essay Essay Example 🎓

According to neoclassical theory, the employment policy has to face the imperfections in the labor market. The concept of labor market flexibility, as used by the neoclassical theory, Bentolia and Saint-Paul 1992:1013-1053, Emerson 1988:775-817 , is not suitable for a scientific analysis of today ongoing changes. First, it refers to the grade of version of the production construction, which becomes possible due to the new signifiers of mechanization and secondly it refers to the grade of internal and external mobility, from undertaking to undertaking, both in footings of specialisation and in footings of workplace conditions Arestis 1986:84. Neoclassical economists argue that the long-run aggregate supply curve is located at potential GDP—that is, the long-run aggregate supply curve is a vertical line drawn at the level of potential GDP, as shown in Figure 2. The Impact of a Recession In the previous example we looked how an economy naturally slows down when it exceeds its potential GDP. The technology available to modern workers is extraordinarily better than a century ago: cars, airplanes, electrical machinery, smartphones, computers, chemical and biological advances, materials science, health care—the list of technological advances could run on and on. Thus, in neoclassical economics, the value of In terms of their approaches, the study of classical economics is more empirical.
Next







