Qualitative and quantitative research are two distinct approaches to gathering and analyzing data. While they differ in several ways, the main differences lie in the type of data they gather and the methods they use to analyze that data.
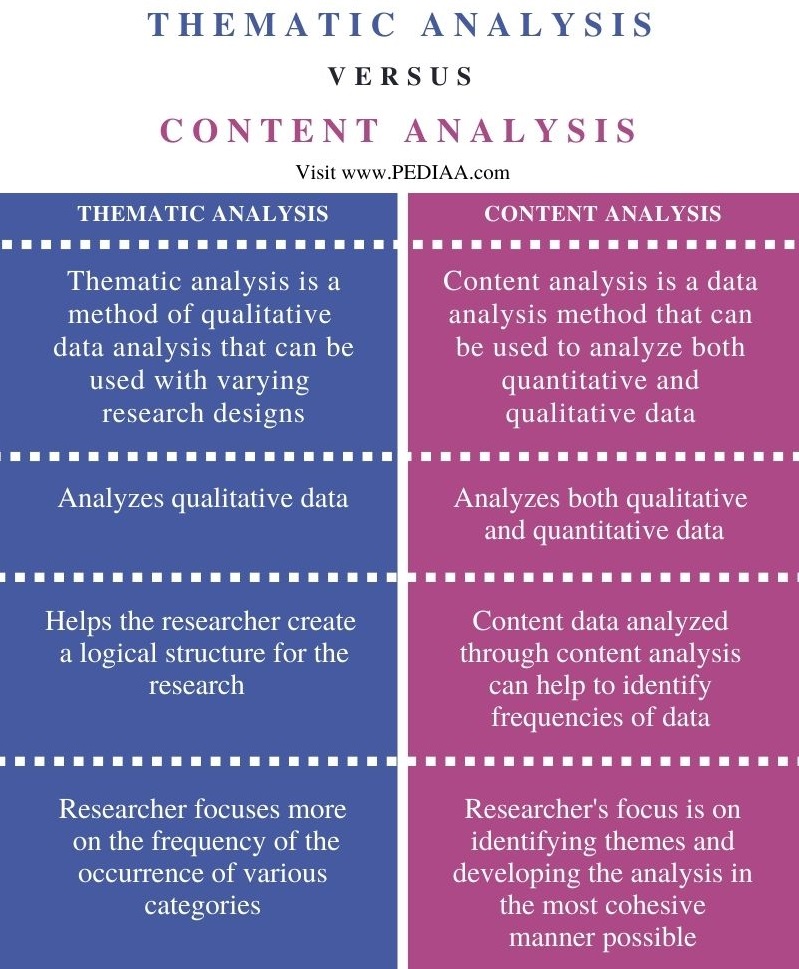
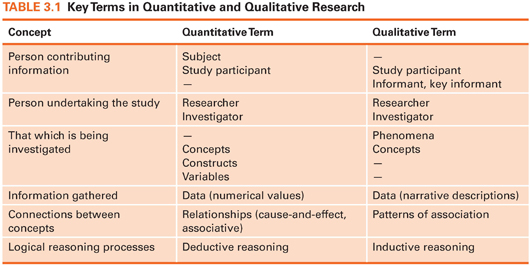
Qualitative research is a type of research that involves collecting and analyzing data in the form of words, images, or sounds. This type of research is focused on understanding the experiences, perspectives, and meanings of the people being studied. It is often used to explore complex social and cultural phenomena, such as people's attitudes, values, and beliefs. Qualitative research typically involves small sample sizes and is often conducted through in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations.
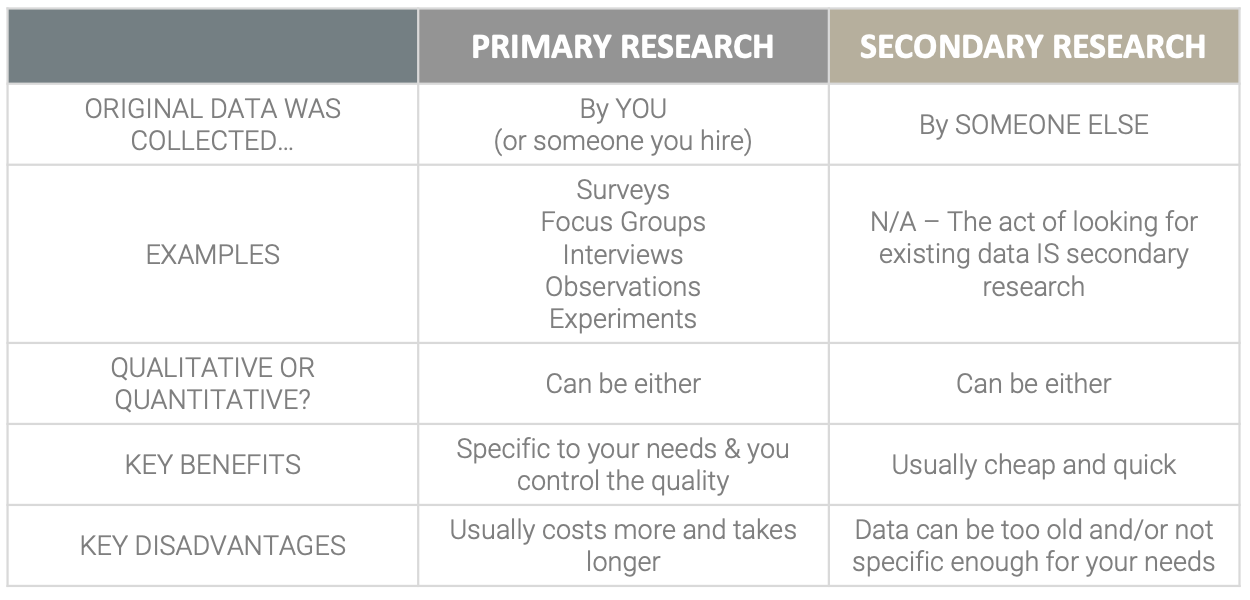
Quantitative research, on the other hand, involves collecting and analyzing data in the form of numbers. This type of research is focused on testing hypotheses and measuring relationships between variables. It is often used to establish cause-and-effect relationships and to generalize findings to a larger population. Quantitative research typically involves large sample sizes and is often conducted through surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
One key difference between qualitative and quantitative research is the level of detail and depth of analysis. Qualitative research tends to provide a more detailed and in-depth understanding of the subject matter, as it is focused on collecting and analyzing rich, descriptive data. Quantitative research, on the other hand, tends to be more focused on collecting and analyzing numerical data, which may not provide as much depth and detail.
Another key difference is the level of subjectivity involved in the research process. Qualitative research is often considered to be more subjective, as it involves the researcher's own interpretation and understanding of the data. Quantitative research, on the other hand, is generally considered to be more objective, as it involves the use of statistical analysis to test hypotheses and measure relationships between variables.
Overall, qualitative and quantitative research are two distinct approaches to collecting and analyzing data, each with its own strengths and limitations. While qualitative research provides a detailed and in-depth understanding of complex social and cultural phenomena, quantitative research allows for the testing of hypotheses and the generalization of findings to a larger population. Both approaches are valuable tools for gaining insights and understanding the world around us.