A light microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify and examine small objects or structures that are not visible to the naked eye. It uses light as its source of illumination, and is an essential tool in many fields of science and medicine, including biology, physics, chemistry, and engineering. There are several main components of a light microscope, each of which plays a specific role in the functioning of the instrument.
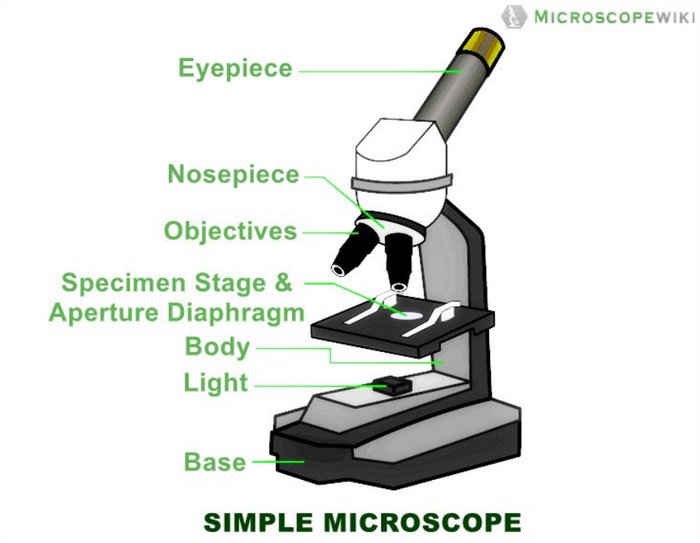
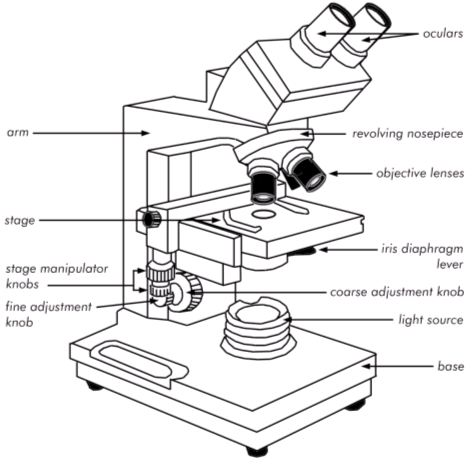
The first component of a light microscope is the objective lens. This is a small, high-powered lens that is located on the end of the microscope near the specimen being viewed. The objective lens is responsible for gathering light from the specimen and focusing it onto the eyepiece lens. There are typically several objective lenses of different magnifications available on a microscope, allowing the user to select the best lens for the task at hand.
The second component of a light microscope is the eyepiece lens. This is the lens that the user looks through to view the specimen, and it is located at the top of the microscope. The eyepiece lens magnifies the image produced by the objective lens, allowing the user to see the specimen in greater detail. Most light microscopes have a single eyepiece lens, but some models have two eyepieces for stereo viewing.
The third component of a light microscope is the stage. This is the platform on which the specimen is placed, and it is located below the objective lens. The stage is typically equipped with a movable stage clamp or stage micrometer, which allows the user to accurately position the specimen under the objective lens. The stage may also have a built-in light source, such as a halogen lamp, to illuminate the specimen.
The fourth component of a light microscope is the condenser lens. This is a lens located below the stage that focuses light onto the specimen. The condenser lens helps to evenly illuminate the specimen and increase the contrast of the image. Some light microscopes have a diaphragm or iris located below the condenser lens, which allows the user to adjust the amount of light passing through the lens.
The fifth and final component of a light microscope is the base. This is the foundation of the microscope and provides support for the other components. The base is typically made of a sturdy material, such as metal or plastic, and may also include a mechanical stage for precise movement of the specimen.
In conclusion, a light microscope is a sophisticated instrument that allows scientists and researchers to view small objects and structures in great detail. It is composed of several main components, including the objective lens, eyepiece lens, stage, condenser lens, and base, each of which plays a vital role in the functioning of the microscope.