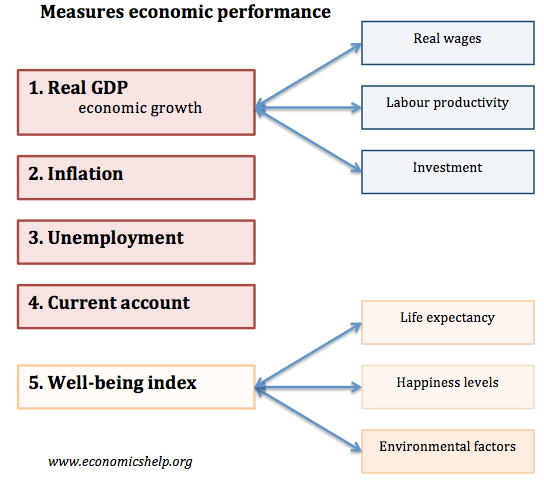
Macroeconomic objectives are goals that governments, central banks, and other economic policy makers aim to achieve in order to promote economic stability, growth, and prosperity. These objectives vary across countries and may be influenced by a range of factors, including the specific economic conditions, political climate, and social values of each nation.
One of the main macroeconomic objectives is price stability, which refers to the ability of the economy to maintain relatively stable prices over time. This is important because high levels of inflation, or a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, can lead to a decline in the purchasing power of money, which can disrupt economic activity and reduce confidence in the economy. On the other hand, deflation, or a sustained decline in the general price level, can also be harmful to the economy, as it can lead to a decrease in demand for goods and services, which can result in lower production and employment.
Another important macroeconomic objective is full employment, which refers to the situation in which all members of the labor force who are willing and able to work have jobs. High levels of unemployment can have negative consequences for individuals, families, and the overall economy, as it can lead to reduced income, increased poverty, and reduced economic growth. Governments and central banks may use a range of tools, such as monetary and fiscal policy, to try to achieve full employment.
Growth is another key macroeconomic objective, as it refers to the increase in the output of goods and services produced by an economy over time. Economic growth is important because it can lead to higher incomes and standards of living, as well as increased investment and innovation. However, economic growth also needs to be balanced with other objectives, such as price stability and full employment, in order to avoid negative consequences, such as inflation or resource depletion.
Sustainable development is another important macroeconomic objective, which refers to the ability of an economy to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This involves balancing economic, social, and environmental considerations, and may involve a range of policies, such as investment in renewable energy, conservation of natural resources, and social welfare programs.
In conclusion, the main macroeconomic objectives are price stability, full employment, growth, and sustainable development. These goals are interrelated and can be influenced by a range of factors, including economic conditions, political climate, and social values. Governments, central banks, and other economic policy makers strive to achieve these objectives in order to promote economic stability, growth, and prosperity.