The concept of marginal utility refers to the additional satisfaction or benefit that a person derives from consuming one more unit of a particular good or service. This concept is central to the economic theory of consumer behavior, as it helps to explain how individuals make decisions about what to purchase and how much to pay for it.
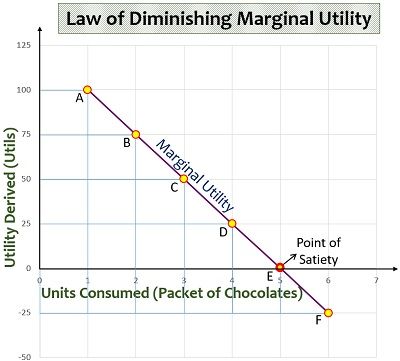
The marginal utility approach suggests that as a person consumes more units of a particular good, the additional utility or benefit that they derive from each successive unit will decline. This is known as the law of diminishing marginal utility. For example, the first slice of pizza that a person eats may provide a high level of utility or satisfaction, but as they continue to eat more slices, the marginal utility of each additional slice will decrease.
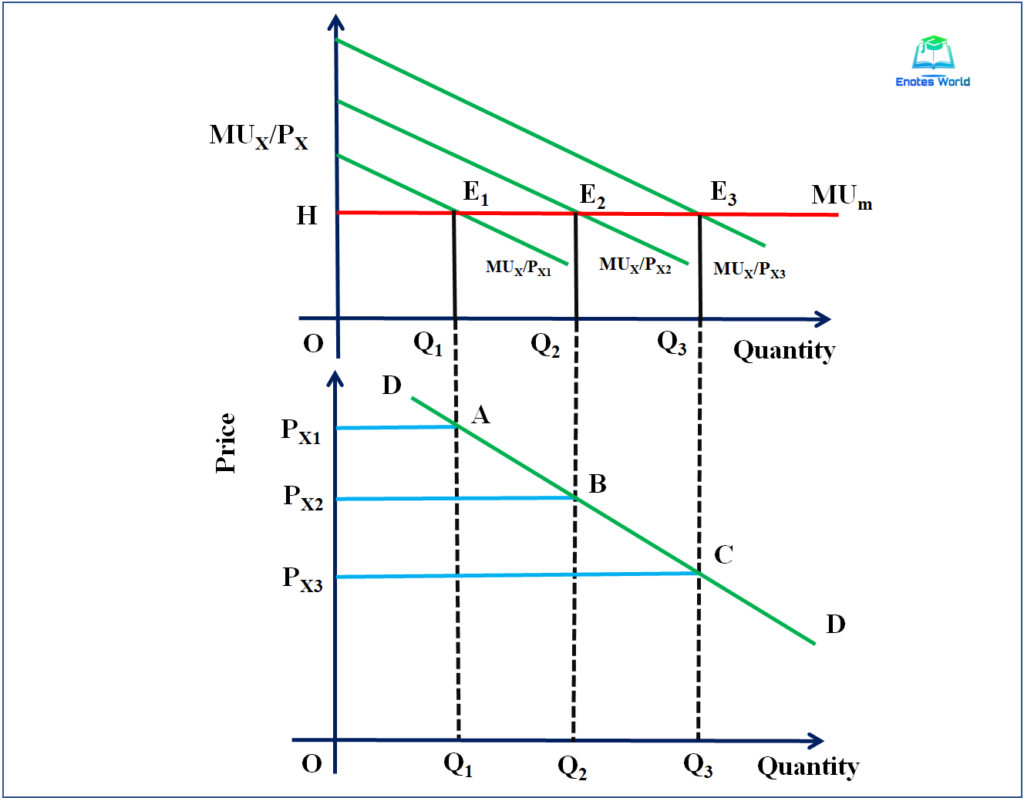
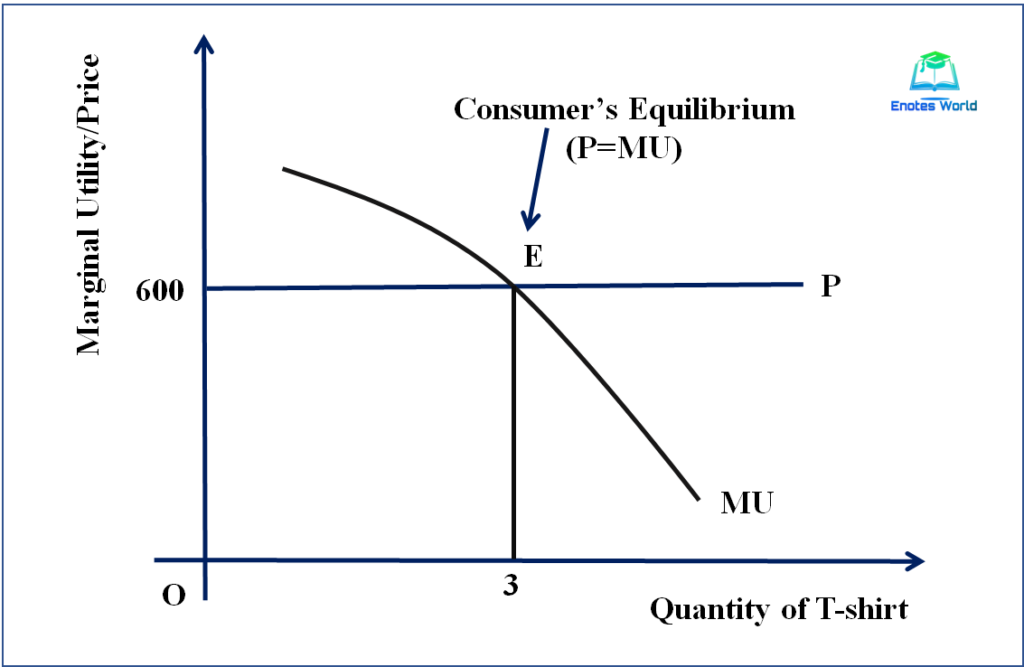
This concept has important implications for how individuals make decisions about what to purchase. If the marginal utility of a good is high, a person may be willing to pay a higher price for it. However, if the marginal utility of a good is low, a person may be less willing to pay a high price for it.
The marginal utility approach can also be used to explain why individuals may be willing to pay more for a good or service that is scarce or hard to obtain. If the supply of a good is limited, the marginal utility of that good may be higher, as consumers will be willing to pay more to obtain it.
In conclusion, the concept of marginal utility is a key concept in economics that helps to explain how individuals make decisions about what to purchase and how much to pay for it. It suggests that as a person consumes more units of a particular good, the additional utility or benefit that they derive from each successive unit will decline. This concept has important implications for how individuals make decisions about what to purchase and the prices they are willing to pay for goods and services.
Marginal Utility Theory: Types and Applications
The marginal unit secures the least important end. However, if they decide to spend money on the public sector, the budget increases. First, however, we must reckon with the fact that the ability of consumers to purchase goods and services is limited by their budgets. Apply the formula With both final differences found, apply the information to the formula. Perhaps some day a hedonimeter will be invented. Economists examine utils over a broad range and determine the level of satisfaction gained from a particular unit of consumption. It says that the value of something is not just about how much work went into making it, but also about how much we want it and how much it makes us happy.
Marginal utility theory

Indifference Curve for Bads : A bad is a commodity that the consumer does not like. Note that the first loaf of bread is employed to secure the most important end, the second loaf of bread the second most important end, etc. However, if the utility of that product declines with the consumption of each subsequent additional unit, then the consumer will stop when marginal utility reaches zero or becomes negative. It is impossible to distribute it in any other way to increase his utility. It is important to notice that, to arrive at this conclusion, no mention of the abstract concept of utility was made. Generally, consumer behavior is based on maximizing total utility by acquiring units that enable them to gain maximum utility for the amount they spend.
How to Calculate Marginal Utility (With Example)

Through maximizing utility, the consumer will buy an item that produces the greatest marginal utility with the least amount of spending. Marginal Utility and Total Utility : The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility States: Other things being constant, as more and more units of a commodity are consumed, the additional satisfaction or utility derived from the consumption of each successive unit will decrease. Definitely, we have to give him some extra pepperoni to compensate him. The market demand, column 5 , is found by adding columns 2 , 3 and 4 to determine the total quantity demanded at each price. Since the slope of an indifference curve is called the marginal rate of substitution MRS , the proposition is sometimes summed up as the diminishing marginal rate of substitution.
The marginal utility theory: mainstream vs the Austrian framework
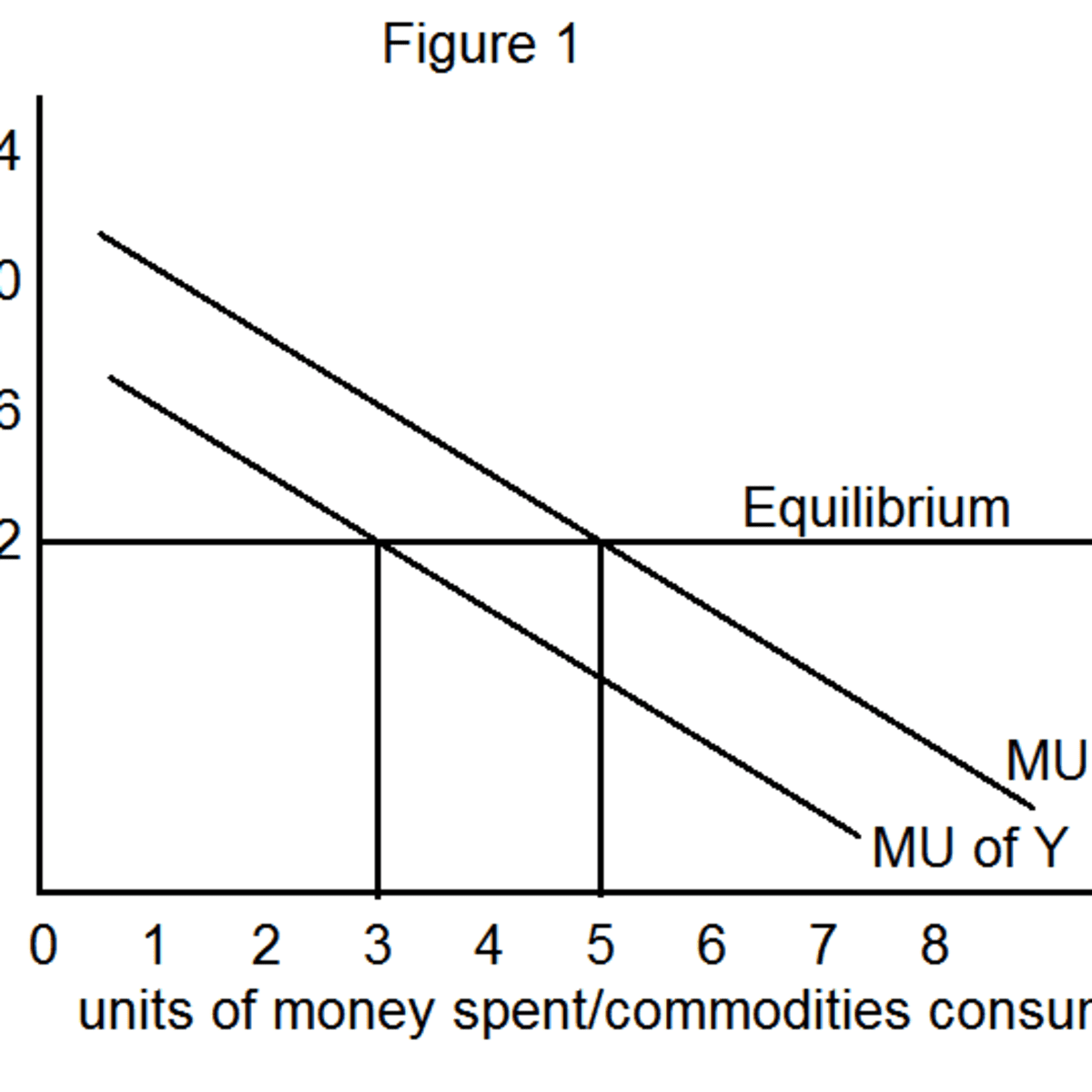
The market demand curve can then be obtained by aggregating horizontally all the individual demand curves. Observe that to attain the second and the third end John had to exchange his resources — loaves of bread — for goods that would serve to achieve his ends. His preferences reflect what he believes should be allocated for police spending and what he feels citizens would prefer to have available for private consumption. Consumer Choice : Given preferences and budget constraints, we can choose how much of each good to buy. Observe that to satisfy his second end, which is to have five tomatoes; John would have to exchange one loaf of bread for five tomatoes. This problem, known as the paradox of value, was solved by the application of the concept of marginal utility.
marginal utility approach, reading webapi.bu.edu
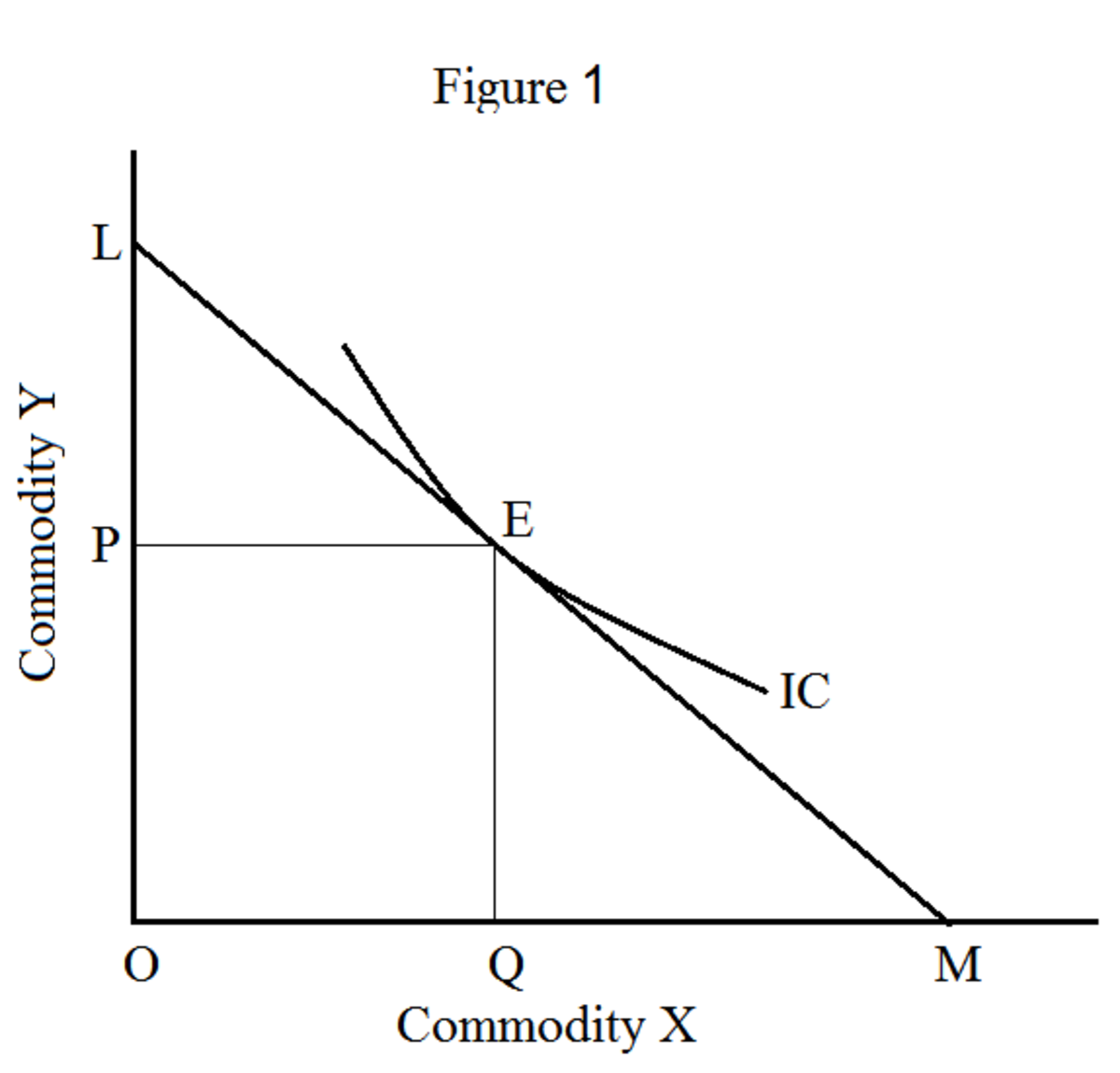
Demand and Marginal Utility 20. We assume that the consumer can rank his preference over the entire field of choice. Suppose that you are really thirsty and you decide to consume a soft drink. Marginal utility is the increase in total utility obtained by consuming one more unit of a good, service, or activity. At that point, which is 5 glasses of water, the total utility reaches its maximum and starts declining. Indifference Curves can never Intersect : This is shown in Fig. For example, goods like fans, furniture, etc fall under this category of human wants.
Marginal Utility: Definition, Types & Example
For example, we know that consumption of any basket on IC 3, such as E, is preferred to consumption of any basket on IC 2, such as D. A matching grant acts like a price decrease in the traditional consumer analysis. Chris Brown — In preparation for sitting in the slow, crowded lanes for single-occupancy-vehicles, T. For example, the central government might offer to pay £1 for every £2 that the local government raises to pay for police. On the other hand, Kevin may have purchased more milk than he can reasonably consume, meaning his marginal utility might be zero. We see that rice consumption increases initially as income increases. In economics, the standard rule is that marginal utility is equal to the total utility change divided by the change in amount of goods.