The marginal rate of consumption refers to the amount by which a consumer's utility or satisfaction increases with an additional unit of consumption of a good or service. In other words, it is the additional utility or satisfaction that a consumer derives from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Economists use the concept of the marginal rate of consumption to understand how consumers make decisions about how much of a good or service to consume. When the marginal rate of consumption is positive, it means that the consumer derives additional utility from consuming one more unit of the good or service. This means that the consumer is willing to pay more for the additional unit of consumption. On the other hand, when the marginal rate of consumption is negative, it means that the consumer derives less utility from consuming one more unit of the good or service. In this case, the consumer would be willing to pay less for the additional unit of consumption.
The marginal rate of consumption can be influenced by a number of factors, including the consumer's income, the price of the good or service, and the consumer's preferences. For example, if a consumer has a high income, they may be willing to pay more for an additional unit of consumption because they have more disposable income available to spend. Similarly, if the price of a good or service is high, the consumer may be less willing to pay for an additional unit of consumption because the cost is too high. On the other hand, if the price of a good or service is low, the consumer may be more willing to pay for an additional unit of consumption because the cost is relatively low.
In addition to these factors, the marginal rate of consumption can also be influenced by the consumer's preferences. For example, if a consumer really enjoys a particular good or service, they may be willing to pay more for an additional unit of consumption because the utility or satisfaction derived from consuming the good or service is high. On the other hand, if a consumer does not enjoy a particular good or service, they may be less willing to pay for an additional unit of consumption because the utility or satisfaction derived from consuming the good or service is low.
Overall, the marginal rate of consumption is an important concept in economics because it helps to explain how consumers make decisions about how much of a good or service to consume. Understanding the marginal rate of consumption can help policymakers, businesses, and other stakeholders better predict consumer behavior and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources.
Marginal rate of consumption (MPC)
In part, such efforts are an attempt to increase economic activity by boosting consumption. Now I do not know my MPC because my consumption and spending changes often with my schedule, But I would say with an increased 1000 dollars a month until retirement I would say my spending would go up by about 200 dollars per month while saving 800 for a while and the older I got the more I would spend per month and less I would save that way I am not losing money overtime. It might have apples X 1 , chicken X 2 , crackers X 3 , and cookies X 4. Moreover, lack of absence of empirical data restricts the visibility of mental disorders in comparison with other diseases in childhood and makes it difficult to advocate for their inclusion as a priority in health initiatives 2. Not to be confused with: Video — Marginal rate of substitution:. Executive Decision in Pricing of Goods Assume a restaurant sells two types of pizzas: Margherita Pizza and Mexican Green Pizza.
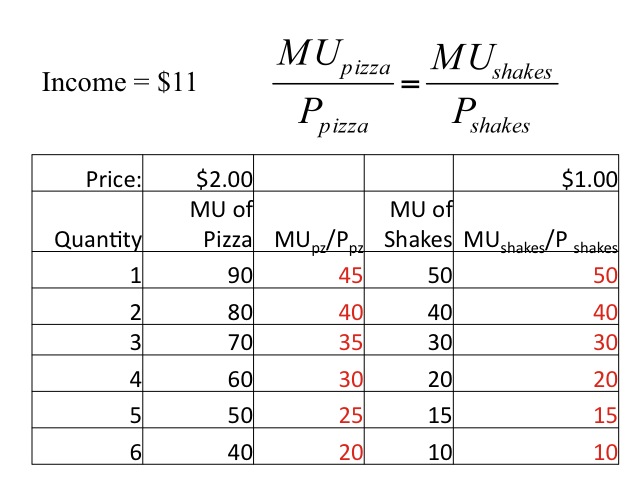
Marginal Utility
I believe the velocity of money is between a 1. According to the same source of evidence, childhood is a crucial life stage on the occurrence of mental disorders, which are likely to affect the quality of life, the learning and social level of a child. After a while, when looking at the firm's profitability, workers may ask for a raise in wages. Product Innovation Motor vehicle manufacturers understand well how to apply the law of marginal utility. Take this indifference curve, for example. What Defines the Convexity of Indifference Curves? The consumption function will shift upward, as in Panel a of References Mc Culloch, J.
Indifference Curves
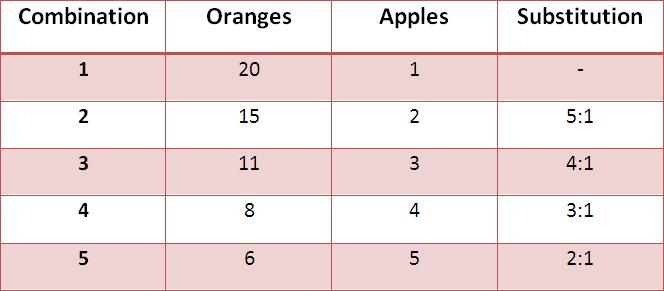
They are constantly getting more and more expensive as the weeks pass. As an analyst what steps would you take for the smooth transition to the new system? Indifference curve analysis operates on a simple two-dimensional graph. But at what rate is the consumer willing to give up coffee for Pepsi? Lesson Summary The marginal rate of substitution is the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for some amount of another good, given that the new good brings the same level of satisfaction. In this case, they are willing to give up 5 hot dogs in exchange for 10 fries because either amount of each respective good brings the same amount of satisfaction. Fortunately for researchers Sumit Agarwal, Chunlin Liu, and Nicholas Souleles, using data from credit card accounts, the 2001 tax rebate checks were distributed over 10 successive weeks from July to September of 2001.
MRS in Economics: What It Is and the Formula for Calculating It
Yes I think it was a good idea Fed helped to bail out investment banks that were failing because it helped strengthen the financial regulations to rebuild the trust of the people in the banking system. As another example, consider a student who faces a tradeoff that involves giving up some free time to get better grades in a particular class by studying more. The proposal to make these tax cuts permanent is aimed toward having a stronger impact on consumption, since tax cuts regarded as permanent have larger effects than do changes regarded as temporary. For instance, Generic Games produces 100,000 copies of its football video game. Utility is not constant, and for every additional unit consumed, often the consumer experiences what economists refer to as the diminishing marginal utility, where each additional unit adds less and less marginal utility. Solve these four questions and respond on two classmates for each one.



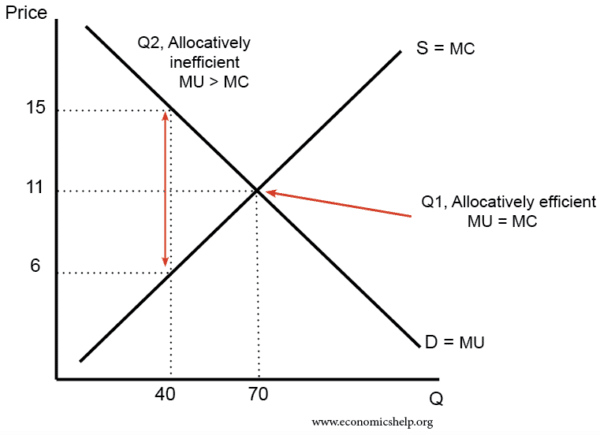

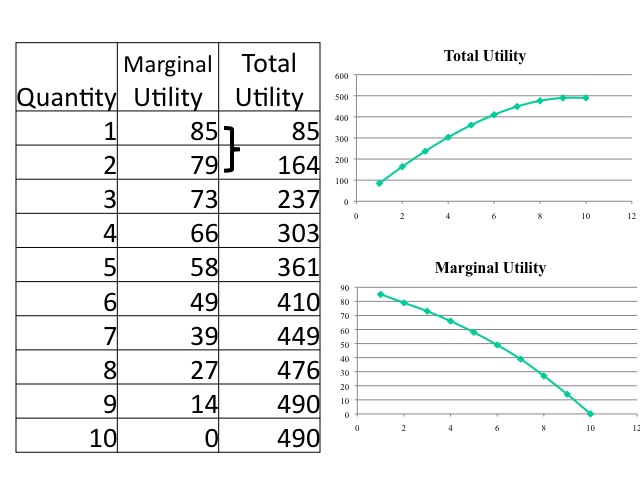
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/marginalutility_Final-425c1cf087a34d4d808a0bacb5bb8714.png)