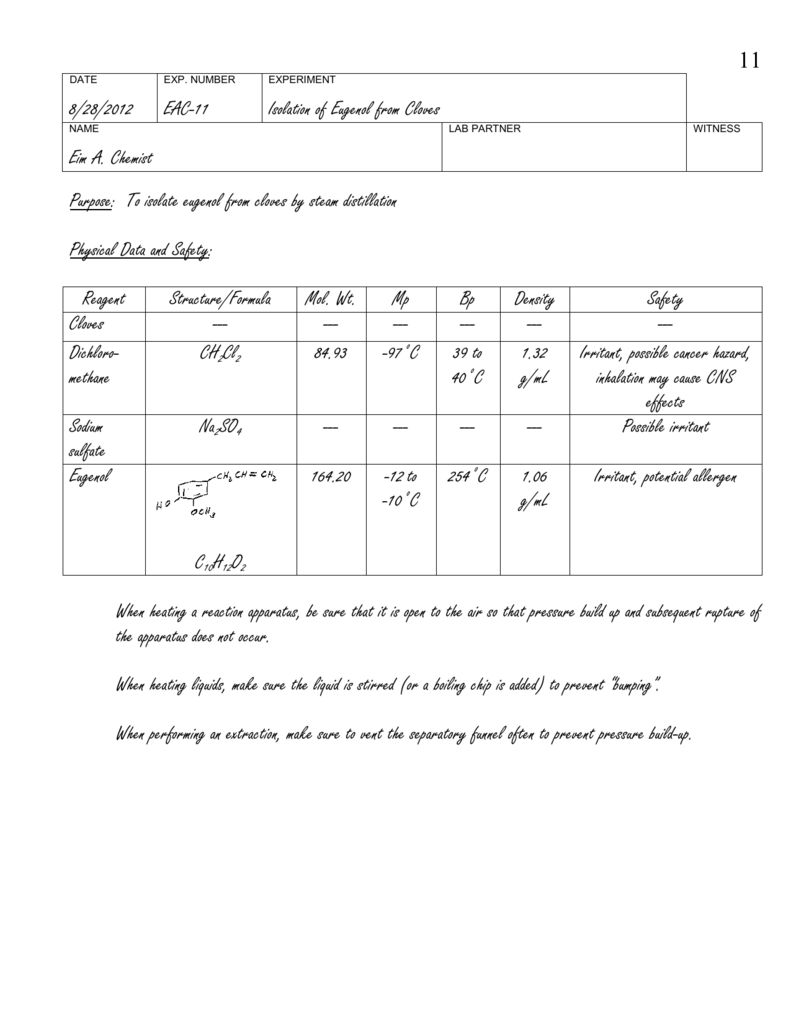
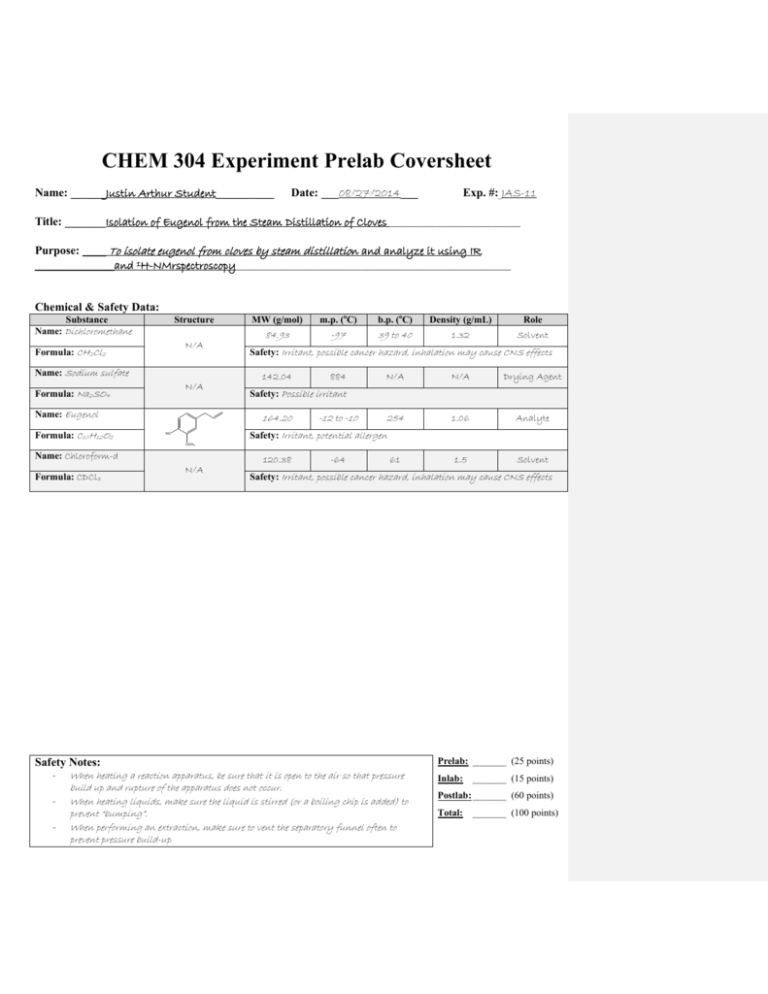
Eugenol is a natural compound that is found in many plants, including cloves. It is known for its pleasant aroma and has been used for centuries in traditional medicine and as a flavoring agent in food and beverages. In this essay, we will discuss the isolation of eugenol from cloves through a chemical reaction known as steam distillation.
The first step in the isolation of eugenol from cloves is to grind the cloves into a fine powder. This is done to increase the surface area of the cloves, which makes it easier for the eugenol to be extracted. The ground cloves are then placed in a distillation flask along with a small amount of water.
Next, the distillation flask is heated to a temperature of around 100°C. As the water boils, the steam that is produced carries with it the volatile oils from the cloves, including eugenol. The steam is then condensed back into a liquid using a condenser.
The liquid that is produced from the condensation of the steam is a mixture of water and the volatile oils from the cloves. To separate the eugenol from this mixture, the liquid is passed through a column filled with a chemical absorbent, such as silica gel. As the liquid passes through the column, the eugenol is absorbed by the chemical absorbent, while the water and other impurities pass through.
The eugenol can then be recovered from the chemical absorbent by eluting it with a solvent, such as ethanol. The resulting solution is then filtered to remove any impurities, and the eugenol is purified through a series of additional steps, including distillation.
The steam distillation method is a simple and effective way to isolate eugenol from cloves. It allows for the separation of eugenol from other compounds present in the cloves, yielding a pure and concentrated form of the compound. In addition to its use in traditional medicine and as a flavoring agent, eugenol has a number of other applications, including use as a natural insecticide and in the production of perfumes and other personal care products.