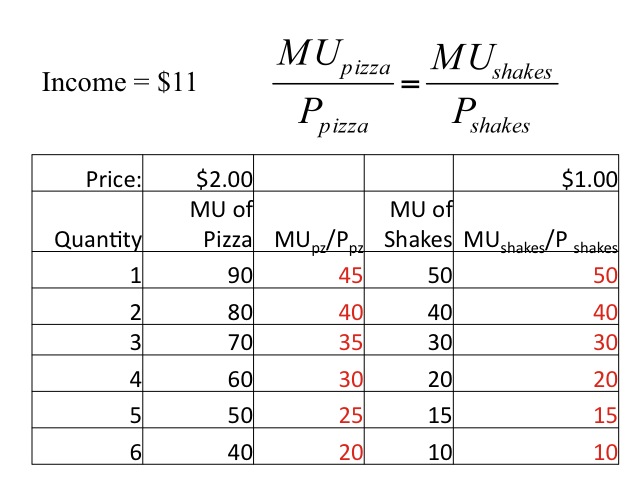
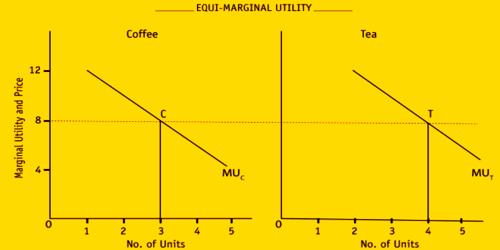
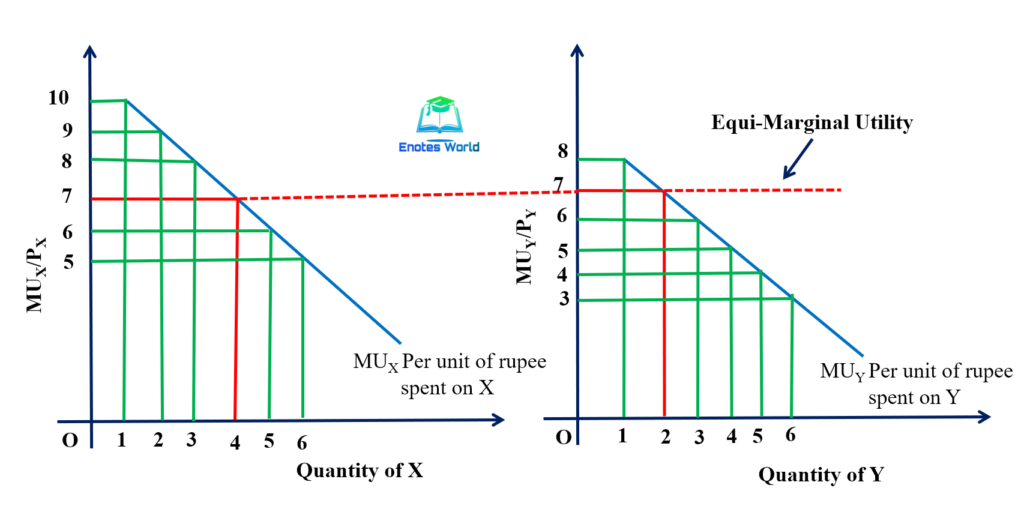
The law of equi marginal utility, also known as the law of diminishing marginal utility, is a fundamental principle in economics that states that the marginal utility (additional satisfaction or benefit) derived from consuming a good or service declines as the quantity consumed increases. This law is based on the idea that as an individual consumes more of a particular good or service, the additional satisfaction or benefit they receive from each additional unit decreases.
For example, consider a person who is hungry and consumes a slice of bread. The first slice of bread provides a significant amount of satisfaction or benefit to the person because it helps to satisfy their hunger. However, if the person continues to eat additional slices of bread, the marginal utility they receive from each additional slice will decrease. Eventually, the person may reach a point where the marginal utility from each additional slice of bread is so low that it is not worth the effort or cost of consuming it.
The law of equi marginal utility has important implications for consumer behavior and the allocation of resources. It helps to explain why individuals make trade-offs when making decisions about what goods and services to consume, and it is a key concept in the analysis of consumer demand.
For example, the law of equi marginal utility can be used to explain why an individual may choose to purchase a more expensive, high-quality product over a cheaper, lower-quality alternative. If the high-quality product provides a higher marginal utility per unit than the lower-quality product, the individual will be willing to pay a higher price for it. Similarly, the law of equi marginal utility can be used to explain why an individual may choose to allocate their time and resources in different ways. For example, if an individual values their leisure time highly, they may be willing to pay a higher price for a product or service that saves them time, even if the product or service is not necessarily of higher quality.
Overall, the law of equi marginal utility is an important principle in economics that helps to explain how individuals make trade-offs and allocate their resources when faced with limited resources and competing demands. It is a key concept that helps to understand consumer behavior and the allocation of resources in the economy.