Monopolistic competition equilibrium. The Price 2022-11-02
Monopolistic competition equilibrium
Rating:
8,8/10
640
reviews
Gran Torino is a film directed by Clint Eastwood that was released in 2008. The film tells the story of Walt Kowalski, an elderly Korean War veteran living in a rapidly changing neighborhood in Detroit. Kowalski is a gruff and isolated man, who is struggling to come to terms with the death of his wife and the changes in his neighborhood.
One of the main themes in Gran Torino is the concept of racism and prejudice. Kowalski is a racist man who has a deep hatred for the Hmong people who have recently moved into his neighborhood. He makes derogatory comments about them and refers to them as "gooks." However, as the film progresses, Kowalski begins to form a relationship with Thao, a young Hmong boy who lives next door. Through this relationship, Kowalski begins to see the Hmong people in a different light and starts to understand the impact of his own prejudices.
Another important theme in the film is the concept of redemption. Kowalski is a bitter and angry man who has lost touch with his family and the world around him. However, through his relationship with Thao and the Hmong community, Kowalski begins to see the value in compassion and understanding. He comes to realize that he has been holding onto his anger and hatred for far too long and that it is time for him to let go.
One of the most poignant moments in the film is when Kowalski makes the decision to stand up to a group of Hmong gang members who are trying to force Thao to join their gang. Kowalski puts himself in harm's way to protect Thao and the Hmong community, showing that he has truly changed and is willing to put aside his own prejudices to do what is right.
Overall, Gran Torino is a powerful film that deals with themes of racism, prejudice, and redemption. It is a poignant reminder that it is never too late to change and that understanding and compassion can go a long way in healing the wounds of the past.
Monopolistic Competition
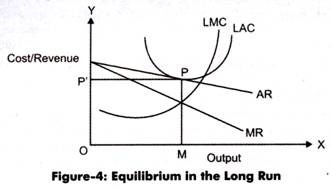
Solved Question on Monopolistic Competition Q1. Thus, since each firm gets some proportional share of the total market demand for the general class of the product, the proportional demand for each firm varies with the number of firms in the product group. The result will be that some firms will leave the group and the proportional demand curve along with perceived demand curve will shift to the right. So, we can conclude that monopolistically competitive output OP M is less than the perfectly competitive output OQ P , and monopolistically competitive price OP M is larger than competitive price OP P. But a firm under monopolistic competition, as is evident from Fig.
Next
Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition
Therefore, it faces a downward sloping demand curve. Production at a higher cost implies wastage of resources or underutilization of resources. They could also help explaining the cyclical behaviour of prices. However, the demand curve will have shifted to the left due to other companies entering the market. Thus E is the equilibrium point. ADVERTISEMENTS: Therefore, the equilibrium adjustment of an individual firm cannot be defined in isolation from the general field of which it is a part However, for the sake of simplicity in analysis, conditions regarding the availability of substitute products produced by the rival firms and prices charged for them are held constant while the equilibrium adjustment of an individual firm is considered in isolation. The best definition is a group of firms who sell products which are close substitutes of each other.
Next
The Price

They also include informative and educative campaigns where the buyer is informed about the benefits of using their product over something else. We have shown this adjustment to reach long-run equilibrium in Fig. As a result of these heterogeneous conditions surrounding each firm, there will be differences in prices, in outputs scales of production and profits of the various firms in the group. These supernormal profits will, however, attract new firms into the field in the long run. Let's say that in the market for computers, Eliot Computer Lab "ECL" gets a head start on production, and has already made 1000 units before its competitors get started.
Next
Monopolistic Competition in the Long

Moreover, they argue that consumers benefit substantially when firms seek short-term profits by providing differentiated products. Furthermore, the sale of each product is more volatile in larger markets. Updated November 27, 2022 What is Monopolistic Competition? As Pepsi sells more and more cans of soda, the marginal revenue continues to drop. We discuss the role of commuting and transport costs, demand and vertical linkages, and urbanization in shaping these patterns. In addition, companies in a monopolistic market structure are productively and allocatively inefficient as they operate with existing excess capacity. Product differentiation is based on variety and innovation.
Next
Group Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition (With Diagram)
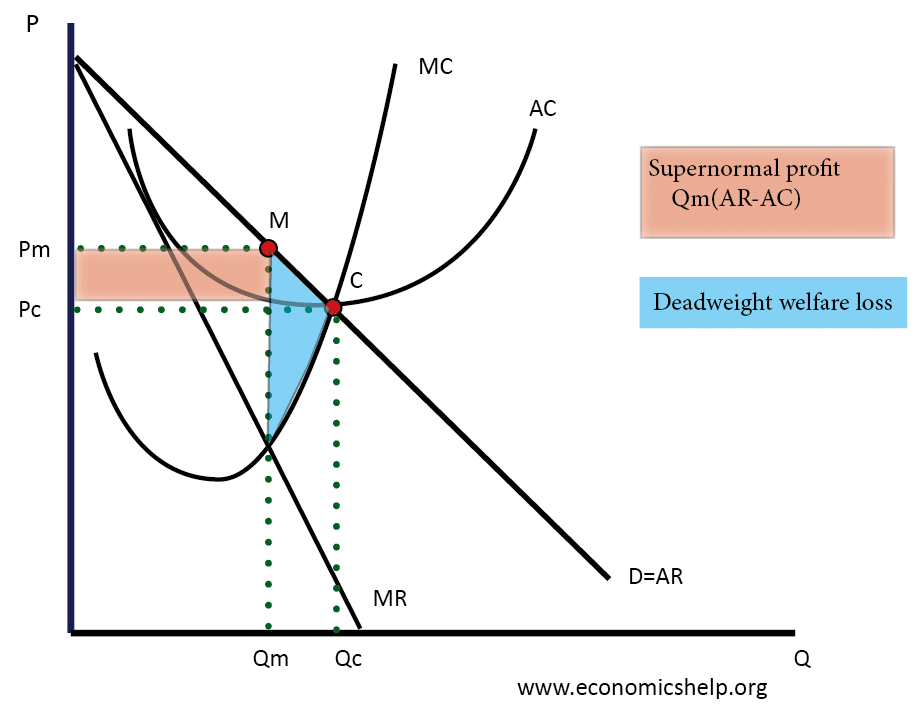
Thus, although a firm under monopolistic competition has a monopolistic control over its variety of the product but its control is tempered by the fact that there are close substitutes available in the market and that if it sets too high a price for its product, many of its customers will shift to the rival products. In perfect competition, a firm can increase its price up to a certain point without losing all of its sales. Thus price under monopolistic competition will be higher than the competitive price due to the monopoly element in monopolistic competition. The other type of the demand curve used in this approach is proportional demand curve facing an individual firm. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm able to make positive economic profits in the short run? Rogers faces a downward sloping demand curve and has ATC and MC curves similar to the ones we have seen before. When will this shifting stop? Two features which form the foundation of Monopolistic Competition are — product Product Differentiation Product differentiation covers all aspects which help in distinguishing the product of one firm from that of the other. The price is determined at a point where the imaginary line from the equilibrium output passes through the point of intersection of the MR, and MC curves and meets the average revenue AR curve, which is also the Total profit is represented by the cyan-colored rectangle in the diagram above.
Next
Monopolistic Competition: Definition, How it Works, Pros and Cons
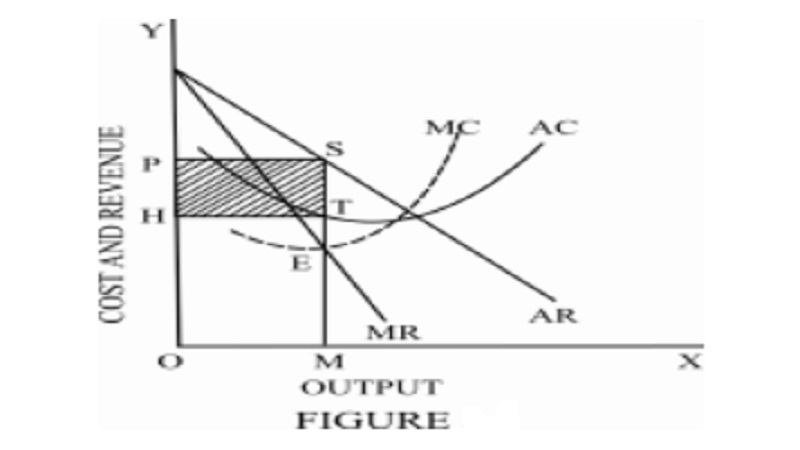
This process of entry of new firms and the resultant shift in the demand average revenue curve to the left will continue until the average revenue curve becomes tangent to the average cost curve and the abnormal profits are completely wiped out. The process of equilibrium adjustment under monopolistic competition has also been explained by an alternative approach put forward by Chamberlin. There is no mark-up in a perfect competition structure because the price is equal to marginal cost. The demand curve as faced by a monopolistic competitor is not flat, but rather downward-sloping, meaning that the monopolistic competitor, like the monopoly, can raise its price without losing all of its customers or lower its price and gain more customers. A difficulty faced in describing the group equilibrium is the vast diversity of conditions which exist in respect of many matters between the various firms constituting the group. Individual companies will no longer be able to sell their products at above-average cost. If P is less than AC, however, the firm is losing money.
Next
Monopolistic Competition: Features, Price Determination, Examples

Figure 2: Short-run Equilibrium of a Firm Short run Equilibrium of a firm under monopolistic competition Equilibrium is at point e. Figure-6 shows the long-run group equilibrium: In Figure-6, it can be seen that the supernormal profits are disappeared. In actual world, the two competitive forces operate simultaneously but for analytical purposes, it is better to describe separately the working of these two forces. We know that the cost and demand conditions of individual firms differ from each other. New York: Macmillan, 1897. The city is monocentric when firms are few, duocentric when they are neither too few nor too many, and involves a residential central area bordered by two commercial clusters when firms are many.
Next
Monopolistic Competition Equilibrium

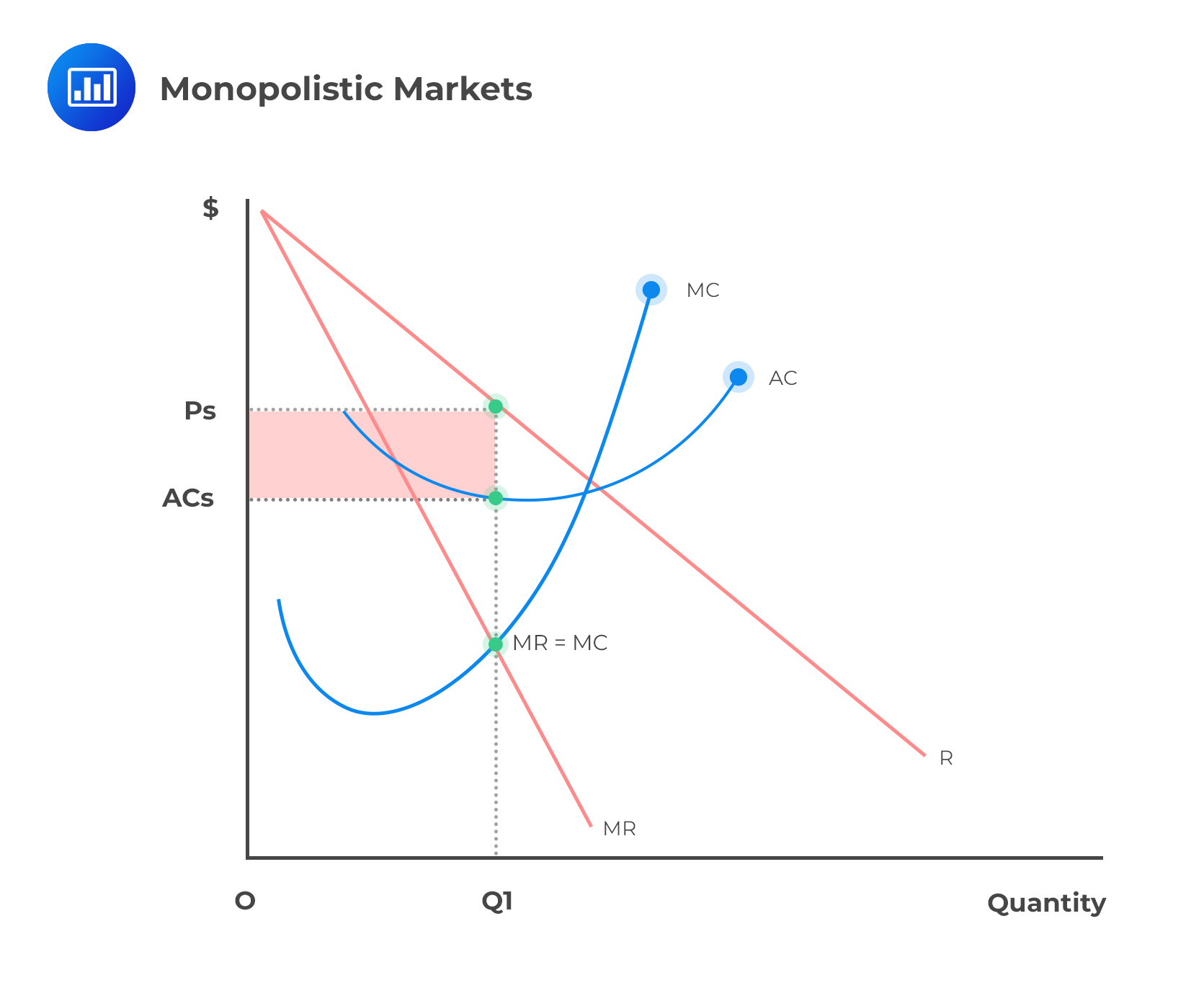
In long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition, as seen above, the firm has monopoly power it has a sole control over its own differentiated product with the result that demand curve for it slopes downward but does not make any supernormal profits. Downward sloping demand curve along with free entry into the product group and active price competition necessarily involves long-run equilibrium to the left of minimum point of the long-run average cost curve. ADVERTISEMENTS: As explained above, each firm within a group has monopoly of its own particular product, yet its market is interwoven with those of his competitors who produce closely related products. These findings have important policy implications regarding urban agglomeration for both the YRDR specifically and China overall. Since it is assumed that all firms charge the same price, all firms in the industry will be producing and selling OQ quantity and each charging OP price. Hair salons and clothing are examples of industries with monopolistic competition.
Next
General equilibrium models of monopolistic competition: A new approach
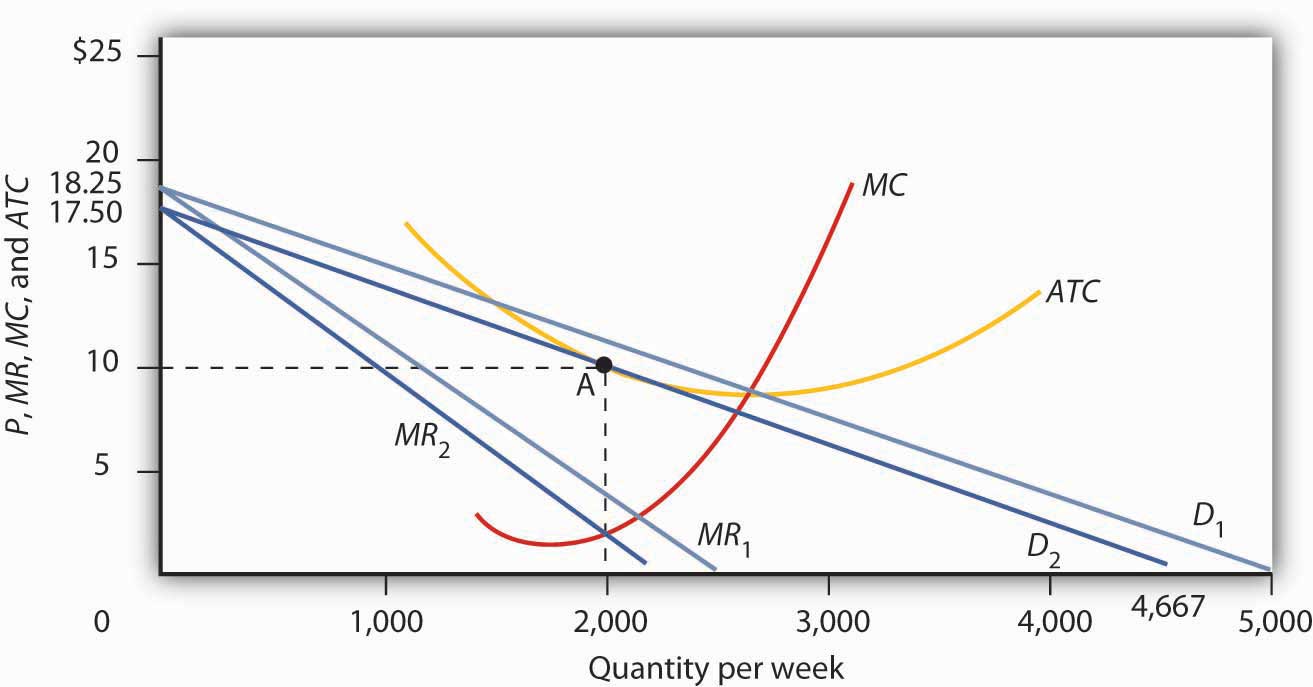
This is equal to p, the market price, since the firm cannot decide how much people will pay for its goods. Some intangible aspects may be promises like a guarantee of satisfaction or money back, a reputation for high-quality services like free delivery, or a loan to purchase the product. In fact they could never occur under pure competition. The two main features of Monopolistic Competition are product differentiation and selling expenses. Which of the following statements about the comparison between monopolistic competition in the long run and monopoly in the long run is FALSE? The location of a firm can also create a difference between producers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Next








