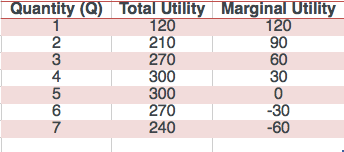
Marginal utility analysis is a concept in economics that helps to explain the relationship between the quantity of a good or service consumed and the satisfaction or utility that an individual derives from it. This concept is used to understand consumer behavior and to predict how consumers will respond to changes in the market, such as changes in price or availability.
At its most basic, the law of diminishing marginal utility states that as an individual consumes more of a good or service, the additional utility or satisfaction that they receive from each additional unit will decrease. This is because the first units of a good or service that an individual consumes are often the most valuable to them. As they continue to consume more of the good or service, they may eventually reach a point of satiation, where the additional utility that they receive from each additional unit becomes negligible or even negative.
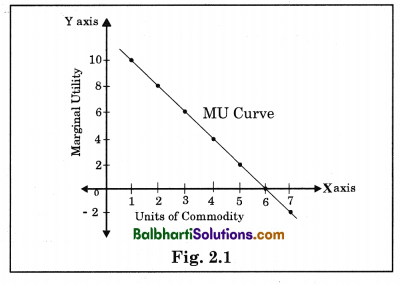
This concept can be demonstrated through the use of a marginal utility curve, which shows the relationship between the quantity of a good or service consumed and the marginal utility that an individual derives from it. The marginal utility curve typically has a downward slope, indicating that as the quantity of a good or service consumed increases, the marginal utility derived from it decreases.
Marginal utility analysis is useful in understanding consumer behavior because it helps to explain why consumers make the choices that they do. For example, if the price of a good or service increases, a consumer may choose to purchase less of it because the marginal utility that they receive from each additional unit has decreased. This can help businesses to better understand how consumers will respond to changes in price and can inform their pricing strategies.
In addition to its use in understanding consumer behavior, marginal utility analysis is also used in the field of cost-benefit analysis. This involves comparing the costs of a particular course of action to the benefits that are expected to be derived from it. By understanding the marginal utility of different goods or services, it is possible to determine the optimal level of consumption or production, as well as the point at which the costs of a particular course of action outweigh the benefits.
Overall, marginal utility analysis is a valuable tool in understanding consumer behavior and making informed decisions in the marketplace. It helps to explain the relationship between the quantity of a good or service consumed and the satisfaction or utility that an individual derives from it, and can inform pricing strategies and cost-benefit analyses.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/marginalutility_Final-425c1cf087a34d4d808a0bacb5bb8714.png)



