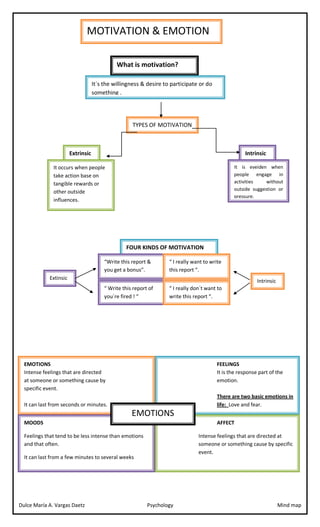
Motivation and emotion are two closely related psychological concepts. Motivation refers to the forces that drive us to do things and the factors that influence our choices, behaviors, and actions. It is the reason behind why we do what we do and the factors that influence us to make certain decisions. Emotion, on the other hand, refers to the feelings and experiences that we have in response to certain stimuli or events.
Motivation can be intrinsic or extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation refers to the desire to do something for its own sake, because it is personally meaningful or fulfilling. This type of motivation comes from within and is often driven by our values, interests, and passions. Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, refers to the desire to do something for a reward or to avoid punishment. This type of motivation comes from outside sources, such as rewards, recognition, grades, or praise.
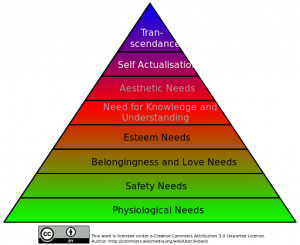
There are many different theories of motivation, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, self-determination theory, and Self-perception theory. Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that we have a set of basic needs that must be met in order for us to feel motivated, such as physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. Self-determination theory suggests that we are motivated by the desire to feel competent, autonomous, and related to others. Self-perception theory proposes that we infer our own motivations by observing our own behaviors and the situations in which they occur.
Emotion is a complex psychological experience that is characterized by a range of physiological arousal, expressive behaviors, and conscious experiences. There are many different emotions that we can experience, including happiness, sadness, anger, fear, love, and disgust. Emotions play a crucial role in our lives, as they help us to navigate and respond to the world around us.
There are many different theories of emotion, including the James-Lange theory, the Cannon-Bard theory, and the Schachter-Singer theory. The James-Lange theory proposes that our emotions are the result of physiological arousal and that we experience different emotions based on the specific pattern of arousal that we experience. The Cannon-Bard theory suggests that emotions and physiological arousal occur simultaneously and that they are not necessarily linked. The Schachter-Singer theory proposes that our emotions are the result of both physiological arousal and cognitive interpretation.
In conclusion, motivation and emotion are two important psychological concepts that influence our behavior and decision-making. Motivation is the driving force behind why we do what we do, while emotion is the experience of feeling in response to certain stimuli or events. Understanding these concepts can help us to better understand ourselves and the world around us, and can also help us to make more informed and meaningful choices in our lives.
(114).jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/theories-of-emotion-2795717-FINAL-2081b006dfd546209d32b1dfc69958d5.png)